|
|
The Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes was formed in 1918; its name was changed to Yugoslavia in 1929. Various paramilitary bands resisted Nazi Germany's occupation and division of Yugoslavia from 1941 to 1945, but fought each other and ethnic opponents as much as the invaders. The military and political movement headed by Josip "TITO" Broz (Partisans) took full control of Yugoslavia when German and Croatian separatist forces were defeated in 1945. Although Communist, TITO's new government and his successors (he died in 1980) managed to steer their own path between the Warsaw Pact nations and the West for the next four and a half decades. In 1989, Slobodan MILOSEVIC became president of the Republic of Serbia and his ultranationalist calls for Serbian domination led to the violent breakup of Yugoslavia along ethnic lines. In 1991, Croatia, Slovenia, and Macedonia declared independence, followed by Bosnia in 1992. The remaining republics of Serbia and Montenegro declared a new Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY) in April 1992 and under MILOSEVIC's leadership, Serbia led various military campaigns to unite ethnic Serbs in neighboring republics into a "Greater Serbia." These actions led to Yugoslavia being ousted from the UN in 1992, but Serbia continued its - ultimately unsuccessful - campaign until signing the Dayton Peace Accords in 1995. MILOSEVIC kept tight control over Serbia and eventually became president of the FRY in 1997. In 1998, an ethnic Albanian insurgency in the formerly autonomous Serbian province of Kosovo provoked a Serbian counterinsurgency campaign that resulted in massacres and massive expulsions of ethnic Albanians living in Kosovo. The MILOSEVIC government's rejection of a proposed international settlement led to NATO's bombing of Serbia in the spring of 1999 and to the eventual withdrawal of Serbian military and police forces from Kosovo in June 1999. UNSC Resolution 1244 in June 1999 authorized the stationing of a NATO-led force (KFOR) in Kosovo to provide a safe and secure environment for the region's ethnic communities, created a UN interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK) to foster self-governing institutions, and reserved the issue of Kosovo's final status for an unspecified date in the future. FRY elections in September 2000 led to the ouster of MILOSEVIC, and in December 2000 a broad coalition of democratic reformist parties known as DOS (the Democratic Opposition of Serbia) was elected to parliament. DOS arrested MILOSEVIC in 2001 and sent him to be tried in The Hague for crimes against humanity. (MILOSEVIC died in March 2006 before the completion of his trial.) In 2001, the country's suspension from the UN was lifted. In 2003, the FRY became Serbia and Montenegro, a loose federation of the two republics with a federal level parliament. Widespread violence predominantly targeting ethnic Serbs in Kosovo in March 2004 caused the international community to open negotiations on the future status of Kosovo in January 2006. In May 2006, Montenegro invoked its right to secede from the federation and - following a successful referendum - it declared itself an independent nation on 3 June 2006. Two days later, Serbia declared that it was the successor state to the union of Serbia and Montenegro. A new Serbian constitution was approved in October 2006 and adopted the following month. In February 2008, after nearly two years of inconclusive negotiations, the UNMIK-administered province of Kosovo declared itself independent of Serbia - an action Serbia was powerless to stop, but which it refuses to recognize.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Southeastern Europe, between Macedonia and Hungary
|
|
|
|
|
44 00 N, 21 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 77,474 sq km
country comparison to the world: 116
land:
77,474 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than South Carolina
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,026 km
border countries:
Bosnia and Herzegovina 302 km, Bulgaria 318 km, Croatia 241 km, Hungary 151 km, Kosovo 352 km, Macedonia 62 km, Montenegro 124 km, Romania 476 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
