|
|
The Indus Valley civilization, one of the world's oldest, flourished during the 3rd and 2nd millennia B.C. and extended into northwestern India. Aryan tribes from the northwest infiltrated onto the Indian subcontinent about 1500 B.C.; their merger with the earlier Dravidian inhabitants created the classical Indian culture. The Maurya Empire of the 4th and 3rd centuries B.C. - which reached its zenith under ASHOKA - united much of South Asia. The Golden Age ushered in by the Gupta dynasty (4th to 6th centuries A.D.) saw a flowering of Indian science, art, and culture. Islam spread across the subcontinent over a period of 700 years. In the 10th and 11th centuries, Turks and Afghans invaded India and established the Delhi Sultanate. In the early 16th century, the Emperor BABUR established the Mughal Dynasty which ruled India for more than three centuries. European explorers began establishing footholds in India during the 16th century. By the 19th century, Great Britain had become the dominant political power on the subcontinent. The British Indian Army played a vital role in both World Wars. Nonviolent resistance to British rule, led by Mohandas GANDHI and Jawaharlal NEHRU, eventually brought about independence in 1947. Communal violence led to the subcontinent's bloody partition, which resulted in the creation of two separate states, India and Pakistan. The two countries have fought three wars since independence, the last of which in 1971 resulted in East Pakistan becoming the separate nation of Bangladesh. India's nuclear weapons tests in 1998 caused Pakistan to conduct its own tests that same year. In November 2008, terrorists allegedly originating from Pakistan conducted a series of coordinated attacks in Mumbai, India's financial capital. Despite pressing problems such as significant overpopulation, environmental degradation, extensive poverty, and widespread corruption, rapid economic development is fueling India's rise on the world stage.
|
|
|
|
|
|
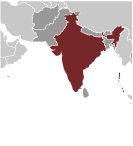
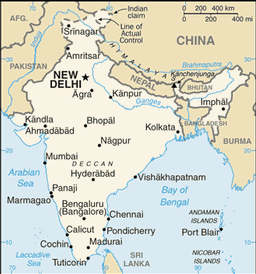
Southern Asia, bordering the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, between Burma and Pakistan
|
|
|
|
|
20 00 N, 77 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,287,263 sq km
country comparison to the world: 7
land:
2,973,193 sq km
water:
314,070 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly more than one-third the size of the US
|
|
|
|
|
total: 14,103 km
border countries:
Bangladesh 4,053 km, Bhutan 605 km, Burma 1,463 km, China 3,380 km, Nepal 1,690 km, Pakistan 2,912 km
|
|
|
|
|
7,000 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
varies from tropical monsoon in south to temperate in north
|
|
|
|
|
upland plain (Deccan Plateau) in south, flat to rolling plain along the Ganges, deserts in west, Himalayas in north
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Kanchenjunga 8,598 m
|
|
|
|
|
coal (fourth-largest reserves in the world), iron ore, manganese, mica, bauxite, titanium ore, chromite, natural gas, diamonds, petroleum, limestone, arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 48.83%
permanent crops:
2.8%
other:
48.37% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
558,080 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
1,907.8 cu km (1999)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 645.84 cu km/yr (8%/5%/86%)
per capita:
585 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
droughts; flash floods, as well as widespread and destructive flooding from monsoonal rains; severe thunderstorms; earthquakes
|
|
|
|
|
deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing; desertification; air pollution from industrial effluents and vehicle emissions; water pollution from raw sewage and runoff of agricultural pesticides; tap water is not potable throughout the country; huge and growing population is overstraining natural resources
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
dominates South Asian subcontinent; near important Indian Ocean trade routes; Kanchenjunga, third tallest mountain in the world, lies on the border with Nepal
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,173,108,018 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 30.1% (male 187,397,168/female 165,403,830)
15-64 years:
64.6% (male 391,430,598/female 366,256,167)
65 years and over:
5.3% (male 29,806,029/female 32,814,226) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 25.9 years
male:
25.4 years
female:
26.6 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.376% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
21.34 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|
|
7.53 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|
|
-0.05 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 29% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
2.4% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.12 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.13 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.07 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.91 male(s)/female
total population:
1.08 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 49.13 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 53
male:
47.7 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
