|
|
Niger became independent from France in 1960 and experienced single-party and military rule until 1991, when Gen. Ali SAIBOU was forced by public pressure to allow multiparty elections, which resulted in a democratic government in 1993. Political infighting brought the government to a standstill and in 1996 led to a coup by Col. Ibrahim BARE. In 1999, BARE was killed in a counter coup by military officers who restored democratic rule and held elections that brought Mamadou TANDJA to power in December of that year. TANDJA was reelected in 2004 and in 2009 spearheaded a constitutional amendment that would allow him to extend his term as president. In February 2010, a military coup deposed TANDJA, immediately suspended the constitution and dissolved the Cabinet, and promised that elections would be held following a transitional period of unspecified duration. Niger is one of the poorest countries in the world with minimal government services and insufficient funds to develop its resource base. The largely agrarian and subsistence-based economy is frequently disrupted by extended droughts common to the Sahel region of Africa. A predominately Tuareg ethnic group emerged in February 2007, the Nigerien Movement for Justice (MNJ), and attacked several military targets in Niger's northern region throughout 2007 and 2008. Successful government offensives in 2009 limited the rebels' operational capabilities.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Western Africa, southeast of Algeria
|
|
|
|
|
16 00 N, 8 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1.267 million sq km
country comparison to the world: 22
land:
1,266,700 sq km
water:
300 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly less than twice the size of Texas
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5,697 km
border countries:
Algeria 956 km, Benin 266 km, Burkina Faso 628 km, Chad 1,175 km, Libya 354 km, Mali 821 km, Nigeria 1,497 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
desert; mostly hot, dry, dusty; tropical in extreme south
|
|
|
|
|
predominately desert plains and sand dunes; flat to rolling plains in south; hills in north
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Niger River 200 m
highest point:
Mont Bagzane 2,022 m
|
|
|
|
|
uranium, coal, iron ore, tin, phosphates, gold, molybdenum, gypsum, salt, petroleum
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 11.43%
permanent crops:
0.01%
other:
88.56% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
730 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
33.7 cu km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2.18 cu km/yr (4%/0%/95%)
per capita:
156 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
recurring droughts
|
|
|
|
|
overgrazing; soil erosion; deforestation; desertification; wildlife populations (such as elephant, hippopotamus, giraffe, and lion) threatened because of poaching and habitat destruction
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Law of the Sea
|
|
|
|
|
landlocked; one of the hottest countries in the world; northern four-fifths is desert, southern one-fifth is savanna, suitable for livestock and limited agriculture
|
|
|
|
|
|
15,878,271 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 49.7% (male 3,983,853/female 3,901,313)
15-64 years:
48% (male 3,797,815/female 3,823,518)
65 years and over:
2.3% (male 165,264/female 206,508) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 15.2 years
male:
15 years
female:
15.4 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.66% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
51.08 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
14.47 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 16% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
4% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.99 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.8 male(s)/female
total population:
1 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 114.5 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 3
male:
119.52 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
109.34 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 52.99 years
country comparison to the world: 204
male:
51.75 years
female:
54.26 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
7.68 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
0.8% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
|
|
|
|
|
60,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|
|
4,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne disease:
malaria
water contact disease:
schistosomiasis
animal contact disease:
rabies
respiratory disease:
meningococcal meningitis
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Nigerien(s)
adjective:
Nigerien
|
|
|
|
|
Haoussa 55.4%, Djerma Sonrai 21%, Tuareg 9.3%, Peuhl 8.5%, Kanouri Manga 4.7%, other 1.2% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim 80%, other (includes indigenous beliefs and Christian) 20%
|
|
|
|
|
French (official), Hausa, Djerma
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
28.7%
male:
42.9%
female:
15.1% (2005 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4 years
male:
5 years
female:
3 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
3.4% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Niger
conventional short form:
Niger
