| Introduction ::Equatorial Guinea |
|
|
Equatorial Guinea gained independence in 1968 after 190 years of Spanish rule. This tiny country, composed of a mainland portion plus five inhabited islands, is one of the smallest on the African continent. President Teodoro OBIANG NGUEMA MBASOGO has ruled the country since 1979 when he seized power in a coup. Although nominally a constitutional democracy since 1991, the 1996, 2002, and 2009 presidential elections - as well as the 1999 and 2004 legislative elections - were widely seen as flawed. The president exerts almost total control over the political system and has discouraged political opposition. Equatorial Guinea has experienced rapid economic growth due to the discovery of large offshore oil reserves, and in the last decade has become Sub-Saharan Africa's third largest oil exporter. Despite the country's economic windfall from oil production resulting in a massive increase in government revenue in recent years, there have been few improvements in the population's living standards.
|
|
|
|
| Geography ::Equatorial Guinea |
|
|
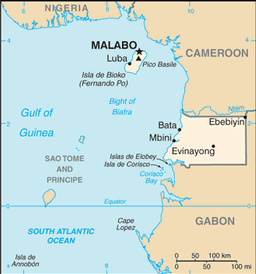
Western Africa, bordering the Bight of Biafra, between Cameroon and Gabon
|
|
|
|
|
2 00 N, 10 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 28,051 sq km
country comparison to the world: 145
land:
28,051 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Maryland
|
|
|
|
|
total: 539 km
border countries:
Cameroon 189 km, Gabon 350 km
|
|
|
|
|
296 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
tropical; always hot, humid
|
|
|
|
|
coastal plains rise to interior hills; islands are volcanic
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Pico Basile 3,008 m
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, natural gas, timber, gold, bauxite, diamonds, tantalum, sand and gravel, clay
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 4.63%
permanent crops:
3.57%
other:
91.8% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
26 cu km (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 0.11 cu km/yr (83%/16%/1%)
per capita:
220 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
violent windstorms; flash floods
|
|
|
|
|
tap water is not potable; deforestation
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
insular and continental regions widely separated
|
|
|
|
| People ::Equatorial Guinea |
|
|
650,702 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 41.7% (male 137,913/female 133,326)
15-64 years:
54.2% (male 173,378/female 179,203)
65 years and over:
4.1% (male 11,735/female 15,147) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 19 years
male:
18.4 years
female:
19.6 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.674% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|
|
36 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
|
|
|
|
|
9.26 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 39% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
2.8% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.03 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.78 male(s)/female
total population:
0.99 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 79.47 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 15
male:
80.55 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
78.36 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 61.98 years
country comparison to the world: 179
male:
61.05 years
female:
62.94 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
3.4% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|
|
11,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
|
|
|
|
|
370 (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne disease:
malaria and yellow fever
animal contact disease:
rabies (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Equatorial Guinean(s) or Equatoguinean(s)
adjective:
Equatorial Guinean or Equatoguinean
|
|
|
|
|
Fang 85.7%, Bubi 6.5%, Mdowe 3.6%, Annobon 1.6%, Bujeba 1.1%, other 1.4% (1994 census)
|
|
|
|
|
nominally Christian and predominantly Roman Catholic, pagan practices
|
|
|
|
|
Spanish 67.6% (official), other 32.4% (includes French (official), Fang, Bubi) (1994 census)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
87%
male:
93.4%
female:
80.5% (2000 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10 years
male:
10 years
female:
9 years (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
0.6% of GDP (2003)
country comparison to the world: 181
|
|
|
|
| Government ::Equatorial Guinea |
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Equatorial Guinea
conventional short form:
Equatorial Guinea
local long form:
Republica de Guinea Ecuatorial/Republique de Guinee equatoriale
local short form:
Guinea Ecuatorial/Guinee equatoriale
former:
Spanish Guinea
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Malabo
geographic coordinates:
3 45 N, 8 47 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
