|
|
As Europe's largest economy and second most populous nation (after Russia), Germany is a key member of the continent's economic, political, and defense organizations. European power struggles immersed Germany in two devastating World Wars in the first half of the 20th century and left the country occupied by the victorious Allied powers of the US, UK, France, and the Soviet Union in 1945. With the advent of the Cold War, two German states were formed in 1949: the western Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) and the eastern German Democratic Republic (GDR). The democratic FRG embedded itself in key Western economic and security organizations, the EC, which became the EU, and NATO, while the Communist GDR was on the front line of the Soviet-led Warsaw Pact. The decline of the USSR and the end of the Cold War allowed for German unification in 1990. Since then, Germany has expended considerable funds to bring Eastern productivity and wages up to Western standards. In January 1999, Germany and 10 other EU countries introduced a common European exchange currency, the euro.
|
|
|
|
|
|
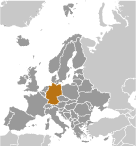
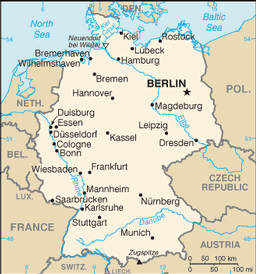
Central Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, between the Netherlands and Poland, south of Denmark
|
|
|
|
|
51 00 N, 9 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 357,022 sq km
country comparison to the world: 62
land:
348,672 sq km
water:
8,350 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Montana
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,621 km
border countries:
Austria 784 km, Belgium 167 km, Czech Republic 646 km, Denmark 68 km, France 451 km, Luxembourg 138 km, Netherlands 577 km, Poland 456 km, Switzerland 334 km
|
|
|
|
|
2,389 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
temperate and marine; cool, cloudy, wet winters and summers; occasional warm mountain (foehn) wind
|
|
|
|
|
lowlands in north, uplands in center, Bavarian Alps in south
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Neuendorf bei Wilster -3.54 m
highest point:
Zugspitze 2,963 m
|
|
|
|
|
coal, lignite, natural gas, iron ore, copper, nickel, uranium, potash, salt, construction materials, timber, arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 33.13%
permanent crops:
0.6%
other:
66.27% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
4,850 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
188 cu km (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 38.01 cu km/yr (12%/68%/20%)
per capita:
460 cu m/yr (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
flooding
|
|
|
|
|
emissions from coal-burning utilities and industries contribute to air pollution; acid rain, resulting from sulfur dioxide emissions, is damaging forests; pollution in the Baltic Sea from raw sewage and industrial effluents from rivers in eastern Germany; hazardous waste disposal; government established a mechanism for ending the use of nuclear power over the next 15 years; government working to meet EU commitment to identify nature preservation areas in line with the EU's Flora, Fauna, and Habitat directive
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location on North European Plain and along the entrance to the Baltic Sea
|
|
|
|
|
|
82,282,988 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 13.5% (male 5,720,367/female 5,425,389)
15-64 years:
66.1% (male 27,704,691/female 26,668,140)
65 years and over:
20.4% (male 7,048,438/female 9,715,963) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 44.3 years
male:
43 years
female:
45.6 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-0.061% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
|
|
|
|
|
8.21 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 219
|
|
|
|
|
11 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
|
2.19 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 74% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
0.1% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.055 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.72 male(s)/female
total population:
0.97 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3.95 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 209
male:
4.36 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
3.51 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 79.41 years
country comparison to the world: 33
male:
76.41 years
female:
82.57 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.42 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
|
|
|
|
|
0.1% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
|
|
|
|
|
53,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 500 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
|
|
|
|
|
noun: German(s)
adjective:
German
|
|
|
|
|
German 91.5%, Turkish 2.4%, other 6.1% (made up largely of Greek, Italian, Polish, Russian, Serbo-Croatian, Spanish)
|
|
|
|
|
Protestant 34%, Roman Catholic 34%, Muslim 3.7%, unaffiliated or other 28.3%
|
|
|
|
|
German
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99%
male:
99%
female:
99% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 16 years
male:
16 years
female:
16 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
4.6% of GDP (2004)
country comparison to the world: 81
|
|
|
|
|
second most populous country in Europe after Russia
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Federal Republic of Germany
conventional short form:
Germany
local long form:
Bundesrepublik Deutschland
local short form:
Deutschland
former:
German Empire, German Republic, German Reich
|
|
|
|
|
federal republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Berlin
geographic coordinates:
52 31 N, 13 24 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
