| Introduction ::Liechtenstein |
|
|
The Principality of Liechtenstein was established within the Holy Roman Empire in 1719. Occupied by both French and Russian troops during the Napoleonic wars, it became a sovereign state in 1806 and joined the Germanic Confederation in 1815. Liechtenstein became fully independent in 1866 when the Confederation dissolved. Until the end of World War I, it was closely tied to Austria, but the economic devastation caused by that conflict forced Liechtenstein to enter into a customs and monetary union with Switzerland. Since World War II (in which Liechtenstein remained neutral), the country's low taxes have spurred outstanding economic growth. In 2000, shortcomings in banking regulatory oversight resulted in concerns about the use of financial institutions for money laundering. However, Liechtenstein implemented anti-money-laundering legislation and a Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty with the US that went into effect in 2003.
|
|
|
|
| Geography ::Liechtenstein |
|
|
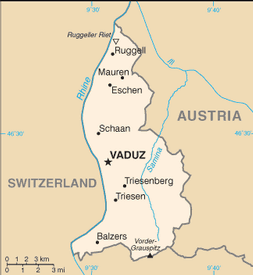
Central Europe, between Austria and Switzerland
|
|
|
|
|
47 16 N, 9 32 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 160 sq km
country comparison to the world: 218
land:
160 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
about 0.9 times the size of Washington, DC
|
|
|
|
|
total: 76 km
border countries:
Austria 34.9 km, Switzerland 41.1 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (doubly landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
continental; cold, cloudy winters with frequent snow or rain; cool to moderately warm, cloudy, humid summers
|
|
|
|
|
mostly mountainous (Alps) with Rhine Valley in western third
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Ruggeller Riet 430 m
highest point:
Vorder-Grauspitz 2,599 m
|
|
|
|
|
hydroelectric potential, arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 25%
permanent crops:
0%
other:
75% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Law of the Sea
|
|
|
|
|
along with Uzbekistan, one of only two doubly landlocked countries in the world; variety of microclimatic variations based on elevation
|
|
|
|
|
|
35,002 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 210
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 16.4% (male 2,845/female 2,888)
15-64 years:
69.2% (male 11,941/female 12,263)
65 years and over:
14.5% (male 2,197/female 2,868) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 41.4 years
male:
40.8 years
female:
41.9 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.683% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
|
|
|
|
|
9.69 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
|
|
|
|
|
7.49 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
|
|
|
|
|
4.63 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 14% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
0.5% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.006 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
0.98 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.77 male(s)/female
total population:
0.94 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4.2 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 205
male:
5.45 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
2.94 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 80.19 years
country comparison to the world: 20
male:
76.73 years
female:
83.66 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.53 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Liechtensteiner(s)
adjective:
Liechtenstein
|
|
|
|
|
Liechtensteiner 65.6%, other 34.4% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 76.2%, Protestant 7%, unknown 10.6%, other 6.2% (June 2002)
|
|
|
|
|
German (official), Alemannic dialect
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 10 and over can read and write
total population:
100%
male:
100%
female:
100%
|
|
|
|
|
total: 15 years
male:
16 years
female:
13 years (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
| Government ::Liechtenstein |
|
|
conventional long form: Principality of Liechtenstein
conventional short form:
Liechtenstein
local long form:
Fuerstentum Liechtenstein
local short form:
Liechtenstein
|
|
|
|
|
constitutional monarchy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Vaduz
geographic coordinates:
47 08 N, 9 31 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
11 communes (Gemeinden, singular - Gemeinde); Balzers, Eschen, Gamprin, Mauren, Planken, Ruggell, Schaan, Schellenberg, Triesen, Triesenberg, Vaduz
|
|
|
|
|
23 January 1719 (Principality of Liechtenstein established); 12 July 1806 (independence from the Holy Roman Empire)
|
|
|
|
|
Assumption Day, 15 August
|
|
|
|
|
5 October 1921; amended 15 September 2003
|
|
|
|
|
local civil and penal codes based on civil law system; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: Prince HANS ADAM II (since 13 November 1989, assumed executive powers on 26 August 1984); Heir Apparent Prince ALOIS, son of the monarch (born 11 June 1968); note - on 15 August 2004, HANS ADAM transferred the official duties of the ruling prince to ALOIS, but HANS ADAM retains status of chief of state
head of government:
Head of Government Klaus TSCHUETSCHER (since 25 March 2009)
cabinet:
Cabinet elected by the Parliament, confirmed by the monarch
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
the monarchy is hereditary; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party in the Landtag usually appointed the head of government by the monarch and the leader of the largest minority party in the Landtag usually appointed the deputy head of government by the monarch if there is a coalition government
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Parliament or Landtag (25 seats; members elected by popular vote under proportional representation to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 8 February 2009 (next to be held in February 2013)
election results:
percent of vote by party - VU 47.6%, FBP 43.5%, FL 8.9%; seats by party - VU 13, FBP 11, FL 1
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court or Oberster Gerichtshof; Court of Appeal or Obergericht
|
|
|
|
|
Die Freie Liste (The Free List) or FL [Wolfgang MARXER]; Fortschrittliche Buergerpartei (Progressive Citizens' Party) or FBP [Alexander BATLINER]; Vaterlaendische Union (Fatherland Union) or VU [Adolf HEEB]
