| Introduction ::Saudi Arabia |
|
|
Saudi Arabia is the birthplace of Islam and home to Islam's two holiest shrines in Mecca and Medina. The king's official title is the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques. The modern Saudi state was founded in 1932 by ABD AL-AZIZ bin Abd al-Rahman Al SAUD (Ibn Saud) after a 30-year campaign to unify most of the Arabian Peninsula. A male descendent of Ibn Saud, his son ABDALLAH bin Abd al-Aziz, rules the country today as required by the country's 1992 Basic Law. Following Iraq's invasion of Kuwait in 1990, Saudi Arabia accepted the Kuwaiti royal family and 400,000 refugees while allowing Western and Arab troops to deploy on its soil for the liberation of Kuwait the following year. The continuing presence of foreign troops on Saudi soil after the liberation of Kuwait became a source of tension between the royal family and the public until all operational US troops left the country in 2003. Major terrorist attacks in May and November 2003 spurred a strong on-going campaign against domestic terrorism and extremism. King ABDALLAH has continued the cautious reform program begun when he was crown prince. To promote increased political participation, the government held elections nationwide from February through April 2005 for half the members of 179 municipal councils. In December 2005, King ABDALLAH completed the process by appointing the remaining members of the advisory municipal councils. The king instituted an Inter-Faith Dialogue initiative in 2008 to encourage religious tolerance on a global level; in February 2009, he reshuffled the cabinet, which led to more moderates holding ministerial and judicial positions, and appointed the first female to the cabinet. The country remains a leading producer of oil and natural gas and holds more than 20% of the world's proven oil reserves. The government continues to pursue economic reform and diversification, particularly since Saudi Arabia's accession to the WTO in December 2005, and promotes foreign investment in the kingdom. A burgeoning population, aquifer depletion, and an economy largely dependent on petroleum output and prices are all ongoing governmental concerns.
|
|
|
|
|
|
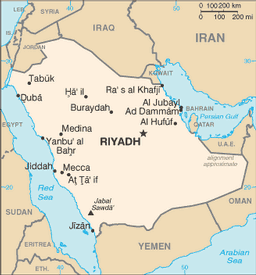
Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf and the Red Sea, north of Yemen
|
|
|
|
|
25 00 N, 45 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,149,690 sq km
country comparison to the world: 14
land:
2,149,690 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly more than one-fifth the size of the US
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4,431 km
border countries:
Iraq 814 km, Jordan 744 km, Kuwait 222 km, Oman 676 km, Qatar 60 km, UAE 457 km, Yemen 1,458 km
|
|
|
|
|
2,640 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
18 nm
continental shelf:
not specified
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
harsh, dry desert with great temperature extremes
|
|
|
|
|
mostly uninhabited, sandy desert
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Persian Gulf 0 m
highest point:
Jabal Sawda' 3,133 m
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, gold, copper
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 1.67%
permanent crops:
0.09%
other:
98.24% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
16,200 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
2.4 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 17.32 cu km/yr (10%/1%/89%)
per capita:
705 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
frequent sand and dust storms
|
|
|
|
|
desertification; depletion of underground water resources; the lack of perennial rivers or permanent water bodies has prompted the development of extensive seawater desalination facilities; coastal pollution from oil spills
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
extensive coastlines on Persian Gulf and Red Sea provide great leverage on shipping (especially crude oil) through Persian Gulf and Suez Canal
|
|
|
|
|
|
29,207,277
country comparison to the world: 41
note:
includes 5,576,076 non-nationals (July 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 38% (male 5,657,533/female 5,435,799)
15-64 years:
59.5% (male 9,731,831/female 7,655,385)
65 years and over:
2.5% (male 369,538/female 357,191) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 21.6 years
male:
22.9 years
female:
20 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.75% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
28.21 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
2.45 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 219
|
|
|
|
|
-8.26 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 82% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
2.5% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.27 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
1.03 male(s)/female
total population:
1.17 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 11.2 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 147
male:
12.73 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
9.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 76.51 years
country comparison to the world: 69
male:
74.41 years
female:
78.71 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.77 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
0.01% (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Saudi(s)
adjective:
Saudi or Saudi Arabian
|
|
|
|
|
Arab 90%, Afro-Asian 10%
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim 100%
|
|
|
|
|
Arabic
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
78.8%
male:
84.7%
female:
70.8% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.8% of GDP (2004)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|
| Government ::Saudi Arabia |
|
|
conventional long form: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
conventional short form:
Saudi Arabia
local long form:
Al Mamlakah al Arabiyah as Suudiyah
local short form:
Al Arabiyah as Suudiyah
|
|
|
|
|
monarchy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Riyadh
geographic coordinates:
24 38 N, 46 43 E
time difference:
UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
13 provinces (mintaqat, singular - mintaqah); Al Bahah, Al Hudud ash Shamaliyah (Northern Border), Al Jawf, Al Madinah, Al Qasim, Ar Riyad (Riyadh), Ash Sharqiyah (Eastern), 'Asir, Ha'il, Jizan, Makkah, Najran, Tabuk
|
|
|
|
|
23 September 1932 (unification of the kingdom)
|
|
|
|
|
Unification of the Kingdom, 23 September (1932)
|
|
|
|
|
governed according to Islamic law; the Basic Law that articulates the government's rights and responsibilities was promulgated by royal decree in 1992
|
|
|
|
|
based on sharia law, several secular codes have been introduced; commercial disputes handled by special committees; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
21 years of age; male
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: King and Prime Minister ABDALLAH bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud (since 1 August 2005); Heir Apparent Crown Prince SULTAN bin Abd al- Aziz Al Saud (half brother of the monarch); note - the monarch is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
King and Prime Minister ABDALLAH bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud (since 1 August 2005); Deputy Prime Minister SULTAN bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud; Second Deputy Prime Minister NAYIF bin Abd Al-Aziz Al Saud
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the monarch every four years and includes many royal family members
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
none; the monarchy is hereditary; note - an Allegiance Commission created by royal decree in October 2006 established a committee of Saudi princes that will play a role in selecting future Saudi kings, but the system will not take effect until after Crown Prince Sultan becomes king
|
|
|
|
|
Consultative Council or Majlis al-Shura (150 members and a chairman appointed by the monarch to serve four-year terms); note - though the Council of Ministers announced in October 2003 its intent to introduce elections for half of the members of local and provincial assemblies and a third of the members of the national Consultative Council or Majlis al-Shura incrementally over a period of four to five years, to date no such elections have been held or announced
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Council of Justice
|
|
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
Ansar Al Marah (supports women's rights)
other:
gas companies; religious groups
|
|
|
|
|
ABEDA, AfDB (nonregional member), AFESD, AMF, BIS, FAO, G-20, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAPEC, OAS (observer), OIC, OPCW, OPEC, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Adil al-Ahmad al-JUBAYR
chancery:
601 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20037
telephone:
[1] (202) 342-3800
FAX:
[1] (202) 944-3113
consulate(s) general:
Houston, Los Angeles, New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador James B. SMITH
embassy:
Collector Road M, Diplomatic Quarter, Riyadh
mailing address:
American Embassy, Unit 61307, APO AE 09803-1307; International Mail: P. O. Box 94309, Riyadh 11693
telephone:
[966] (1) 488-3800
FAX:
[966] (1) 488-7360
consulate(s) general:
Dhahran, Jiddah (Jeddah)
|
|
|
|
|
green, a traditional color in Islamic flags, with the Shahada or Muslim creed in large white Arabic script (translated as "There is no god but God; Muhammad is the Messenger of God") above a white horizontal saber (the tip points to the hoist side); design dates to the early twentieth century and is closely associated with the Al Saud family which established the kingdom in 1932
|
|
|
|
|
|
