|
|
Formed from the merger of the British colony of the Gold Coast and the Togoland trust territory, Ghana in 1957 became the first sub-Saharan country in colonial Africa to gain its independence. Ghana endured a long series of coups before Lt. Jerry RAWLINGS took power in 1981 and banned political parties. After approving a new constitution and restoring multiparty politics in 1992, RAWLINGS won presidential elections in 1992 and 1996, but was constitutionally prevented from running for a third term in 2000. John KUFUOR succeeded him and was reelected in 2004. John Atta MILLS took over as head of state in early 2009.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Western Africa, bordering the Gulf of Guinea, between Cote d'Ivoire and Togo
|
|
|
|
|
8 00 N, 2 00 W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 238,533 sq km
country comparison to the world: 81
land:
227,533 sq km
water:
11,000 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Oregon
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,094 km
border countries:
Burkina Faso 549 km, Cote d'Ivoire 668 km, Togo 877 km
|
|
|
|
|
539 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
tropical; warm and comparatively dry along southeast coast; hot and humid in southwest; hot and dry in north
|
|
|
|
|
mostly low plains with dissected plateau in south-central area
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Mount Afadjato 880 m
|
|
|
|
|
gold, timber, industrial diamonds, bauxite, manganese, fish, rubber, hydropower, petroleum, silver, salt, limestone
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 17.54%
permanent crops:
9.22%
other:
73.24% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
310 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
53.2 cu km (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 0.98 cu km/yr (24%/10%/66%)
per capita:
44 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
dry, dusty, northeastern harmattan winds occur from January to March; droughts
|
|
|
|
|
recurrent drought in north severely affects agricultural activities; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; poaching and habitat destruction threatens wildlife populations; water pollution; inadequate supplies of potable water
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Marine Life Conservation
|
|
|
|
|
Lake Volta is the world's largest artificial lake
|
|
|
|
|
|
24,339,838
country comparison to the world: 47
note:
estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 36.8% (male 4,529,594/female 4,429,802)
15-64 years:
59.6% (male 7,252,245/female 7,262,757)
65 years and over:
3.6% (male 395,007/female 470,433) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 21.1 years
male:
20.8 years
female:
21.3 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.855% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
28.09 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|
|
8.93 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|
|
-0.61 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 50% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
3.5% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.84 male(s)/female
total population:
1 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 49.89 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 52
male:
53.38 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
46.29 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 60.55 years
country comparison to the world: 186
male:
59.36 years
female:
61.78 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.57 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
1.9% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
260,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
21,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
malaria
water contact disease:
schistosomiasis
respiratory disease:
meningococcal meningitis
animal contact disease:
rabies
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds
(2009)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Ghanaian(s)
adjective:
Ghanaian
|
|
|
|
|
Akan 45.3%, Mole-Dagbon 15.2%, Ewe 11.7%, Ga-Dangme 7.3%, Guan 4%, Gurma 3.6%, Grusi 2.6%, Mande-Busanga 1%, other tribes 1.4%, other 7.8% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Christian 68.8% (Pentecostal/Charismatic 24.1%, Protestant 18.6%, Catholic 15.1%, other 11%), Muslim 15.9%, traditional 8.5%, other 0.7%, none 6.1% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Asante 14.8%, Ewe 12.7%, Fante 9.9%, Boron (Brong) 4.6%, Dagomba 4.3%, Dangme 4.3%, Dagarte (Dagaba) 3.7%, Akyem 3.4%, Ga 3.4%, Akuapem 2.9%, other 36.1% (includes English (official)) (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
57.9%
male:
66.4%
female:
49.8% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 9 years
male:
10 years
female:
9 years (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
5.4% of GDP (2005)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Ghana
conventional short form:
Ghana
former:
Gold Coast
|
|
|
|
|
constitutional democracy
|
|
|
|
|
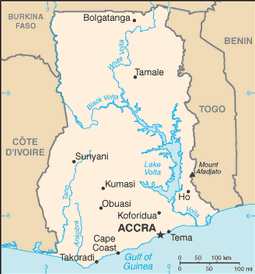
name: Accra
geographic coordinates:
5 33 N, 0 13 W
time difference:
UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