local long form:
Republique du Niger
local short form:
Niger
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
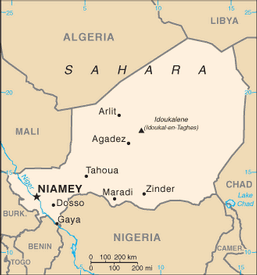
name: Niamey
geographic coordinates:
13 31 N, 2 07 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
8 regions (regions, singular - region) includes 1 capital district* (communite urbaine); Agadez, Diffa, Dosso, Maradi, Niamey*, Tahoua, Tillaberi, Zinder
|
|
|
|
|
3 August 1960 (from France)
|
|
|
|
|
Republic Day, 18 December (1958)
|
|
|
|
|
adopted 18 July 1999
|
|
|
|
|
based on French civil law system and customary law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: Salou DJIBO, chairman of the Supreme Council for the Restoration of Democracy, and a leader of the military coup that deposed President Mamadou TANDJA on 18 February 2010
head of government:
Prime Minister Mahamadou DANDA (since 19 February 2010); appointed by the president and shares some executive responsibilities with the president
cabinet:
26-member Cabinet appointed by the president (Cabinet dissolved following the 18 February 2010 coup)
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); second round of election last held on 4 December 2004 (no presidential election currently scheduled)
election results:
Mamadou TANDJA reelected president; percent of vote - Mamadou TANDJA 65.5%, Mahamadou ISSOUFOU 34.5%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Assembly (113 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections:
last held on 20 October 2009 (next to be held in 2014)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - MNSD 76, RSD 15, RDP 7, PNA-Alouma 1, Alkalami 1, Nigerien Party of the Masses for Labor 1, independents 12
|
|
|
|
|
State Court or Cour d'Etat; Court of Appeals or Cour d'Appel
|
|
|
|
|
Alkalama; Democratic and Social Convention-Rahama or CDS-Rahama [Mahamane OUSMANE]; National Movement for a Developing Society-Nassara or MNSD-Nassara [Hama AMADOU]; Niger Social Democratic Party or PSDN; Nigerien Alliance for Democracy and Social Progress-Zaman Lahiya or ANDP-Zaman Lahiya [Moumouni DJERMAKOYE]; Nigerien Party for Autonomy or PNA-Alouma [Sanousi JACKOU]; Nigerien Party for Democracy and Socialism or PNDS-Tarrayya [Issifou MAHAMADOU]; Nigerien Party of the Masses for Labor; Nigerien Progressive Party or PPN-RDA; Rally for Democracy and Progress or RDP-jama'a [Hamid ALGABID]; Social and Democratic Rally or RSD-Gaskiyya [Cheiffou AMADOU]
|
|
|
|
|
The Nigerien Movement for Justice or MNJ, a predominantly Tuareg rebel group
|
|
|
|
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, ECOWAS, Entente, FAO, FZ, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MONUC, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WADB (regional), WAEMU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Aminata Djibrilla Maiga TOURE
chancery:
2204 R Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 483-4224 through 4227
FAX:
[1] (202)483-3169
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Bernadette M. ALLEN
embassy:
Rue Des Ambassades, Niamey
mailing address:
B. P. 11201, Niamey
telephone:
[227] 20-72-26-61 thru 64
FAX:
[227] 20-73-31-67
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of orange (top), white, and green with a small orange disk (representing the sun) centered in the white band
note:
similar to the flag of India, which has a blue spoked wheel centered in the white band
|
|
|
|
|
|
Niger is one of the poorest countries in the world, ranking near last on the United Nations Development Fund index of human development. It is a landlocked, Sub-Saharan nation, whose economy centers on subsistence crops, livestock, and some of the world's largest uranium deposits. Drought cycles, desertification, and strong population growth have undercut the economy. Niger shares a common currency, the CFA franc, and a common central bank, the Central Bank of West African States (BCEAO), with seven other members of the West African Monetary Union. In December 2000, Niger qualified for enhanced debt relief under the International Monetary Fund program for Highly Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) and concluded an agreement with the Fund on a Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility (PRGF). Debt relief provided under the enhanced HIPC initiative significantly reduces Niger's annual debt service obligations, freeing funds for expenditures on basic health care, primary education, HIV/AIDS prevention, rural infrastructure, and other programs geared at poverty reduction. In December 2005, Niger received 100% multilateral debt relief from the IMF, which translates into the forgiveness of approximately US $86 million in debts to the IMF, excluding the remaining assistance under HIPC. Nearly half of the government's budget is derived from foreign donor resources. Future growth may be sustained by exploitation of oil, gold, coal, and other mineral resources. Uranium prices have increased sharply in the last few years.
|
|
|
|
|
$10.45 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
$10.25 billion (2008 est.)
$9.358 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$5.386 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
9.5% (2008 est.)
3.2% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$700 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 222
$700 (2008 est.)
