|
|
Hungary became a Christian kingdom in A.D. 1000 and for many centuries served as a bulwark against Ottoman Turkish expansion in Europe. The kingdom eventually became part of the polyglot Austro-Hungarian Empire, which collapsed during World War I. The country fell under Communist rule following World War II. In 1956, a revolt and an announced withdrawal from the Warsaw Pact were met with a massive military intervention by Moscow. Under the leadership of Janos KADAR in 1968, Hungary began liberalizing its economy, introducing so-called "Goulash Communism." Hungary held its first multiparty elections in 1990 and initiated a free market economy. It joined NATO in 1999 and the EU in 2004.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Central Europe, northwest of Romania
|
|
|
|
|
47 00 N, 20 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 93,028 sq km
country comparison to the world: 109
land:
89,608 sq km
water:
3,420 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Indiana
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,185 km
border countries:
Austria 366 km, Croatia 329 km, Romania 443 km, Serbia 166 km, Slovakia 676 km, Slovenia 102 km, Ukraine 103 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
temperate; cold, cloudy, humid winters; warm summers
|
|
|
|
|
mostly flat to rolling plains; hills and low mountains on the Slovakian border
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Tisza River 78 m
highest point:
Kekes 1,014 m
|
|
|
|
|
bauxite, coal, natural gas, fertile soils, arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 49.58%
permanent crops:
2.06%
other:
48.36% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
2,300 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
120 cu km (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 21.03 cu km/yr (9%/59%/32%)
per capita:
2,082 cu m/yr (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
the upgrading of Hungary's standards in waste management, energy efficiency, and air, soil, and water pollution to meet EU requirements will require large investments
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
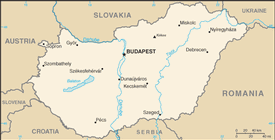
landlocked; strategic location astride main land routes between Western Europe and Balkan Peninsula as well as between Ukraine and Mediterranean basin; the north-south flowing Duna (Danube) and Tisza Rivers divide the country into three large regions
|
|
|
|
|
|
9,880,059 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 14.8% (male 753,733/female 710,482)
15-64 years:
69.2% (male 3,376,391/female 3,462,522)
65 years and over:
16% (male 571,877/female 1,005,054) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 39.7 years
male:
37.5 years
female:
42.2 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-0.26% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 217
|
|
|
|
|
9.43 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
|
|
|
|
|
12.9 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
0.87 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 68% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
0.3% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.062 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.57 male(s)/female
total population:
0.91 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 7.7 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 164
male:
8.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
6.95 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 73.69 years
country comparison to the world: 109
male:
69.53 years
female:
78.11 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.36 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
|
|
|
|
|
0.1% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
|
|
|
|
|
3,300 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 130
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 100 (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: intermediate
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea and hepatitis A
vectorborne diseases:
tickborne encephalitis (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Hungarian(s)
adjective:
Hungarian
|
|
|
|
|
Hungarian 92.3%, Roma 1.9%, other or unknown 5.8% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 51.9%, Calvinist 15.9%, Lutheran 3%, Greek Catholic 2.6%, other Christian 1%, other or unspecified 11.1%, unaffiliated 14.5% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Hungarian 93.6%, other or unspecified 6.4% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99.4%
male:
99.5%
female:
99.3% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 15 years
male:
15 years
female:
16 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
5.5% of GDP (2005)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Hungary
conventional short form:
Hungary
local long form:
Magyar Koztarsasag
local short form:
Magyarorszag
|
|
|
|
|
parliamentary democracy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Budapest
geographic coordinates:
47 30 N, 19 05 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
19 counties (megyek, singular - megye), 23 urban counties (singular - megyei varos), and 1 capital city (fovaros)
counties:
Bacs-Kiskun, Baranya, Bekes, Borsod-Abauj-Zemplen, Csongrad, Fejer, Gyor-Moson-Sopron, Hajdu-Bihar, Heves, Jasz-Nagykun-Szolnok, Komarom-Esztergom, Nograd, Pest, Somogy, Szabolcs-Szatmar-Bereg, Tolna, Vas, Veszprem, Zala
urban counties:
Bekescsaba, Debrecen, Dunaujvaros, Eger, Erd, Gyor, Hodmezovasarhely, Kaposvar, Kecskemet, Miskolc, Nagykanizsa, Nyiregyhaza, Pecs, Salgotarjan, Sopron, Szeged, Szekesfehervar, Szekszard, Szolnok, Szombathely, Tatabanya, Veszprem, Zalaegerszeg
capital city:
Budapest
|
|
|
|
|