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
CE, EBRD, EFTA, IAEA, ICCt, ICRM, IFRCS, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention (de facto member), UN, UNCTAD, UPU, WIPO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Claudia FRITSCHE
chancery:
2900 K Street, NW, Suite 602B, Washington, DC 20007
telephone:
[1] (202) 331-0590
FAX:
[1] (202) 331-3221
|
|
|
|
|
the US does not have an embassy in Liechtenstein; the US Ambassador to Switzerland is accredited to Liechtenstein
|
|
|
|
|
two equal horizontal bands of blue (top) and red with a gold crown on the hoist side of the blue band; the colors may derive from the blue and red livery design used in the principality's household in the 18th century; the prince's crown was introduced in 1937 to distinguish the flag from that of Haiti
|
|
|
|
|
|
Despite its small size and limited natural resources, Liechtenstein has developed into a prosperous, highly industrialized, free-enterprise economy with a vital financial service sector and the highest per capita income in the world. The Liechtenstein economy is widely diversified with a large number of small businesses. Low business taxes - the maximum tax rate is 20% - and easy incorporation rules have induced many holding companies to establish nominal offices in Liechtenstein providing 30% of state revenues. The country participates in a customs union with Switzerland and uses the Swiss franc as its national currency. It imports more than 90% of its energy requirements. Liechtenstein has been a member of the European Economic Area (an organization serving as a bridge between the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) and the EU) since May 1995. The government is working to harmonize its economic policies with those of an integrated Europe. In 2008, Liechtenstein came under renewed international pressure - particularly from Germany - to improve transparency in its banking and tax systems. In December 2008, Liechtenstein signed a Tax Information Exchange Agreement with the US. Upon Liechtenstein's conclusion of 12 bilateral information-sharing agreements, the OECD in October 2009 removed the principality from its "grey list" of countries that had yet to implement the organization's Model Tax Convention.
|
|
|
|
|
$4.16 billion (2007)
country comparison to the world: 166
$4.035 billion (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.603 billion (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
3.1% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|
|
$122,100 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 8%
industry:
39%
services:
54% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
32,440 of whom 16,200 commute from Austria, Switzerland, and Germany to work each day (2008)
country comparison to the world: 202
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 1.7%
industry:
43.5%
services:
55.4% (December 2006)
|
|
|
|
|
1.5% (31 December 2007)
country comparison to the world: 7
1.3% (September 2002)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $943 million
expenditures:
$820 million (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.5% (2009)
country comparison to the world: 32
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
wheat, barley, corn, potatoes; livestock, dairy products
|
|
|
|
|
electronics, metal manufacturing, dental products, ceramics, pharmaceuticals, food products, precision instruments, tourism, optical instruments
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
$3.92 billion (2008)
country comparison to the world: 113
|
|
|
|
|
small specialty machinery, connectors for audio and video, parts for motor vehicles, dental products, hardware, prepared foodstuffs, electronic equipment, optical products
|
|
|
|
|
$2.59 billion (2008)
country comparison to the world: 142
|
|
|
|
|
agricultural products, raw materials, energy products, machinery, metal goods, textiles, foodstuffs, motor vehicles
|
|
|
|
|
$0 (2001)
country comparison to the world: 195
|
|
|
|
|
Swiss francs (CHF) per US dollar - 1.1081 (2009), 1.0774 (2008), 1.1973 (2007), 1.2539 (2006), 1.2452 (2005)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Liechtenstein |
|
|
19,600 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 195
|
|
|
|
|
34,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 201
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: automatic telephone system
domestic:
fixed-line and mobile-cellular services widely available; combined telephone service subscribership exceeds 150 per 100 persons
international:
country code - 423; linked to Swiss networks by cable and microwave radio relay (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 0, FM 4, shortwave 0 (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
NA (linked to Swiss networks) (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
.li
|
|
|
|
|
9,287 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 118
|
|
|
|
|
23,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 187
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Liechtenstein |
|
|
gas 20 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
9 km 1.435-m gauge (electrified)
note:
belongs to the Austrian Railway System connecting Austria and Switzerland (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 380 km
country comparison to the world: 199
paved:
380 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
28 km (2008)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
|
no regular military forces (constitutionally prohibited); Principality of Liechtenstein National Police (Landespolizei, LP) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 8,041 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 6,559
females age 16-49:
6,782 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 209
female:
208 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Liechtenstein has no military forces but is interested in European security policy and is an active member of the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Liechtenstein |
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
has strengthened money laundering controls, but money laundering remains a concern due to Liechtenstein's sophisticated offshore financial services sector
|
|
|
|
|