10 regions; Ashanti, Brong-Ahafo, Central, Eastern, Greater Accra, Northern, Upper East, Upper West, Volta, Western
|
|
|
|
|
6 March 1957 (from the UK)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 6 March (1957)
|
|
|
|
|
approved 28 April 1992
|
|
|
|
|
based on English common law and customary law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President John Evans Atta MILLS (since 7 January 2009); Vice President John Dramani MAHAMA (since 7 January 2009); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President John Evans Atta MILLS (since 7 January 2009); Vice President John Dramani MAHAMA (since 7 January 2009)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers; president nominates members subject to approval by Parliament
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for four-year terms (eligible for a second term); election last held on 7 and 28 December 2008 (next to be held on 7 December 2012)
election results:
John Evans Atta MILLS elected president in run-off election; percent of vote - John Evans Atta MILLS 50.23%, Nana Addo Dankwa AKUFO-ADDO 49.77%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Parliament (230 seats; members elected by direct, popular vote to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 7 December 2008 (next to be held on 7 December 2012)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NDC 114, NPP 107, PNC 2, CPP 1, independent 4, other 2
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court
|
|
|
|
|
Convention People's Party or CPP [Ladi NYLANDER]; Democratic Freedom Party or DFP [Alhaji Abudu Rahman ISSAKAH]; Every Ghanaian Living Everywhere or EGLE; Great Consolidated Popular Party or GCPP [Dan LARTEY]; National Democratic Congress or NDC [Dr. Kwabena ADJEI]; New Patriotic Party or NPP [Peter MAC-MANU]; People's National Convention or PNC [Alhaji Amed RAMADAN]; Reform Party [Kyeretwie OPUKU]; United Renaissance Party or URP [Charles WAYO]
|
|
|
|
|
Christian Aid (water rights); Committee for Joint Action or CJA (education reform); National Coalition Against the Privatization of Water or CAP (water rights); Oxfam (water rights); Public Citizen (water rights); Students Coalition Against EPA [Kwabena Ososukene OKAI] (education reform); Third World Network (education reform)
|
|
|
|
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, C, ECOWAS, FAO, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MINURCAT, MINURSO, MONUC, NAM, OAS (observer), OIF (associate member), OPCW, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNITAR, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Daniel Ohene AGYEKUM
chancery:
3512 International Drive NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 686-4520
FAX:
[1] (202) 686-4527
consulate(s) general:
New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Donald G. TEITELBAUM
embassy:
24 4th Circular Rd. Cantonments, Accra
mailing address:
P. O. Box 194, Accra
telephone:
[233] (21) 741-000
FAX:
[233] (21) 741-389
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), yellow, and green, with a large black five-pointed star centered in the yellow band; red symbolizes the blood shed for independence, yellow represents the country's mineral wealth, while green stands for its forests and natural wealth; the black star is said to be the lodestar of African freedom
note:
uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia; similar to the flag of Bolivia, which has a coat of arms centered in the yellow band
|
|
|
|
|
|
Well endowed with natural resources, Ghana has roughly twice the per capita output of the poorest countries in West Africa. Even so, Ghana remains heavily dependent on international financial and technical assistance. Gold and cocoa production and individual remittances are major sources of foreign exchange. Oil production is expected to expand in late 2010 or early 2011. The domestic economy continues to revolve around agriculture, which accounts for more than a third of GDP and employs more than half of the work force, mainly small landholders. Ghana signed a Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC) Compact in 2006, which aims to assist in transforming Ghana's agricultural sector. Ghana opted for debt relief under the Heavily Indebted Poor Country (HIPC) program in 2002, and is also benefiting from the Multilateral Debt Relief Initiative that took effect in 2006. Thematic priorities under its current Growth and Poverty Reduction Strategy, which also provides the framework for development partner assistance, are: macroeconomic stability; private sector competitiveness; human resource development; and good governance and civic responsibility. Sound macro-economic management along with high prices for gold and cocoa helped sustain GDP growth in 2008 and 2009.
|
|
|
|
|
$36.57 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$34.93 billion (2008 est.)
$32.55 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$14.93 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.7% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
7.3% (2008 est.)
6.3% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1,500 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 199
$1,500 (2008 est.)