50.73 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 66.46 years
country comparison to the world: 159
male:
65.46 years
female:
67.57 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.65 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|
|
0.3% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
|
|
|
|
|
2.4 million (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|
|
310,000 (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
chikungunya, dengue fever, Japanese encephalitis, and malaria
animal contact disease:
rabies
water contact disease:
leptospirosis
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Indian(s)
adjective:
Indian
|
|
|
|
|
Indo-Aryan 72%, Dravidian 25%, Mongoloid and other 3% (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
Hindu 80.5%, Muslim 13.4%, Christian 2.3%, Sikh 1.9%, other 1.8%, unspecified 0.1% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Hindi 41%, Bengali 8.1%, Telugu 7.2%, Marathi 7%, Tamil 5.9%, Urdu 5%, Gujarati 4.5%, Kannada 3.7%, Malayalam 3.2%, Oriya 3.2%, Punjabi 2.8%, Assamese 1.3%, Maithili 1.2%, other 5.9%
note:
English enjoys the status of subsidiary official language but is the most important language for national, political, and commercial communication; Hindi is the most widely spoken language and primary tongue of 41% of the people; there are 14 other official languages: Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, Tamil, Urdu, Gujarati, Malayalam, Kannada, Oriya, Punjabi, Assamese, Kashmiri, Sindhi, and Sanskrit; Hindustani is a popular variant of Hindi/Urdu spoken widely throughout northern India but is not an official language (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
61%
male:
73.4%
female:
47.8% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10 years
male:
11 years
female:
9 years (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
3.2% of GDP (2005)
country comparison to the world: 140
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of India
conventional short form:
India
local long form:
Republic of India/Bharatiya Ganarajya
local short form:
India/Bharat
|
|
|
|
|
federal republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: New Delhi
geographic coordinates:
28 36 N, 77 12 E
time difference:
UTC+5.5 (10.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
28 states and 7 union territories*; Andaman and Nicobar Islands*, Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chandigarh*, Chhattisgarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli*, Daman and Diu*, Delhi*, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep*, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Orissa, Puducherry*, Punjab, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal
|
|
|
|
|
15 August 1947 (from the UK)
|
|
|
|
|
Republic Day, 26 January (1950)
|
|
|
|
|
26 January 1950; amended many times
|
|
|
|
|
based on English common law; judicial review of legislative acts; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; separate personal law codes apply to Christians, Hindus, and Muslims
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Pratibha PATIL (since 25 July 2007); Vice President Hamid ANSARI (since 11 August 2007)
head of government:
Prime Minister Manmohan SINGH (since 22 May 2004)
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by an electoral college consisting of elected members of both houses of Parliament and the legislatures of the states for a five-year term (no term limits); election last held in July 2007 (next to be held in July 2012); vice president elected by both houses of Parliament for a five-year term; election last held in August 2007 (next to be held August 2012); prime minister chosen by parliamentary members of the majority party following legislative elections; election last held April - May 2009 (next to be held no later than May 2014)
election results:
Pratibha PATIL elected president; percent of vote - Pratibha PATIL 65.8%, Bhairon Singh SHEKHAWAT - 34.2%
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral Parliament or Sansad consists of the Council of States or Rajya Sabha (a body consisting of not more than 250 members up to 12 of whom are appointed by the president, the remainder are chosen by the elected members of the state and territorial assemblies; members serve six-year terms) and the People's Assembly or Lok Sabha (545 seats; 543 members elected by popular vote, 2 appointed by the president; members serve five-year terms)
elections:
People's Assembly - last held in five phases on 16, 22-23, 30 April and 7, 13 May 2009 (next must be held by May 2014)
election results:
People's Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - INC 206, BJP 116, SP 23, BSP 21, JD (U) 20, AITC 19, DMK 18, CPI-M 16, BJD 14, SS 11, AIADMK 9, NCP 9, other 61, vacant 2
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court (one chief justice and 25 associate justices are appointed by the president and remain in office until they reach the age of 65 or are removed for "proved misbehavior")
|
|
|
|
|