in the north, continental climate (cold winters and hot, humid summers with well distributed rainfall); in other parts, continental and Mediterranean climate (relatively cold winters with heavy snowfall and hot, dry summers and autumns)
|
|
|
|
|
extremely varied; to the north, rich fertile plains; to the east, limestone ranges and basins; to the southeast, ancient mountains and hills
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: NA
highest point:
Midzor 2,169 m
|
|
|
|
|
oil, gas, coal, iron ore, copper, zinc, antimony, chromite, gold, silver, magnesium, pyrite, limestone, marble, salt, arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: NA
permanent crops:
NA
other:
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
208.5 cu km (note - includes Kosovo) (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
destructive earthquakes
|
|
|
|
|
air pollution around Belgrade and other industrial cities; water pollution from industrial wastes dumped into the Sava which flows into the Danube
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
controls one of the major land routes from Western Europe to Turkey and the Near East
|
|
|
|
|
|
7,344,847
country comparison to the world: 97
note:
does not include the population of Kosovo (July 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 15.2% (male 577,534/female 541,231)
15-64 years:
68.1% (male 2,503,260/female 2,501,844)
65 years and over:
16.6% (male 500,794/female 720,184) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 41.1 years
male:
39.4 years
female:
42.9 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-0.469% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 224
|
|
|
|
|
9.2 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
|
|
|
|
|
13.89 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 52% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
0.5% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.065 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.07 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1 male(s)/female
65 years and above:
0.7 male(s)/female
total population:
0.95 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 6.65 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 175
male:
7.68 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
5.56 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 74.09 years
country comparison to the world: 101
male:
71.26 years
female:
77.1 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.39 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200
|
|
|
|
|
0.1% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
|
|
|
|
|
6,400 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: intermediate
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne disease:
Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds
(2009)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Serb(s)
adjective:
Serbian
|
|
|
|
|
Serb 82.9%, Hungarian 3.9%, Romany (Gypsy) 1.4%, Yugoslavs 1.1%, Bosniaks 1.8%, Montenegrin 0.9%, other 8% (2002 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Serbian Orthodox 85%, Catholic 5.5%, Protestant 1.1%, Muslim 3.2%, unspecified 2.6%, other, unknown, or atheist 2.6% (2002 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Serbian 88.3% (official), Hungarian 3.8%, Bosniak 1.8%, Romany (Gypsy) 1.1%, other 4.1%, unknown 0.9% (2002 census)
note:
Romanian, Hungarian, Slovak, Ukrainian, and Croatian all official in Vojvodina
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
96.4%
male:
98.9%
female:
94.1% (2003 census)
note:
includes Montenegro
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Serbia
conventional short form:
Serbia
local long form:
Republika Srbija
local short form:
Srbija
former:
People's Republic of Serbia, Socialist Republic of Serbia
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
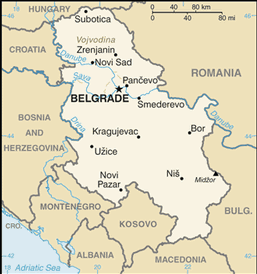
name: Belgrade (Beograd)
geographic coordinates:
44 50 N, 20 30 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
167 municipalities (opcstine, singular - opcstina)
Serbia Proper:
Belgrade City (Beograd): Barajevo, Cukarica, Grocka, Lazarevac, Mladenovac, Novi Beograd, Obrenovac, Palilula, Rakovica, Savski Venac, Sopot, Stari Grad, Surcin, Vozdovac, Vracar, Zemun, Zvezdara; Bor: Bor, Kladovo, Majdanpek, Negotin; Branicevo: Golubac, Kucevo, Malo Crnice, Petrovac, Pozarevac, Veliko Gradiste, Zabari, Zagubica; Grad Nis: Crveni Krst, Mediana, Niska Banja, Palilula, Pantelej Jablanica: Bojnik, Crna Trava, Lebane, Leskovac, Medveda, Vlasotince; Kolubara: Lajkovac, Ljig, Mionica, Osecina, Ub, Valjevo; Macva: Bogatic, Koceljeva, Krupanj, Ljubovija, Loznica, Mali Zvornik, Sabac, Vladimirci; Moravica: Cacak, Gornkji Milanovac, Ivanjica, Lucani; Nisava: Aleksinac, Doljevac, Gadzin Han, Merosina, Nis, Razanj, Svrljig; Pcinja: Bosilegrad, Bujanovac, Presevo, Surdulica, Trgoviste, Vladicin Han, Vranje; Pirot: Babusnica, Bela Palanka, Dimitrovgrad, Pirot; Podunavlje: Smederevo, Smederevskia Palanka, Velika Plana; Pomoravlje: Cuprija, Despotovac, Jagodina, Paracin, Rekovac, Svilajnac; Rasina: Aleksandrovac, Brus, Cicevac, Krusevac, Trstenik, Varvarin; Raska: Kraljevo, Novi Pazar, Raska, Tutin, Vrnjacka Banja; Sumadija: Arandelovac, Batocina, Knic, Kragujevac, Lapovo, Raca, Topola; Toplica: Blace, Kursumlija, Prokuplje, Zitorada; Zajecar: Boljevac, Knjazevac, Sokobanja, Zajecar; Zlatibor: Arilje, Bajina Basta, Cajetina, Kosjeric, Nova Varos, Pozega, Priboj, Prijepolje, Sjenica, Uzice
Vojvodina Autonomous Province:
South Backa: Bac, Backa Palanka, Backi Petrovac, Becej, Beocin, Novi Sad, Sremski Karlovci, Srobobran, Temerin, Titel, Vrbas, Zabalj; South Banat: Alibunar, Bela Crkva, Kovacica, Kovin, Opovo, Pancevo, Plandiste, Vrsac; North Backa: Backa Topola, Mali Idjos, Subotica; North Banat: Ada, Coka, Kanjiza, Kikinda, Novi Knezevac, Senta; Central Banat: Nova Crnja, Novi Becej, Secanj, Zitiste, Zrenjanin; Srem: Indija, Irig, Pecinci, Ruma, Sid, Sremska Mitrovica, Stara Pazova; West Backa: Apatin, Kula, Odzaci, Sombor
|
|
|
|
|
5 June 2006 (from Serbia and Montenegro)
|
|
|
|
|
National Day, 15 February
|
|
|
|
|
adopted 8 November 2006; effective 10 November 2006
|
|
|
|
|
based on civil law system
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Boris TADIC (since 11 July 2004)
head of government:
Prime Minister Mirko CVETKOVIC (since 7 July 2008)
cabinet:
Republican Ministries act as cabinet
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by direct vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 3 February 2008 (next to be held in 2013); prime minister elected by the National Assembly
election results:
Boris TADIC elected president in the second round of voting; Boris TADIC received 51.2% of the vote and Tomislav NIKOLIC 48.8%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Assembly (250 seats; deputies elected according to party lists to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 11 May 2008 (next to be held in May 2012)
election results:
percent of vote by party - For a European Serbia coalition 38.4%, SRS 29.5%, DSS-NS 11.6%, SPS-led coalition 7.6%, LPD 5.2%, other 7.7%; seats by party - For a European Serbia coalition 102, SRS 59, DSS-NS 30, SNS 19, SPS-led coalition 20, LDP 13, other 7; note - the seat allocation for the SNS and SRS is in flux because of an ongoing dispute between the parties
|
|
|
|
|
courts of general jurisdiction (municipal courts, district courts, Appellate Courts, the Supreme Court of Cassation); courts of special jurisdiction (commercial courts, the High Commercial Court, the High Magistrates Court, the Administrative Court)
|
|
|
|
|
Coalition for Sandzak or KZS [Sulejman UGLJANIN]; Democratic Party or DS [Boris TADIC]; Democratic Party of Albanians or PDSh [Ragmi MUSTAFA]; Democratic Party of Serbia or DSS [Vojislav KOSTUNICA]; Democratic Union of the Valley or BDL [Skender DESTANI]; Force of Serbia Movement or PSS [Bogoljub KARIC]; G17 Plus [Mladjan DINKIC]; League of Social Democrats of Vojvodina or LSV [Nenad CANAK]; League of Vojvodina Hungarians or SVM [Istvan PASTOR]; Liberal Democratic Party or LDP [Cedomir JOVANOVIC]; Movement for Democratic Progress or LPD [Jonuz MUSLIU]; New Serbia or NS [Velimir ILIC]; Party of Democratic Action or PVD [Riza HALIMI]; Party of United Pensioners of Serbia or PUPS [Jovan KRKOBABIC]; People's Party or NS [Maja GOJKOVIC]; Roma Party or RP [Srdjan SAJN]; Sanzak Democratic Party or SDP [Resad HODZIC]; Serbian Progressive Party or SNS [Tomislav NIKOLIC]; Serbian Radical Party or SRS [Vojislav SESELJ (currently on trial at The Hague), with Dragan TODOROVIC as acting leader]; Serbian Renewal Movement or SPO [Vuk DRASKOVIC]; Social Democratic Party of Serbia or SDPS [Rasim LJAJIC]; Socialist Party of Serbia or SPS [Ivica DACIC]; Union of Roma of Serbia or URS [Rajko DJURIC]; United Serbia or JS [Dragan "Palma" MARKOVIC]