25 December 1000 (crowning of King STEPHEN I, traditional founding date)
|
|
|
|
|
Saint Stephen's Day, 20 August
|
|
|
|
|
18 August 1949, effective 20 August 1949; revised 19 April 1972; 18 October 1989; and 1997
note:
18 October 1989 revision ensured legal rights for individuals and constitutional checks on the authority of the prime minister and also established the principle of parliamentary oversight; 1997 amendment streamlined the judicial system
|
|
|
|
|
based on the German-Austrian legal system; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Laszlo SOLYOM (since 5 August 2005)
head of government:
Prime Minister Gordon BAJNAI (since 20 April 2009)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers prime minister elected by the National Assembly on the recommendation of the president; other ministers proposed by the prime minister and appointed and relieved of their duties by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by the National Assembly for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 6-7 June 2005 (next to be held by June 2010); prime minister elected by the National Assembly on the recommendation of the president; election last held 14 April 2009
election results:
Laszlo SOLYOM was elected president by a simple majority in the third round of voting, 185 to 182; Gordon BAJNAI was elected prime minister; result of legislative vote - 204 to 0
note:
to be elected, the president must win two-thirds of legislative vote in the first two rounds or a simple majority in the third round
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Assembly or Orszaggyules (386 seats; members elected by popular vote under a system of proportional and direct representation to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 11 and 25 April 2010 (next to be held in April 2014)
election results:
percent of vote by party (5% or more of the vote required for parliamentary representation in the first round) - Fidesz 52.7%, MSzP %, Jobbik %, LMP %; seats by party - Fidesz 263, MSzP 59, Jobbik 47, LMP 16
|
|
|
|
|
Constitutional Court (judges are elected by the National Assembly for nine-year terms)
|
|
|
|
|
Alliance of Free Democrats or SzDSz [Attila RETKES]; Christian Democratic People's Party or KDNP [Semjen ZSOLT]; Hungarian Civic Alliance or Fidesz [Viktor ORBAN, chairman]; Hungarian Democratic Forum or MDF [Ibolya DAVID]; Hungarian Socialist Party or MSzP [Ildiko LENDVAI]; Movement for a Better Hungary or Jobbik [Gabor VONA]; Politics Can Be Different or LMP [13-member leadership]
|
|
|
|
|
Air Work Group (works to reduce air pollution in towns and cities); Company For Freedom Rights (Tarsasag a Szabadsagjogokert) or TASZ (personal data protection); Danube Circle (protests the building of the Gabchikovo-Nagymaros dam); Green Future (protests the impact of lead contamination of local factory on health of the people); environmentalists: Hungarian Ornithological and Nature Conservation Society (Magyar Madartani Egyesulet)or MME; Green Alternative (Zold Alternativa)
|
|
|
|
|
Australia Group, BIS, CE, CEI, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, ESA (cooperating state), EU, FAO, G-9, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MINURSO, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, SECI, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Bela SZOMBATI
chancery:
3910 Shoemaker Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 362-6730
FAX:
[1] (202) 966-8135
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, Los Angeles, New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Tsakopoulos KOUNALAKIS
embassy:
Szabadsag ter 12, H-1054 Budapest
mailing address:
pouch: American Embassy Budapest, 5270 Budapest Place, US Department of State, Washington, DC 20521-5270
telephone:
[36] (1) 475-4400
FAX:
[36] (1) 475-4764
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), white, and green; the flag dates to the national movement of the 18th and 19th centuries, and fuses the medieval colors of the Hungarian coat of arms with the revolutionary tricolor form of the French flag; folklore attributes virtues to the colors: red for strength, white for faithfulness, and green for hope; alternatively, the red is seen as being for the blood spilled in defense of the land, white for freedom, and green for the pasturelands that make up so much of the country
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hungary has made the transition from a centrally planned to a market economy, with a per capita income nearly two-thirds that of the EU-25 average. The private sector accounts for more than 80% of GDP. Foreign ownership of and investment in Hungarian firms is widespread, with cumulative foreign direct investment totaling more than $200 billion since 1989. The government's austerity measures, imposed since late 2006, have reduced the budget deficit from over 9% of GDP in 2006 to 3.3% in 2008. Hungary's impending inability to service its short-term debt - brought on by the global financial crisis in late 2008 - led Budapest to seek and receive an IMF-arranged financial assistance package worth over $25 billion. The global economic downturn, declining exports, and low domestic consumption and fixed asset accumulation, dampened by government austerity measures, resulted in an economic contraction of 6.7% in 2009.
|
|
|
|
|
$184.9 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
$198.2 billion (2008 est.)
$197 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$125.7 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-6.7% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 199
0.6% (2008 est.)
1.2% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$18,600 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
$20,000 (2008 est.)