All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam or AIADMK [J. JAYALALITHAA]; All India Trinamool Congress or AITC [Mamata BANERJEE]; Bahujan Samaj Party or BSP [MAYAWATI]; Bharatiya Janata Party or BJP [Nitin GADKARI]; Biju Janata Dal or BJD [Naveen PATNAIK]; Communist Party of India or CPI [B. BARDHAN]; Communist Party of India-Marxist or CPI-M [Prakash KARAT]; Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam or DMK [Kalaignar M.KARUNANIDHI]; Indian National Congress or INC [Sonia GANDHI]; Janata Dal (United) or JD(U) [Sharad YADAV]; Left Front (an alliance of Indian leftist parties); Nationalist Congress Party or NCP [Sharad PAWAR]; Rashtriya Lok Dal or RLD [Ajit SINGH]; Samajwadi Party or SP [Mulayam Singh YADAV]; Shiromani Akali Dal or SAD [Parkash Singh BADAL]; Shiv Sena or SS [Bal THACKERAY]; Telugu Desam Party or TDP [Chandrababu NAIDU]; note - India has dozens of national and regional political parties; only parties or coalitions with four or more seats in the People's Assembly are listed
|
|
|
|
|
All Parties Hurriyat Conference in the Kashmir Valley (separatist group); Bajrang Dal (religious organization); National Socialist Council of Nagaland in the northeast (separatist group); Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh [Mohan BHAGWAT] (religious organization); Vishwa Hindu Parishad [Ashok SINGHAL] (religious organization)
other:
numerous religious or militant/chauvinistic organizations; various separatist groups seeking greater communal and/or regional autonomy
|
|
|
|
|
ADB, AfDB (nonregional member), ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), BIMSTEC, BIS, C, CD, CERN (observer), CICA, CP, EAS, FAO, G-15, G-20, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, LAS (observer), MIGA, MONUC, NAM, OAS (observer), OPCW, PCA, PIF (partner), SAARC, SACEP, SCO (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNITAR, UNMIS, UNMIT, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Meera SHANKAR
chancery:
2107 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008; note - Consular Wing located at 2536 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 939-7000
FAX:
[1] (202) 265-4351
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, Houston, New York, San Francisco
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Timothy J. ROEMER
embassy:
Shantipath, Chanakyapuri, New Delhi 110021
mailing address:
use embassy street address
telephone:
[91] (011) 2419-8000
FAX:
[91] (11) 2419-0017
consulate(s) general:
Chennai (Madras), Hyderabad; Kolkata (Calcutta), Mumbai (Bombay)
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of saffron (subdued orange) (top), white, and green, with a blue chakra (24-spoked wheel) centered in the white band
note:
similar to the flag of Niger, which has a small orange disk centered in the white band
|
|
|
|
|
|
India is developing into an open-market economy, yet traces of its past autarkic policies remain. Economic liberalization, including reduced controls on foreign trade and investment, began in the early 1990s and has served to accelerate the country's growth, which has averaged more than 7% per year since 1997. India's diverse economy encompasses traditional village farming, modern agriculture, handicrafts, a wide range of modern industries, and a multitude of services. Slightly more than half of the work force is in agriculture, but services are the major source of economic growth, accounting for more than half of India's output, with only one-third of its labor force. India has capitalized on its large educated English-speaking population to become a major exporter of information technology services and software workers. An industrial slowdown early in 2008, followed by the global financial crisis, led annual GDP growth to slow to 6.5% in 2009, still second highest growth in the world among major economies. India escaped the brunt of the global financial crisis because of cautious banking policies and a relatively low dependence on exports for growth. Domestic demand, driven by purchases of consumer durables and automobiles, has re-emerged as a key driver of growth, as exports have fallen since the global crisis started. India's fiscal deficit increased substantially in 2008 due to fuel and fertilizer subsidies, a debt waiver program for farmers, a job guarantee program for rural workers, and stimulus expenditures. The government abandoned its deficit target and allowed the deficit to reach 6.8% of GDP in FY10. Nevertheless, as shares of GDP, both government spending and taxation are among the lowest in the world. The government has expressed a commitment to fiscal stimulus in FY10, and to deficit reduction the following two years. It has increased the pace of privatization of government-owned companies, partly to offset the deficit. India's long term challenges include widespread poverty, inadequate physical and social infrastructure, limited employment opportunities, and insufficient access to basic and higher education. Over the long-term, a growing population and changing demographics will only exacerbate social, economic, and environmental problems.
|
|
|
|
|
$3.56 trillion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
$3.343 trillion (2008 est.)
$3.113 trillion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$1.095 trillion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.5% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
7.4% (2008 est.)
9% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$3,100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 164
$2,900 (2008 est.)