$1,400 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 37.3%
industry:
25.3%
services:
37.5% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10.33 million (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 56%
industry:
15%
services:
29% (2005 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
11% (2000 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
|
28.5% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 2%
highest 10%:
32.8% (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
39.4 (2005-06)
country comparison to the world: 65
40.7 (1999)
|
|
|
|
|
35% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $4.547 billion
expenditures:
$6.124 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
67.5% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
53.8% of GDP (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
19.6% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 218
16.5% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
17% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 19
13.5% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$2.179 billion (31 December 2006)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$2.174 billion (31 December 2006)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$4.173 billion (31 December 2006)
|
|
|
|
|
$3.394 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 95
$2.38 billion (31 December 2007)
$3.233 billion (31 December 2006)
|
|
|
|
|
cocoa, rice, cassava (tapioca), peanuts, corn, shea nuts, bananas; timber
|
|
|
|
|
mining, lumbering, light manufacturing, aluminum smelting, food processing, cement, small commercial ship building
|
|
|
|
|
4.5% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|
|
6.746 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|
|
5.702 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|
|
249 million kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
435 million kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
7,399 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
|
|
|
|
|
56,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
4,843 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
45,380 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
|
|
|
|
|
15 million bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178
|
|
|
|
|
22.65 billion cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
-$2.666 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
-$3.471 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$5.737 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$5.275 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
gold, cocoa, timber, tuna, bauxite, aluminum, manganese ore, diamonds, horticulture
|
|
|
|
|
Netherlands 13.4%, Ukraine 11.7%, UK 8%, France 5.7%, US 5.1% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$9.807 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
$10.26 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
capital equipment, petroleum, foodstuffs
|
|
|
|
|
China 16%, Nigeria 15%, India 5.6%, US 5.6%, France 4.5%, UK 4.5% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.854 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
$2.028 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$5.84 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
$5.055 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
cedis (GHC) per US dollar - 1.4 (2009), 1.1 (2008), 0.95 (2007), 9,174.8 (2006), 9,072.5 (2005)
note:
in 2007 Ghana revalued its currency with 10,000 old cedis equal to 1 new cedis
|
|
|
|
|
|
143,900 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|
|
11.57 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: primarily microwave radio relay; wireless local loop has been installed; outdated and unreliable fixed-line infrastructure heavily concentrated in Accra
domestic:
competition among multiple mobile-cellular providers has spurred growth with a subscribership of 50 per 100 persons and rising
international:
country code - 233; landing point for the SAT-3/WASC, Main One, and GLO-1 fiber-optic submarine cables that provide connectivity to South Africa, Europe and Asia; satellite earth stations - 4 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean); microwave radio relay link to Panaftel system connects Ghana to its neighbors (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 0, FM 86, shortwave 3 (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
7 (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.gh
|
|
|
|
|
23,850 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|
|
997,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 91
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 155
|
|
|
|
|
total: 7
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
3
914 to 1,523 m:
2 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4
914 to 1,523 m:
3
under 914 m:
1 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
oil 5 km; refined products 309 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 947 km
country comparison to the world: 93
narrow gauge:
947 km 1.067-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 62,221 km
country comparison to the world: 72
paved:
9,955 km
unpaved:
52,266 km (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
1,293 km
country comparison to the world: 58
note:
168 km for launches and lighters on Volta, Ankobra, and Tano rivers; 1,125 km of arterial and feeder waterways on Lake Volta (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4
country comparison to the world: 136
by type:
petroleum tanker 1, refrigerated cargo 3
foreign-owned:
1 (Brazil 1) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Tema
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ghanaian Army, Ghanaian Navy, Ghanaian Air Force (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 6,126,707
females age 16-49:
6,058,958 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 4,022,056
females age 16-49:
4,101,964 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 270,993
female:
263,961 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.7% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 92
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Ghana |
|
|
Ghana struggles to accommodate returning nationals who worked in the cocoa plantations and escaped fighting in Cote d'Ivoire
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 35,653 (Liberia); 8,517 (Togo) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
illicit producer of cannabis for the international drug trade; major transit hub for Southwest and Southeast Asian heroin and, to a lesser extent, South American cocaine destined for Europe and the US; widespread crime and money laundering problem, but the lack of a well developed financial infrastructure limits the country's utility as a money laundering center; significant domestic cocaine and cannabis use
|
|
|
|
|