16 states (Laender, singular - Land); Baden-Wurttemberg, Bayern (Bavaria), Berlin, Brandenburg, Bremen, Hamburg, Hessen, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania), Niedersachsen (Lower Saxony), Nordrhein-Westfalen (North Rhine-Westphalia), Rheinland-Pfalz (Rhineland-Palatinate), Saarland, Sachsen (Saxony), Sachsen-Anhalt (Saxony-Anhalt), Schleswig-Holstein, Thuringen (Thuringia); note - Bayern, Sachsen, and Thuringen refer to themselves as free states (Freistaaten, singular - Freistaat)
|
|
|
|
|
18 January 1871 (German Empire unification); divided into four zones of occupation (UK, US, USSR, and later, France) in 1945 following World War II; Federal Republic of Germany (FRG or West Germany) proclaimed 23 May 1949 and included the former UK, US, and French zones; German Democratic Republic (GDR or East Germany) proclaimed 7 October 1949 and included the former USSR zone; West Germany and East Germany unified 3 October 1990; all four powers formally relinquished rights 15 March 1991
|
|
|
|
|
Unity Day, 3 October (1990)
|
|
|
|
|
23 May 1949, known as Basic Law; became constitution of the united Germany 3 October 1990
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system with indigenous concepts; judicial review of legislative acts in the Federal Constitutional Court; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Horst KOEHLER (since 1 July 2004)
head of government:
Chancellor Angela MERKEL (since 22 November 2005)
cabinet:
Cabinet or Bundesminister (Federal Ministers) appointed by the president on the recommendation of the chancellor
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected for a five-year term (eligible for a second term) by a Federal Convention, including all members of the Federal Assembly and an equal number of delegates elected by the state parliaments; election last held on 23 May 2009 (next scheduled for 23 May 2014); chancellor elected by an absolute majority of the Federal Assembly for a four-year term; Bundestag vote for Chancellor last held after 27 September 2009 (next to follow the legislative election to be held no later than 2013)
election results:
Horst KOEHLER reelected president; received 613 votes of the Federal Convention against 503 for Gesine SCHWAN; Angela MERKEL reelected chancellor; vote by Federal Assembly 323 to 285 with four abstentions
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral legislature consists of the Federal Council or Bundesrat (69 votes; state governments sit in the Council; each has three to six votes in proportion to population and are required to vote as a block) and the Federal Assembly or Bundestag (622 seats; members elected by popular vote for a four-year term under a system of personalized proportional representation; a party must win 5% of the national vote or three direct mandates to gain proportional representation and caucus recognition)
elections:
Bundestag - last held on 27 September 2009 (next to be held no later than autumn 2013); note - there are no elections for the Bundesrat; composition is determined by the composition of the state-level governments; the composition of the Bundesrat has the potential to change any time one of the 16 states holds an election
election results:
Bundestag - percent of vote by party - CDU/CSU 33.8%, SPD 23%, FDP 14.6%, Left 11.9%, Greens 10.7%, other 6%; seats by party - CDU/CSU 239, SPD 146, FDP 93, Left 76, Greens 68
|
|
|
|
|
Federal Constitutional Court or Bundesverfassungsgericht (half the judges are elected by the Bundestag and half by the Bundesrat)
|
|
|
|
|
Alliance '90/Greens [Claudia ROTH and Cem OZDEMIR]; Christian Democratic Union or CDU [Angela MERKEL]; Christian Social Union or CSU [Horst SEEHOFER]; Free Democratic Party or FDP [Guido WESTERWELLE]; Left Party or Die Linke [Lothar BISKY and Oskar LAFONTAINE]; Social Democratic Party or SPD [Sigmar GABRIEL]
|
|
|
|
|
business associations and employers' organizations; trade unions; religious, immigrant, expellee, and veterans groups
|
|
|
|
|
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council (observer), Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CBSS, CDB, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-20, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, Schengen Convention, SECI (observer), SICA (observer), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WADB (nonregional), WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Klaus SCHARIOTH
chancery:
4645 Reservoir Road NW, Washington, DC 20007
telephone:
[1] (202) 298-4000
FAX:
[1] (202) 298-4249
consulate(s) general:
Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, San Francisco
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Philip D. MURPHY
embassy:
Pariser Platz 2, 14191 Berlin; note - new embassy opened 4 July 2008
mailing address:
PSC 120, Box 1000, APO AE 09265, Clayallee 170, 14195 Berlin
telephone:
[49] (030) 2385174
FAX:
[49] (030) 8305-1215
consulate(s) general:
Duesseldorf, Frankfurt am Main, Hamburg, Leipzig, Munich
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of black (top), red, and gold; these colors have played an important role in German history and can be traced back to the medieval banner of the Holy Roman Emperor - a black eagle with red claws and beak on a gold field
|
|
|
|
|
|