$2,800 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 17.5%
industry:
20%
services:
62.6% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
467 million (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 52%
industry:
14%
services:
34% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10.7% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
10.4% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
25% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3.6%
highest 10%:
31.1% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
36.8 (2004)
country comparison to the world: 79
37.8 (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
32.1% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $129.9 billion
expenditures:
$237.2 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
59.6% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
57.6% of GDP (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10.7% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
8.3% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.75% (9 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 75
6% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
11% (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
13.31% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$278.8 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 6
$239.8 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$853.4 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 6
$687.7 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$1 trillion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 12
$828.3 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.301 trillion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 17
$645.5 billion (31 December 2008)
$1.819 trillion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
rice, wheat, oilseed, cotton, jute, tea, sugarcane, lentils, onions, potatoes; dairy products, sheep, goats, poultry; fish
|
|
|
|
|
textiles, chemicals, food processing, steel, transportation equipment, cement, mining, petroleum, machinery, software, pharmaceuticals
|
|
|
|
|
7.6% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
|
|
|
|
|
723.8 billion kWh (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|
|
568 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|
|
810 million kWh (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.27 billion kWh (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.72 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
2.67 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|
|
738,600 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
|
2.9 million bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|
|
5.625 billion bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
32.85 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
|
|
|
|
|
42.99 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
10.79 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
1.075 trillion cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
-$8.399 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 172
-$30.41 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$165 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
$200.9 billion (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum products, precious stones, machinery, iron and steel, chemicals, vehicles, apparel
|
|
|
|
|
UAE 12.3%, US 11.7%, China 5.4%, Singapore 4.5% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$253.9 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
$322.3 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
crude oil, precious stones, machinery, fertilizer, iron and steel, chemicals
|
|
|
|
|
China 10.8%, Saudi Arabia 6.9%, US 6.7%, UAE 6.7%, Iran 4.2% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$287.5 billion (31 October 2009)
country comparison to the world: 4
$254 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$223.9 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
$232.5 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$161.3 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
$123.4 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$77.42 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
$61.77 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Indian rupees (INR) per US dollar - 46.78 (2009), 43.319 (2008), 41.487 (2007), 45.3 (2006), 44.101 (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
|
36.76 million (2010)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
545 million (2010)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: supported by recent deregulation and liberalization of telecommunications laws and policies, India has emerged as one of the fastest growing telecom markets in the world; total telephone subscribership base is approaching 600 million, an overall teledensity of 50%, and subscribership is currently growing nearly 20 million per month; urban teledensity has reached 100% and rural teledensity is about 20% and steadily growing
domestic:
mobile cellular service introduced in 1994 and organized nationwide into four metropolitan areas and 19 telecom circles each with multiple private service providers and one or more state-owned service providers; in recent years significant trunk capacity added in the form of fiber-optic cable and one of the world's largest domestic satellite systems, the Indian National Satellite system (INSAT), with 6 satellites supporting 33,000 very small aperture terminals (VSAT)
international:
country code - 91; a number of major international submarine cable systems, including Sea-Me-We-3 with landing sites at Cochin and Mumbai (Bombay), Sea-Me-We-4 with a landing site at Chennai, Fiber-Optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) with a landing site at Mumbai (Bombay), South Africa - Far East (SAFE) with a landing site at Cochin, the i2i cable network linking to Singapore with landing sites at Mumbai (Bombay) and Chennai (Madras), and Tata Indicom linking Singapore and Chennai (Madras), provide a significant increase in the bandwidth available for both voice and data traffic; satellite earth stations - 8 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) and 1 Inmarsat (Indian Ocean region); 9 gateway exchanges operating from Mumbai (Bombay), New Delhi, Kolkata (Calcutta), Chennai (Madras), Jalandhar, Kanpur, Gandhinagar, Hyderabad, and Ernakulam (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 149, FM 171, shortwave 54 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
1,400 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
.in
|
|
|
|
|
3.611 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
81 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|
|
|
349 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
|
total: 250
over 3,047 m:
20
2,438 to 3,047 m:
56
1,524 to 2,437 m:
76
914 to 1,523 m:
84
under 914 m:
14 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 99
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
1,524 to 2,437 m:
8
914 to 1,523 m:
42
under 914 m:
47 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