7 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia); Annobon, Bioko Norte, Bioko Sur, Centro Sur, Kie-Ntem, Litoral, Wele-Nzas
|
|
|
|
|
12 October 1968 (from Spain)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 12 October (1968)
|
|
|
|
|
approved by national referendum 17 November 1991; amended January 1995
|
|
|
|
|
partly based on Spanish civil law and tribal custom; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Brig. Gen. (Ret.) Teodoro OBIANG NGUEMA MBASOGO (since 3 August 1979 when he seized power in a military coup)
head of government:
Prime Minister Ignacio Milan TANG (since 8 July 2008);
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a seven-year term (no term limits); election last held on 29 November 2009 (next to be held in 2016); prime minister and deputy prime ministers appointed by the president
election results:
Teodoro OBIANG NGUEMA MBASOGO reelected president; percent of vote - Teodoro OBIANG NGUEMA MBASOGO 95.8%, Placido Mico ABOGO 3.6%; elections marred by widespread fraud
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral House of People's Representatives or Camara de Representantes del Pueblo (100 seats; members directly elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections:
last held on 4 May 2008 (next to be held in 2012)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PDGE 89, EC 10, CPDS 1
note:
Parliament has little power since the constitution vests all executive authority in the president
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Tribunal
|
|
|
|
|
Convergence Party for Social Democracy or CPDS [Placido MICO Abogo]; Democratic Party for Equatorial Guinea or PDGE [Teodoro OBIANG NGUEMA MBASOGO] (ruling party); Electoral Coalition or EC; Party for Progress of Equatorial Guinea or PPGE [Severo MOTO]; Popular Action of Equatorial Guinea or APGE [Avelino MOCACHE]; Popular Union or UP
|
|
|
|
|
ASODEGUE (Madrid-based pressure group for democratic reform); Global Witness (anti-corruption)
|
|
|
|
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, BDEAC, CEMAC, CPLP (associate), FAO, FZ, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OAS (observer), OIF, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WTO (observer)
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Purificacion ANGUE ONDO
chancery:
2020 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone:
[1] (202) 518-5700
FAX:
[1] (202) 518-5252
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Alberto M. FERNANDEZ
embassy:
K-3, Carreterade Aeropuerto, al lado de Restaurante El Paraiso, Malabo; note - relocated embassy is opened for limited functions; inquiries should continue to be directed to the US Embassy in Yaounde, Cameroon
mailing address:
B.P. 817, Yaounde, Cameroon; US Embassy Yaounde, US Department of State, Washington, DC 20521-2520
telephone:
[237] 2220-1500
FAX:
[237] 2220-1572
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of green (top), white, and red, with a blue isosceles triangle based on the hoist side and the coat of arms centered in the white band; the coat of arms has six yellow six-pointed stars (representing the mainland and five offshore islands) above a gray shield bearing a silk-cotton tree and below which is a scroll with the motto UNIDAD, PAZ, JUSTICIA (Unity, Peace, Justice); green symbolizes the jungle and natural resources, blue represents the sea that connects the mainland to the islands, white stands for peace, and red recalls the fight for independence
|
|
|
|
| Economy ::Equatorial Guinea |
|
|
The discovery and exploitation of large oil reserves have contributed to dramatic economic growth in recent years. Forestry, farming, and fishing are also major components of GDP. Subsistence farming predominates. Although pre-independence Equatorial Guinea counted on cocoa production for hard currency earnings, the neglect of the rural economy under successive regimes has diminished potential for agriculture-led growth (the government has stated its intention to reinvest some oil revenue into agriculture). A number of aid programs sponsored by the World Bank and the IMF have been cut off since 1993 because of corruption and mismanagement. No longer eligible for concessional financing because of large oil revenues, the government has been trying to agree on a "shadow" fiscal management program with the World Bank and IMF. Government officials and their family members own most businesses. Undeveloped natural resources include titanium, iron ore, manganese, uranium, and alluvial gold. Growth remained strong in 2008, led by oil, but dropped in 2009, as the price of oil fell.
|
|
|
|
|
$23.2 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
$23.63 billion (2008 est.)
$21.04 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$11.31 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-1.8% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 140
12.3% (2008 est.)
22.5% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$36,600 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
$38,300 (2008 est.)
