| Introduction ::Gaza Strip |
|
|
The September 1993 Israel-PLO Declaration of Principles on Interim Self-Government Arrangements provided for a transitional period of Palestinian self-rule in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Under a series of agreements signed between May 1994 and September 1999, Israel transferred to the Palestinian Authority (PA) security and civilian responsibility for many Palestinian-populated areas of the West Bank and Gaza. Negotiations to determine the permanent status of the West Bank and Gaza stalled following the outbreak of an intifada in September 2000. In April 2003, the Quartet (US, EU, UN, and Russia) presented a roadmap to a final settlement of the conflict by 2005 based on reciprocal steps by the two parties leading to two states, Israel and a democratic Palestine. Following Palestinian leader Yasir ARAFAT's death in late 2004, Mahmud ABBAS was elected PA president in January 2005. A month later, Israel and the PA agreed to the Sharm el-Sheikh Commitments in an effort to move the peace process forward. In September 2005, Israel unilaterally withdrew all its settlers and soldiers and dismantled its military facilities in the Gaza Strip and withdrew settlers and redeployed soldiers from four small northern West Bank settlements. Nonetheless, Israel still controls maritime, airspace, and most access to the Gaza Strip; and it enforces a restricted zone along the border inside Gaza. In January 2006, the Islamic Resistance Movement, HAMAS, won control of the Palestinian Legislative Council (PLC). HAMAS took control of the PA government in March 2006, but President ABBAS had little success negotiating with HAMAS to present a political platform acceptable to the international community so as to lift economic sanctions on Palestinians. Violent clashes between Fatah and HAMAS supporters in the Gaza Strip in 2006 and early 2007 resulted in numerous Palestinian deaths and injuries. In February 2007, ABBAS and HAMAS Political Bureau Chief MISHAL signed the Mecca Agreement in Saudi Arabia that resulted in the formation of a Palestinian National Unity Government (NUG) headed by HAMAS member Ismail HANIYA. However, fighting continued in the Gaza Strip, and in June 2007, HAMAS militants succeeded in a violent takeover of all military and governmental institutions in the Gaza Strip. ABBAS dismissed the NUG and through a series of presidential decrees formed a PA government in the West Bank led by independent Salam FAYYAD. HAMAS rejected the NUG's dismissal, and despite multiple rounds of Egyptian-brokered reconciliation negotiations, the two groups have failed to bridge their differences. Late November 2007 through June 2008 witnessed a substantial increase in Israeli-Palestinian violence. An Egyptian-brokered truce in June 2008 between Israel and HAMAS brought about a five-month pause in hostilities, but spiraling end-of-year violence resulted in the deaths of an estimated 1,100 to 1,400 Palestinians and left tens of thousands of people homeless. International donors pledged $4.5 billion in aid to rebuild the Gaza Strip, but by the end of 2009 large-scale reconstruction had not begun.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Middle East, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Egypt and Israel
|
|
|
|
|
31 25 N, 34 20 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 360 sq km
country comparison to the world: 205
land:
360 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly more than twice the size of Washington, DC
|
|
|
|
|
total: 62 km
border countries:
Egypt 11 km, Israel 51 km
|
|
|
|
|
40 km
|
|
|
|
|
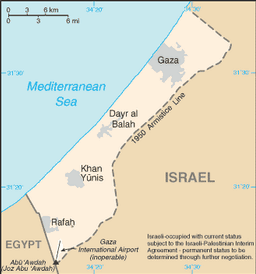
Israeli-occupied with current status subject to the Israeli-Palestinian Interim Agreement - permanent status to be determined through further negotiation
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
temperate, mild winters, dry and warm to hot summers
|
|
|
|
|
flat to rolling, sand- and dune-covered coastal plain
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Mediterranean Sea 0 m
highest point:
Abu 'Awdah (Joz Abu 'Auda) 105 m
|
|
|
|
|
arable land, natural gas
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 29%
permanent crops:
21%
other:
50% (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
155 sq km; (note - includes West Bank) (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
droughts
|
|
|
|
|
desertification; salination of fresh water; sewage treatment; water-borne disease; soil degradation; depletion and contamination of underground water resources
|
|
|
|
|
strategic strip of land along Mideast-North African trade routes has experienced an incredibly turbulent history; the town of Gaza itself has been besieged countless times in its history
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,604,238 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 44.1% (male 363,625/female 344,267)
15-64 years:
53.3% (male 437,031/female 417,636)
65 years and over:
2.6% (male 16,849/female 24,830) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 17.5 years
male:
17.4 years
female:
17.7 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.29% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|
|
36.26 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
3.36 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 215
|
|
|
|
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 72% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
3.3% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.68 male(s)/female
total population:
1.04 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 17.71 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 109
male:
18.87 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
16.48 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 73.68 years
country comparison to the world: 110
male:
72.05 years
female:
75.4 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.9 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
noun: NA
adjective:
NA
|
|
|
|
|
Palestinian Arab
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim (predominantly Sunni) 99.3%, Christian 0.7%
|
|
|
|
|
Arabic, Hebrew (spoken by many Palestinians), English (widely understood)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
92.4%
male:
96.7%
female:
88% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 14 years
male:
13 years
female:
14 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form:
Gaza Strip
local long form:
none
local short form:
Qita Ghazzah
|
|
|
|
|
|
High population density, limited land and sea access, continuing isolation, and strict internal and external security controls have degraded economic conditions in the Gaza Strip - the smaller of the two areas in the Palestinian Territories. Israeli-imposed crossings closures, which became more restrictive after HAMAS violently took over the territory in June 2007, and fighting between HAMAS and Israel during December 2008-January 2009, resulted in the near collapse of most of the private sector, extremely high unemployment, and high poverty rates. Shortages of many goods are met through the HAMAS-controlled black market tunnel trade that flourishes under the Gaza Strip's border with Egypt.
|
|
|
|
|
See entry for West Bank; $NA
|
|
|
|
|
See entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
See entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
See entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
339,000 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 161
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 12%
industry:
5%
services:
83% (June 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
40% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
37% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
70% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
see entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
9.9% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 190
11.5% (2008)
note:
includes West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
see entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
see entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
olives, fruit, vegetables, flowers; beef, dairy products
|
|
|
|
|
textiles, food processing
|
|
|
|
|
see entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
65,000 kWh (2009)
country comparison to the world: 212
|
|
|
|
|
202,000 kWh (2009)
country comparison to the world: 214
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
120,000 kWh; note - from Israeli Electric Company (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
See entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
See entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
See entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
See entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
NA bbl NA bbl
|
|
|
|
|
strawberries, carnations
|
|
|
|
|
see entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
food, consumer goods
note:
Israel permits limited imports through crossings with Gaza, but most commercial goods are smuggled through tunnels beneath Gaza's border with Egypt
|
|
|
|
|
see entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
new Israeli shekels (ILS) per US dollar - 3.93 (2009), 3.56 (2008), 4.14 (2007), 4.4565 (2006), 4.4877 (2005)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Gaza Strip |
|
|
360,400 (includes West Bank) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
2.405 million (includes West Bank) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 118
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: Gaza continues to repair the damage to its telecommunications infrastructure caused by fighting in 2009
domestic:
Israeli company BEZEK and the Palestinian company PALTEL are responsible for fixed line services; the Palestinian JAWWAL company provides cellular services
international:
country code - 970 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 0, FM 10, shortwave 0 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.ps; note - same as West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
356,000 (includes West Bank) (2008)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Gaza Strip |
|
|
1 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 230
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1
over 3,047 m:
1 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
note: see entry for West Bank
|
|
|
|
|
Gaza
|
|
|
|
|
|
Palestinian Authority security forces have operated only in the West Bank, not in the Gaza Strip, since HAMAS seized power in June 2007; law and order and other security functions are performed by HAMAS security organizations (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 372,843 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 324,203
females age 16-49:
308,835 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 18,931
female:
18,010 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Gaza Strip |
|
|
West Bank and Gaza Strip are Israeli-occupied with current status subject to the Israeli-Palestinian Interim Agreement - permanent status to be determined through further negotiation; Israel removed settlers and military personnel from the Gaza Strip in August 2005
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 1.017 million (Palestinian Refugees (UNRWA)) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|