The German economy - the fifth largest economy in the world in PPP terms and Europe's largest - is a leading exporter of machinery, vehicles, chemicals, and household equipment and benefits from a highly skilled labor force. Like its western European neighbors, Germany faces significant demographic challenges to sustained long-term growth. Low fertility rates and declining net immigration are increasing pressure on the country's social welfare system and necessitate structural reforms. The modernization and integration of the eastern German economy - where unemployment can exceed 20% in some municipalities - continues to be a costly long-term process, with annual transfers from west to east amounting in 2008 alone to roughly $12 billion. Reforms launched by the government of Chancellor Gerhard SCHROEDER (1998-2005), deemed necessary to address chronically high unemployment and low average growth, contributed to strong growth in 2006 and 2007 and falling unemployment, which in 2008 reached a new post-reunification low of 7.8%. These advances, as well as a government subsidized, reduced working hour scheme, have helped to explain the relatively modest increase in unemployment during Germany's 2008-09 recession - the deepest since World War II. GDP grew just over 1% in 2008 and contracted roughly 5% in 2009. Germany crept out of recession in the second and third quarters of 2009, thanks largely to rebounding manufacturing orders and exports - primarily outside the Euro Zone - and relatively steady consumer demand. The German economy probably will recover to about 1.5% growth for the year 2010. However, a relatively strong euro, tighter credit markets, and an anticipated bump in unemployment could cloud Germany's medium-term recovery prospects. Stimulus and stabilization efforts initiated in 2008 and 2009 and tax cuts introduced in Chancellor Angela MERKEL's second term will increase Germany's record budget deficit, which is expected to exceed 5% of GDP in 2010. The EU has given Germany until 2013 to get its consolidated budget deficit below 3% of GDP. A new constitutional amendment likewise limits the federal government to structural deficits of no more than 0.35% of GDP per annum as of 2016.
|
|
|
|
|
$2.811 trillion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
$2.959 trillion (2008 est.)
$2.921 trillion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$3.273 trillion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-5% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 190
1.3% (2008 est.)
2.5% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$34,100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
$35,900 (2008 est.)
$35,500 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 0.9%
industry:
27.1%
services:
72% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
43.51 million (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 2.4%
industry:
29.7%
services:
67.8% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
8.2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
7.8% (2008 est.)
note:
this is the International Labor Organization's estimated rate for international comparisons; Germany's Federal Employment Office estimated a seasonally adjusted rate of 10.8%
|
|
|
|
|
11% (2001 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3.6%
highest 10%:
24% (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
27 (2006)
country comparison to the world: 125
30 (1994)
|
|
|
|
|
18.9% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $1.398 trillion
expenditures:
$1.54 trillion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
77.2% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
66% of GDP (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
2.7% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.75% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 129
3% (31 December 2008)
note:
this is the European Central Bank's rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks in the euro area
|
|
|
|
|
5.97% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 139
5.96% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
note:
see entry for the European Union for money supply in the euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 16 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money and quasi money circulating within their own borders
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
$5.019 trillion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 5
$4.457 trillion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 8
$2.106 trillion (31 December 2007)
$1.638 trillion (31 December 2006)
|
|
|
|
|
potatoes, wheat, barley, sugar beets, fruit, cabbages; cattle, pigs, poultry
|
|
|
|
|
among the world's largest and most technologically advanced producers of iron, steel, coal, cement, chemicals, machinery, vehicles, machine tools, electronics, food and beverages, shipbuilding, textiles
|
|
|
|
|
-11% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
|
|
|
|
|
593.4 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|
|
547.3 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
61.7 billion kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
41.67 billion kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
150,800 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
|
|
|
|
|
2.569 million bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
582,900 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
2.777 million bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
276 million bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|
|
16.36 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
95.79 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
12.68 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|
|
91.99 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
175.6 billion cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
|
|
|
|
|
$109.7 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
$243.6 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.121 trillion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
$1.498 trillion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery, vehicles, chemicals, metals and manufactures, foodstuffs, textiles
|
|
|
|
|
France 10.2%, US 6.7%, Netherlands 6.7%, UK 6.6%, Italy 6.3%, Austria 6%, China 4.5%, Switzerland 4.4% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$931.3 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
$1.232 trillion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery, vehicles, chemicals, foodstuffs, textiles, metals
|
|
|
|
|
Netherlands 8.5%, China 8.2%, France 8.2%, US 5.9%, Italy 5.9%, UK 4.9%, Belgium 4.3%, Austria 4.3%, Switzerland 4.2% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2009 est.)