|
|
|
|
|
Obraz (Orthodox clero-fascist organization); 1389 (Serbian national movement)
|
|
|
|
|
BSEC, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, FAO, G-9, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MONUC, NAM (observer), OAS (observer), OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, PFP, SECI, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Vladimir PETROVIC
chancery:
2134 Kalorama Road NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 332-0333
FAX:
[1] (202) 332-3933
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Mary WARLICK
embassy:
Kneza Milosa 50, 11000 Belgrade
mailing address:
5070 Belgrade Place, Washington, DC 20521-5070
telephone:
[381] (11) 361-9344
FAX:
[381] (11) 361-8230
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal stripes of red (top), blue, and white - the Pan-Slavic colors representing freedom and revolutionary ideals; charged with the coat of arms of Serbia shifted slightly to the hoist side; the principal field of the coat of arms represents the Serbian state and displays a white bicephalic eagle on a red shield; a smaller red shield on the eagle represents the Serbian nation, and is divided into four quarters by a white cross; a white Cyrillic "C" in each quarter stands for the phrase "Only Unity Saves the Serbs"; a royal crown surmounts the coat of arms
|
|
|
|
|
|
MILOSEVIC-era mismanagement of the economy, an extended period of international economic sanctions, and the damage to Yugoslavia's infrastructure and industry during the NATO airstrikes in 1999 left the economy only half the size it was in 1990. After the ousting of former Federal Yugoslav President MILOSEVIC in September 2000, the Democratic Opposition of Serbia (DOS) coalition government implemented stabilization measures and embarked on a market reform program. After renewing its membership in the IMF in December 2000, Yugoslavia continued to reintegrate into the international community by rejoining the World Bank (IBRD) and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD). Belgrade has made progress in trade liberalization and enterprise restructuring and privatization, including telecommunications and small- and medium-size firms. It has made some progress towards EU membership, signing a Stabilization and Association Agreement with Brussels in May 2008, and with full implementation of the Interim Trade Agreement with the EU in February 2010. Serbia is also pursuing membership in the World Trade Organization. Reforms needed to ensure the country's long-term viability have largely stalled since the onset of the global financial crisis. Serbia is grappling with fallout from crisis, which has led to a sharp drop in exports to Western Europe and a decline in manufacturing output. Unemployment and limited export earnings remain ongoing political and economic problems. Serbia signed an augmented $4 billion Stand By Arrangement with the IMF in May 2009. IMF conditions on Serbia constrain the use of stimulus efforts to revive the economy, while Serbia's concerns about inflation and exchange rate stability preclude the use of expansionary monetary policy. Nevertheless, the IMF projects that Serbia's economy will grow by 1.5% in 2010 after a 3% contraction in 2009 as a recovery in Western Europe takes hold.
|
|
|
|
|
$78.36 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
$80.78 billion (2008 est.)
$76.57 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$42.88 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-3% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
5.5% (2008 est.)
6.9% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$10,400 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
$10,900 (2008 est.)