Saudi Arabia has an oil-based economy with strong government controls over major economic activities. It possesses about 20% of the world's proven petroleum reserves, ranks as the largest exporter of petroleum, and plays a leading role in OPEC. The petroleum sector accounts for roughly 80% of budget revenues, 45% of GDP, and 90% of export earnings. Saudi Arabia is encouraging the growth of the private sector in order to diversify its economy and to employ more Saudi nationals. Diversification efforts are focusing on power generation, telecommunications, natural gas exploration, and petrochemical sectors. Roughly 5.5 million foreign workers play an important role in the Saudi economy, particularly in the oil and service sectors, while Riyadh is struggling to reduce unemployment among its own nationals. Saudi officials are particularly focused on employing its large youth population, which generally lacks the education and technical skills the private sector needs. Riyadh has substantially boosted spending on job training and education, most recently with the opening of the King Abdallah University of Science and Technology - Saudi Arabia's first co-educational university. As part of its effort to attract foreign investment, Saudi Arabia acceded to the WTO in December 2005 after many years of negotiations. The government has begun establishing six "economic cities" in different regions of the country to promote economic development. Five years of high oil prices during 2004-08 gave the Kingdom ample financial reserves to manage the impact of the global financial crisis, but tight international credit, falling oil prices, and the global economic slowdown reduced Saudi economic growth in 2009, prompting the postponement of some economic development projects. Saudi authorities supported the banking sector during the crisis by making direct capital injections into banks, reducing rates, and publicly affirming the government's guarantee of bank deposits.
|
|
|
|
|
$585.8 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
$584.7 billion (2008 est.)
$560 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$384 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
4.4% (2008 est.)
3.3% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$20,400 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
$20,800 (2008 est.)
$20,300 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 3.2%
industry:
60.4%
services:
36.4% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.922 million
country comparison to the world: 62
note:
about 80% of the labor force is non-national (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 6.7%
industry:
21.4%
services:
71.9% (2005 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
11.6% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
11.8% (2008 est.)
note:
data are for Saudi males only (local bank estimates; some estimates range as high as 25%)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
24.2% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $167.7 billion
expenditures:
$164.3 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
20.3% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
18.9% of GDP (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
9.9% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.5% (31 December 2008)
NA% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
$113.2 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 15
$102.4 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$134.3 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 19
$109.5 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$66.94 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$246.3 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 20
$515.1 billion (31 December 2007)
$326.9 billion (31 December 2006)
|
|
|
|
|
wheat, barley, tomatoes, melons, dates, citrus; mutton, chickens, eggs, milk
|
|
|
|
|
crude oil production, petroleum refining, basic petrochemicals, ammonia, industrial gases, sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), cement, fertilizer, plastics, metals, commercial ship repair, commercial aircraft repair, construction
|
|
|
|
|
-7.2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
|
179.1 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
165.1 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10.78 million bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
2.38 million bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
|
8.728 million bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
79,250 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|
|
266.7 billion bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
80.44 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
|
80.44 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
|
|
|
|
|
7.319 trillion cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
$24.56 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
$132.6 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$180.5 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
$313.4 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum and petroleum products 90%
|
|
|
|
|
US 17.2%, Japan 15.3%, South Korea 10.2%, China 9.4%, India 5.9%, Taiwan 4.6%, Singapore 4.4% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$86.61 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$108.3 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, foodstuffs, chemicals, motor vehicles, textiles
|
|
|
|
|
US 12%, China 10.4%, Japan 7.6%, Germany 7.3%, South Korea 5.1%, Italy 4.7%, India 4.5%, UK 4% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$39.98 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
$30.59 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$72.45 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
$82.13 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$149.3 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
$108.5 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$20.57 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