$700 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 39%
industry:
17%
services:
44% (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
4.688 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 90%
industry:
6%
services:
4% (1995)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
63% (1993 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 2.3%
highest 10%:
35.7% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
50.5 (1995)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $320 million (includes $134 million from foreign sources)
expenditures:
$320 million (2002 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.1% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|
|
4.75% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 114
4.25% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$604.5 million (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$193.7 million (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$318.9 million (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
cowpeas, cotton, peanuts, millet, sorghum, cassava (tapioca), rice; cattle, sheep, goats, camels, donkeys, horses, poultry
|
|
|
|
|
uranium mining, cement, brick, soap, textiles, food processing, chemicals, slaughterhouses
|
|
|
|
|
5.1% (2003 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
|
150 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
|
|
|
|
|
589.5 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
450 million kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
|
|
|
|
|
6,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 180
|
|
|
|
|
5,367 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|
|
-$321 million (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
|
|
|
|
|
$428 million (2006)
country comparison to the world: 169
|
|
|
|
|
uranium ore, livestock, cowpeas, onions
|
|
|
|
|
Japan 80.8%, Nigeria 8.5%, France 2.9% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$800 million (2006)
country comparison to the world: 175
|
|
|
|
|
foodstuffs, machinery, vehicles and parts, petroleum, cereals
|
|
|
|
|
France 16.9%, China 11%, Algeria 9.7%, Nigeria 7.5%, French Polynesia 6.6%, Belgium 4.3% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.1 billion (2003 est.)
country comparison to the world: 130
|
|
|
|
|
Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) per US dollar - 481.35 (2009), 447.81 (2008), 493.51 (2007), 522.59 (2006), 527.47 (2005)
note:
since 1 January 1999, the West African CFA franc (XOF) has been pegged to the euro at a rate of 655.957 CFA francs per euro; West African CFA franc (XOF) coins and banknotes are not accepted in countries using Central African CFA francs (XAF), and vice versa, even though the two currencies trade at par
|
|
|
|
|
|
24,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 186
|
|
|
|
|
1.677 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 131
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: inadequate; small system of wire, radio telephone communications, and microwave radio relay links concentrated in the southwestern area of Niger
domestic:
combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity only 13 per 100 persons with cellular subscribership increasing rapidly from a small base; domestic satellite system with 3 earth stations and 1 planned
international:
country code - 227; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Atlantic Ocean and 1 Indian Ocean) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 5, FM 6, shortwave 4 (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
5 (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.ne
|
|
|
|
|
253 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 182
|
|
|
|
|
80,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 160
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 119
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10
2,438 to 3,047 m:
3
1,524 to 2,437 m:
6
914 to 1,523 m:
1 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 18
1,524 to 2,437 m:
2
914 to 1,523 m:
14
under 914 m:
2 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 18,550 km
country comparison to the world: 114
paved:
3,803 km
unpaved:
14,747 km (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
300 km (the Niger, the only major river, is navigable to Gaya between September and March) (2008)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nigerien Armed Forces (Forces Armees Nigeriennes, FAN): Army, Nigerien Air Force (Force Aerienne du Niger) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
17-21 years of age for selective compulsory or voluntary military service; enlistees must be Nigerien citizens and unmarried; 2-year service term; women may serve in health care (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 3,202,237
females age 16-49:
3,151,521 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 2,104,378
females age 16-49:
2,129,985 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 177,985
female:
172,180 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.3% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Niger |
|
|
Libya claims about 25,000 sq km in a currently dormant dispute in the Tommo region; much of Benin-Niger boundary, including tripoint with Nigeria, remains undemarcated; only Nigeria and Cameroon have heeded the Lake Chad Commission's admonition to ratify the delimitation treaty that also includes the Chad-Niger and Niger-Nigeria boundaries
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: Niger is a source, transit, and destination country for children and women trafficked for forced labor and sexual exploitation; caste-based slavery practices, rooted in ancestral master-slave relationships, continue in isolated areas of the country - an estimated 8,800 to 43,000 Nigeriens live under conditions of traditional slavery; children are trafficked within Niger for forced begging, forced labor in gold mines, domestic servitude, sexual exploitation, and possibly for forced labor in agriculture and stone quarries; women and children from neighboring states are trafficked to and through Niger for domestic servitude, sexual exploitation, forced labor in mines and on farms, and as mechanics and welders
tier rating:
Tier 3 - the Government of Niger does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making any significant efforts to do so; the government demonstrated marginal efforts to combat human trafficking, including traditional slavery, during the last year (2009)
|
|
|
|
|