$10,300 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 12.7%
industry:
23.5%
services:
63.8% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.107 million (October 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 23.9%
industry:
20.5%
services:
55.6% (October 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
16.6% (October 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
|
|
|
|
|
7.9% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
26 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 129
30 (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
33.1% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $9.7 billion
expenditures:
$11.3 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
31.3% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
37% of GDP (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.6% (2009)
country comparison to the world: 162
6.8% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
9.5% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 11
17.75% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
11.78% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 24
18.11% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$3.69 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 68
$3.831 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$14.11 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 53
$11.95 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$18.52 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 66
$17.06 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$13.91 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 68
$14.22 billion (31 December 2008)
$23.93 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
wheat, maize, sugar beets, sunflower, raspberries; beef, pork, milk
|
|
|
|
|
base metals, furniture, food processing, machinery, chemicals, sugar, tires, clothes, pharmaceuticals
|
|
|
|
|
1.8% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|
|
36 billion kWh (2009)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|
|
33.4 billion kWh (2009)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 billion kWh (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
121 million kWh (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
19,810 bbl/day (2008)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|
|
86,700 bbl/day NA bbl/day
country comparison to the world: 81
|
|
|
|
|
5,045 bbl/day (2008)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|
|
72,570 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
77.5 million bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|
|
230 million cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
|
|
|
|
|
2.61 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 130
|
|
|
|
|
2.4 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
48.14 billion cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
-$1.437 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 140
-$975 million (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$8.34 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
$8.824 billion (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
iron and steel, clothes, wheat, fruit and vegetables, non-ferrous metals
|
|
|
|
|
$15.85 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
$18.35 billion (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$17.33 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
|
|
|
|
|
$31.72 billion (30 November 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
$30.4 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2009 est.)
$11.95 billion (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
Serbian dinars (RSD) per US dollar - NA, 62.9 (2008), 54.5 (2007), 59.98 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.085 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 50
|
|
|
|
|
9.619 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 61
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: replacements of, and upgrades to, telecommunications equipment damaged during the 1999 war has resulted in a modern telecommunications system more than 95% digitalized in 2009
domestic:
wireless service, available through multiple providers with national coverage, is growing very rapidly; best telecommunications services are centered in urban centers; 3G mobile network launched in 2007
international:
country code - 381 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
308 (station frequency types NA) (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
138 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
.rs
|
|
|
|
|
181,313 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
2.936 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 59
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 121
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10
over 3,047 m:
2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
3
1,524 to 2,437 m:
3
914 to 1,523 m:
2 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 18
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
9
under 914 m:
8 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
2 (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 1,921 km; oil 323 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,379 km
country comparison to the world: 52
standard gauge:
3,379 km 1.435-m gauge (electrified 1,254 km) (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 36,875 km
country comparison to the world: 92
paved:
31,392 km
unpaved:
5,483 km (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
587 km (primarily on Danube and Sava rivers) (2008)
country comparison to the world: 81
|
|
|
|
|
|
Serbian Armed Forces (Vojska Srbije, VS): Land Forces Command (includes Riverine Component, consisting of a river flotilla on the Danube), Air and Air Defense Forces Command (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
19-35 years of age for male compulsory military service; under a state of war or impending war, conscription can begin at age 16; conscription is to be abolished in 2010; 6-month service obligation, with a reserve obligation to age 60 for men and 50 for women (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,405,391
females age 16-49:
1,368,207 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 43,925
female:
41,342 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Serbia |
|
|
Serbia with several other states protest the U.S. and other states' recognition of Kosovo's declaring itself as a sovereign and independent state in February 2008; ethnic Serbian municipalities along Kosovo's northern border challenge final status of Kosovo-Serbia boundary; several thousand NATO-led KFOR peacekeepers under UNMIK authority continue to keep the peace within Kosovo between the ethnic Albanian majority and the Serb minority in Kosovo; Serbia delimited about half of the boundary with Bosnia and Herzegovina, but sections along the Drina River remain in dispute
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 71,111 (Croatia); 27,414 (Bosnia and Herzegovina); 206,000 (Kosovo), note - mostly ethnic Serbs and Roma who fled Kosovo in 1999 (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
transshipment point for Southwest Asian heroin moving to Western Europe on the Balkan route; economy vulnerable to money laundering
|
|
|
|
|