$138 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$5.208 trillion (30 June 2009)
country comparison to the world: 3
$5.158 trillion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.021 trillion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
$1.027 trillion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.403 trillion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
$1.407 trillion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
euros (EUR) per US dollar - 0.7338 (2009), 0.6827 (2008), 0.7345 (2007), 0.7964 (2006), 0.8041 (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
|
51.5 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
107.245 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: Germany has one of the world's most technologically advanced telecommunications systems; as a result of intensive capital expenditures since reunification, the formerly backward system of the eastern part of the country, dating back to World War II, has been modernized and integrated with that of the western part
domestic:
Germany is served by an extensive system of automatic telephone exchanges connected by modern networks of fiber-optic cable, coaxial cable, microwave radio relay, and a domestic satellite system; cellular telephone service is widely available, expanding rapidly, and includes roaming service to many foreign countries
international:
country code - 49; Germany's international service is excellent worldwide, consisting of extensive land and undersea cable facilities as well as earth stations in the Inmarsat, Intelsat, Eutelsat, and Intersputnik satellite systems (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 51, FM 787, shortwave 4 (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
373 (plus 8,042 repeaters) (1995)
|
|
|
|
|
.de
|
|
|
|
|
23.796 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
61.973 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 6
|
|
|
|
|
|
550 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
total: 330
over 3,047 m:
13
2,438 to 3,047 m:
52
1,524 to 2,437 m:
58
914 to 1,523 m:
72
under 914 m:
135 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 220
1,524 to 2,437 m:
3
914 to 1,523 m:
33
under 914 m:
184 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
25 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 24,364 km; oil 3,379 km; refined products 3,843 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 41,896 km
country comparison to the world: 6
standard gauge:
41,641 km 1.435-m gauge (20,053 km electrified)
narrow gauge:
75 km 1.000-m gauge (75 km electrified); 180 km 0.750-m gauge (24 km electrified) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 644,480 km
country comparison to the world: 11
paved:
644,480 km (includes 12,600 km of expressways)
note:
includes local roads (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
7,467 km
country comparison to the world: 19
note:
Rhine River carries most goods; Main-Danube Canal links North Sea and Black Sea (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 393
country comparison to the world: 26
by type:
bulk carrier 2, cargo 43, chemical tanker 13, container 284, liquefied gas 5, passenger 5, passenger/cargo 27, petroleum tanker 11, roll on/roll off 3
foreign-owned:
11 (China 2, Cyprus 2, Denmark 1, Finland 4, Netherlands 1, Sweden 1)
registered in other countries:
2,998 (Antigua and Barbuda 941, Australia 2, Bahamas 44, Bermuda 22, Brazil 6, Bulgaria 63, Burma 1, Canada 3, Cayman Islands 15, Cyprus 189, Denmark 9, Denmark 1, Estonia 1, Finland 1, France 1, Georgia 2, Gibraltar 129, Hong Kong 6, India 2, Indonesia 1, Isle of Man 56, Jamaica 4, Liberia 849, Luxembourg 5, Malaysia 1, Malta 91, Marshall Islands 235, Mongolia 4, Morocco 2, Netherlands 75, Netherlands Antilles 43, Norway 1, NZ 1, Panama 44, Portugal 20, Russia 1, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 3, Singapore 24, Slovakia 3, Spain 5, Sri Lanka 5, Sweden 5, Turkey 1, UK 76, US 5) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Bremen, Bremerhaven, Duisburg, Hamburg, Karlsruhe, Lubeck, Rostock, Wilhemshaven
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal Armed Forces (Bundeswehr): Army (Heer), Navy (Deutsche Marine, includes naval air arm), Air Force (Luftwaffe), Joint Support Services (Streitkraeftbasis), Central Medical Service (Zentraler Sanitaetsdienst) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age (conscripts serve a 9-month tour of compulsory military service) (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 19,195,804
females age 16-49:
18,159,851 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 15,564,748
females age 16-49:
14,723,200 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 421,227
female:
398,809 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.5% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Germany |
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
source of precursor chemicals for South American cocaine processors; transshipment point for and consumer of Southwest Asian heroin, Latin American cocaine, and European-produced synthetic drugs; major financial center
|
|
|
|
|