$19,800 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 3.4%
industry:
34.3%
services:
62.4% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.8 million (January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 4.5%
industry:
32.1%
services:
63.4% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
10.8% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
7.8% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
12% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3.5%
highest 10%:
24.1% (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
28 (2005)
country comparison to the world: 123
24.4 (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
19% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $44.1 billion
expenditures:
$44.8 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
78% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
72.9% of GDP (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
6.1% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.25% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 45
10% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
6.66% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 86
10.18% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$30.27 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 31
$32.78 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$40.7 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 36
$47.49 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$88.67 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 43
$114.3 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$25.6 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 65
$21.9 billion (31 December 2008)
$47.65 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
wheat, corn, sunflower seed, potatoes, sugar beets; pigs, cattle, poultry, dairy products
|
|
|
|
|
mining, metallurgy, construction materials, processed foods, textiles, chemicals (especially pharmaceuticals), motor vehicles
|
|
|
|
|
-17.7% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
|
|
|
|
|
40.03 billion kWh (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|
|
37.4 billion kWh (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|
|
9.446 billion kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
13.35 billion kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
37,830 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
|
|
|
|
|
162,100 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
72,050 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
|
|
|
|
|
195,400 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
|
|
|
|
|
20.18 million bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|
|
2.643 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|
|
13.17 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
|
|
|
|
|
21 million cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
|
|
|
|
|
11.47 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
8.098 billion cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
|
|
|
|
|
$700 million (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
-$12.98 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$83.34 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
$107.5 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment 61.1%, other manufactures 28.7%, food products 6.5%, raw materials 2%, fuels and electricity 1.6% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 25.4%, Italy 5.2%, Romania 5.1%, Austria 4.7%, Taiwan 4.5%, Slovakia 4.5%, France 4.5%, UK 4.4% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$76.89 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
$107.9 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment 50%, fuels and electricity 11%, food products, raw materials
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 24.6%, Russia 8.7%, China 7.2%, Austria 6%, Taiwan 4.9%, Netherlands 4.4%, France 4.2%, Italy 4.1% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$44.18 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
$33.87 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$116.8 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 31
$212.1 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$238.5 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
$237.1 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$160.2 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
$159.7 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
forints (HUF) per US dollar - 200.64 (2009), 171.8 (2008), 183.83 (2007), 210.39 (2006), 199.58 (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.094 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|
|
12.224 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 50
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: the telephone system has been modernized; the system is digital and highly automated; trunk services are carried by fiber-optic cable and digital microwave radio relay; a program for fiber-optic subscriber connections was initiated in 1996
domestic:
competition among mobile-cellular service providers has led to a sharp increase in the use of mobile-cellular phones since 2000 and a decrease in the number of fixed-line connections
international:
country code - 36; Hungary has fiber-optic cable connections with all neighboring countries; the international switch is in Budapest; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean and Indian Ocean regions), 1 Inmarsat, 1 very small aperture terminal (VSAT) system of ground terminals
|
|
|
|
|
AM 5, FM 90, shortwave 1 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
95 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.hu
|
|
|
|
|
2.261 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|
|
5.873 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
total: 20
over 3,047 m:
2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
8
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4
914 to 1,523 m:
4
under 914 m:
2 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 26
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
1,524 to 2,437 m:
3
914 to 1,523 m:
10
under 914 m:
11 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
5 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 4,407 km; oil 987 km; refined products 335 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 8,057 km
country comparison to the world: 27
broad gauge:
36 km 1.524-m gauge
standard gauge:
7,802 km 1.435-m gauge (2,628 km electrified)
narrow gauge:
219 km 0.760-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 160,057 km
country comparison to the world: 32
paved:
70,539 km (31,363 km of interurban roads including 785 km of expressways)
unpaved:
89,518 km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
1,622 km (most on Danube River) (2008)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|
|
Budapest, Dunaujvaros, Gyor-Gonyu, Csepel, Baja, Mohacs
|
|
|
|
|
|
Land Forces, Hungarian Air Force (Magyar Legiero, ML) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
18-50 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; 6-month service obligation (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 2,380,381
females age 16-49:
2,319,142 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,884,232
females age 16-49:
1,923,902 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 58,894
female:
55,922 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.75% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Hungary |
|
|
bilateral government, legal, technical and economic working group negotiations continue in 2006 with Slovakia over Hungary's failure to complete its portion of the Gabcikovo-Nagymaros hydroelectric dam project along the Danube; as a member state that forms part of the EU's external border, Hungary has implemented the strict Schengen border rules
|
|
|
|
|
transshipment point for Southwest Asian heroin and cannabis and for South American cocaine destined for Western Europe; limited producer of precursor chemicals, particularly for amphetamine and methamphetamine; efforts to counter money laundering, related to organized crime and drug trafficking are improving but remain vulnerable; significant consumer of ecstasy
|
|
|
|
|