$35,100 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 2.4%
industry:
93.3%
services:
4.2% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
195,200 NA
country comparison to the world: 171
|
|
|
|
|
30% (1998 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
44% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $4.481 billion
expenditures:
$3.551 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.1% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
0.9% of GDP (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.5% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
7.5% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.75% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 81
5.25% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
NA% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 48
15% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$835.2 million (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$174.5 million (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
coffee, cocoa, rice, yams, cassava (tapioca), bananas, palm oil nuts; livestock; timber
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, fishing, sawmilling, natural gas
|
|
|
|
|
-2.7% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
28 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
|
|
|
|
|
26.04 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
359,200 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
1,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 202
|
|
|
|
|
362,900 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
1,114 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 187
|
|
|
|
|
1.1 billion bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
|
6.67 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
5.17 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|
|
36.81 billion cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
|
|
|
|
|
-$669 million (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
$1.42 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$8.27 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
$13.03 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, methanol, timber, cocoa
|
|
|
|
|
US 22.8%, Spain 18.3%, China 14.8%, Taiwan 10.8%, France 8%, Italy 6%, South Korea 5.4% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.851 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
$3.114 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum sector equipment, other equipment
|
|
|
|
|
China 18.2%, Spain 13.7%, US 12.1%, France 11.2%, Cote dIvoire 7.8%, Italy 5.7%, UK 5.3% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.575 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
$4.431 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$174 million (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
$190 million (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Cooperation Financiere en Afrique Centrale francs (XAF) per US dollar - 481.35 (2009), 447.81 (2008), 481.83 (2007), 522.4 (2006), 527.47 (2005)
note:
since 1 January 1999, the Central African CFA franc (XAF) has been pegged to the euro at a rate of 655.957 CFA francs per euro; Central African CFA franc (XAF) coins and banknotes are not accepted in countries using West African CFA francs (XOF), and vice versa, even though the two currencies trade at par
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Equatorial Guinea |
|
|
10,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 204
|
|
|
|
|
346,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 165
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: digital fixed-line network in most major urban areas and good mobile coverage
domestic:
fixed-line density is about 2 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular subscribership has been increasing and in 2008 stood at about 55 percent of the population
international:
country code - 240; international communications from Bata and Malabo to African and European countries; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 0, FM 3, shortwave 5 (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
.gq
|
|
|
|
|
9 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 221
|
|
|
|
|
12,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 198
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Equatorial Guinea |
|
|
7 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|
|
total: 6
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
1
under 914 m:
2 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 38 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,880 km (2000)
country comparison to the world: 167
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1
country comparison to the world: 158
by type:
cargo 1 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Bata, Malabo
|
|
|
|
| Military ::Equatorial Guinea |
|
|
National Guard (Guardia Nacional de Guinea Ecuatoria, GNGE (Army), with Coast Guard (Navy) and Air Wing) (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age for selective compulsory military service; service obligation 2 years; women hold only administrative positions in the Coast Guard (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 146,241
females age 16-49:
146,138 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 109,311
females age 16-49:
111,543 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 7,186
female:
6,920 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.1% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 173
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Equatorial Guinea |
|
|
in 2002, ICJ ruled on an equidistance settlement of Cameroon-Equatorial Guinea-Nigeria maritime boundary in the Gulf of Guinea, but a dispute between Equatorial Guinea and Cameroon over an island at the mouth of the Ntem River and imprecisely defined maritime coordinates in the ICJ decision delay final delimitation; UN urges Equatorial Guinea and Gabon to resolve the sovereignty dispute over Gabon-occupied Mbane and lesser islands and to create a maritime boundary in the hydrocarbon-rich Corisco Bay
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: Equatorial Guinea is primarily a destination country for children trafficked for the purpose of forced labor and possibly for the purpose of sexual exploitation; children have been trafficked from nearby countries for domestic servitude, market labor, ambulant vending, and possibly sexual exploitation; women may also be trafficked to Equatorial Guinea from Cameroon, Benin, other neighboring countries, and China for sexual exploitation
tier rating:
Tier 2 Watch List - Equatorial Guinea is on the Tier 2 Watch List for its failure to provide evidence of increasing efforts to eliminate trafficking, particularly in the areas of prosecuting and convicting trafficking offenders and failing to formalize mechanisms to provide assistance to victims; although the government made some effort to enforce laws against child labor exploitation, it failed to report any trafficking prosecutions or convictions in 2007; the government continued to lack shelters or formal procedures for providing care to victims (2008)
|
|
|
|
|