37 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
condensate/gas 2 km; gas 7,542 km; liquid petroleum gas 2,163 km; oil 7,659 km; refined products 7,201 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 64,015 km
country comparison to the world: 4
broad gauge:
52,808 km 1.676-m gauge (18,172 km electrified)
narrow gauge:
8,473 km 1.000-m gauge; 2,734 km 0.762-m gauge and 0.610-m gauge (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,320,410 km (includes 200 km of expressways) (2009)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
14,500 km
country comparison to the world: 9
note:
5,200 km on major rivers and 485 km on canals suitable for mechanized vessels (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 501
country comparison to the world: 23
by type:
bulk carrier 102, cargo 241, carrier 1, chemical tanker 19, container 13, liquefied gas 18, passenger 3, passenger/cargo 11, petroleum tanker 92, roll on/roll off 1
foreign-owned:
12 (China 1, Germany 2, Hong Kong 1, UAE 6, UK 2)
registered in other countries:
61 (Barbados 1, Comoros 2, Cyprus 2, Dominica 2, Liberia 2, Malta 2, Marshall Islands 1, Panama 27, Saint Kitts and Nevis 1, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 7, Singapore 13, unknown 1) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Chennai, Haldia, Jawaharal Nehru, Kandla, Kolkata (Calcutta), Mormugao, Mumbai (Bombay), New Mangalore, Vishakhapatnam
|
|
|
|
|
|
Army, Navy (includes naval air arm), Air Force (Bharatiya Vayu Sena), Coast Guard (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
16 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; women officers allowed in noncombat roles only (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 313,905,989
females age 16-49:
291,755,100 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 244,727,406
females age 16-49:
235,662,750 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 12,011,217
female:
10,639,158 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.5% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 61
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::India |
|
|
since China and India launched a security and foreign policy dialogue in 2005, consolidated discussions related to the dispute over most of their rugged, militarized boundary, regional nuclear proliferation, Indian claims that China transferred missiles to Pakistan, and other matters continue; various talks and confidence-building measures have cautiously begun to defuse tensions over Kashmir, particularly since the October 2005 earthquake in the region; Kashmir nevertheless remains the site of the world's largest and most militarized territorial dispute with portions under the de facto administration of China (Aksai Chin), India (Jammu and Kashmir), and Pakistan (Azad Kashmir and Northern Areas); India and Pakistan have maintained the 2004 cease fire in Kashmir and initiated discussions on defusing the armed stand-off in the Siachen glacier region; Pakistan protests India's fencing the highly militarized Line of Control and construction of the Baglihar Dam on the Chenab River in Jammu and Kashmir, which is part of the larger dispute on water sharing of the Indus River and its tributaries; UN Military Observer Group in India and Pakistan (UNMOGIP) has maintained a small group of peacekeepers since 1949; India does not recognize Pakistan's ceding historic Kashmir lands to China in 1964; to defuse tensions and prepare for discussions on a maritime boundary, India and Pakistan seek technical resolution of the disputed boundary in Sir Creek estuary at the mouth of the Rann of Kutch in the Arabian Sea; Pakistani maps continue to show its Junagadh claim in Indian Gujarat State; discussions with Bangladesh remain stalled to delimit a small section of river boundary, to exchange territory for 51 Bangladeshi exclaves in India and 111 Indian exclaves in Bangladesh, to allocate divided villages, and to stop illegal cross-border trade, migration, violence, and transit of terrorists through the porous border; Bangladesh protests India's attempts to fence off high-traffic sections of the border; India seeks cooperation from Bhutan and Burma to keep Indian Nagaland and Assam separatists from hiding in remote areas along the borders; Joint Border Committee with Nepal continues to examine contested boundary sections, including the 400 square kilometer dispute over the source of the Kalapani River; India maintains a strict border regime to keep out Maoist insurgents and control illegal cross-border activities from Nepal
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 77,200 (Tibet/China); 69,609 (Sri Lanka); 9,472 (Afghanistan)
IDPs:
at least 600,000 (about half are Kashmiri Pandits from Jammu and Kashmir) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: India is a source, destination, and transit country for men, women, and children trafficked for the purposes of forced labor and commercial sexual exploitation; internal forced labor may constitute India's largest trafficking problem; men, women, and children are held in debt bondage and face forced labor working in brick kilns, rice mills, agriculture, and embroidery factories; women and girls are trafficked within the country for the purposes of commercial sexual exploitation and forced marriage; children are subjected to forced labor as factory workers, domestic servants, beggars, and agriculture workers, and have been used as armed combatants by some terrorist and insurgent groups; India is also a destination for women and girls from Nepal and Bangladesh trafficked for the purpose of commercial sexual exploitation; Indian women are trafficked to the Middle East for commercial sexual exploitation; men and women from Bangladesh and Nepal are trafficked through India for forced labor and commercial sexual exploitation in the Middle East
tier rating:
Tier 2 Watch List - India is on the Tier 2 Watch List for a fifth consecutive year for its failure to provide evidence of increasing efforts to combat human trafficking in 2007; despite the reported extent of the trafficking crisis in India, government authorities made uneven efforts to prosecute traffickers and protect trafficking victims; government authorities continued to rescue victims of commercial sexual exploitation and forced child labor and child armed combatants, and began to show progress in law enforcement against these forms of trafficking; a critical challenge overall is the lack of punishment for traffickers, effectively resulting in impunity for acts of human trafficking; India has not ratified the 2000 UN TIP Protocol (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
world's largest producer of licit opium for the pharmaceutical trade, but an undetermined quantity of opium is diverted to illicit international drug markets; transit point for illicit narcotics produced in neighboring countries and throughout Southwest Asia; illicit producer of methaqualone; vulnerable to narcotics money laundering through the hawala system; licit ketamine and precursor production
|
|
|
|
|