$18.07 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Saudi riyals (SAR) per US dollar - 3.75 (2009), 3.75 (2008), 3.745 (2007), 3.745 (2006), 3.747 (2005)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Saudi Arabia |
|
|
4.1 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|
|
36 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: modern system
domestic:
extensive microwave radio relay, coaxial cable, and fiber-optic cable systems; mobile-cellular subscribership has been increasing rapidly
international:
country code - 966; landing point for the international submarine cable Fiber-Optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) and for both the SEA-ME-WE-3 and SEA-ME-WE-4 submarine cable networks providing connectivity to Asia, Middle East, Europe, and US; microwave radio relay to Bahrain, Jordan, Kuwait, Qatar, UAE, Yemen, and Sudan; coaxial cable to Kuwait and Jordan; satellite earth stations - 5 Intelsat (3 Atlantic Ocean and 2 Indian Ocean), 1 Arabsat, and 1 Inmarsat (Indian Ocean region) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 43, FM 31, shortwave 2 (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
117 (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
.sa
|
|
|
|
|
471,217 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|
|
7.7 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Saudi Arabia |
|
|
217 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
total: 80
over 3,047 m:
31
2,438 to 3,047 m:
16
1,524 to 2,437 m:
27
914 to 1,523 m:
2
under 914 m:
4 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 137
2,438 to 3,047 m:
8
1,524 to 2,437 m:
72
914 to 1,523 m:
41
under 914 m:
16 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
9 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
condensate 212 km; gas 1,880 km; liquid petroleum gas 1,183 km; oil 4,241 km; refined products 1,148 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,392 km
country comparison to the world: 83
standard gauge:
1,392 km 1.435-m gauge (with branch lines and sidings) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 221,372 km
country comparison to the world: 24
paved:
47,529 km (includes 3,891 km of expressways)
unpaved:
173,843 km (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 62
country comparison to the world: 64
by type:
cargo 5, chemical tanker 13, container 5, passenger/cargo 8, petroleum tanker 20, refrigerated cargo 3, roll on/roll off 8
foreign-owned:
12 (Egypt 1, Greece 3, Kuwait 7, UAE 1)
registered in other countries:
71 (Bahamas 16, Comoros 1, Dominica 2, France 1, Liberia 27, Marshall Islands 5, Norway 3, Panama 16) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Ad Dammam, Al Jubayl, Jiddah, Yanbu' al Sinaiyah
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ministry of Defense and Aviation Forces: Royal Saudi Land Forces, Royal Saudi Naval Forces (includes Marine Forces and Special Forces), Royal Saudi Air Force (Al-Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Malakiya as-Sa'udiya), Royal Saudi Air Defense Forces, Royal Saudi Strategic Rocket Forces, Saudi Arabian National Guard (SANG)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age (est.); no conscription (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 8,752,167
females age 16-49:
6,680,315 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 7,560,216
females age 16-49:
5,773,033 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 280,041
female:
269,580 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Saudi Arabia |
|
|
Saudi Arabia has reinforced its concrete-filled security barrier along sections of the now fully demarcated border with Yemen to stem illegal cross-border activities; Kuwait and Saudi Arabia continue discussions on a maritime boundary with Iran; Saudi Arabia claims Egyptian-administered islands of Tiran and Sanafir
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 240,015 (Palestinian Territories) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: Saudi Arabia is a destination country for workers from South and Southeast Asia who are subjected to conditions that constitute involuntary servitude including being subjected to physical and sexual abuse, non-payment of wages, confinement, and withholding of passports as a restriction on their movement; domestic workers are particularly vulnerable because some are confined to the house in which they work unable to seek help; Saudi Arabia is also a destination country for Nigerian, Yemeni, Pakistani, Afghan, Somali, Malian, and Sudanese children trafficked for forced begging and involuntary servitude as street vendors; some Nigerian women were reportedly trafficked into Saudi Arabia for commercial sexual exploitation
tier rating:
Tier 3 - Saudi Arabia does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; the government continues to lack adequate anti-trafficking laws and, despite evidence of widespread trafficking abuses, did not report any criminal prosecutions, convictions, or prison sentences for trafficking crimes committed against foreign domestic workers (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
death penalty for traffickers; improving anti-money-laundering legislation and enforcement
|
|
|
|
|