|
|
The French Territory of the Afars and the Issas became Djibouti in 1977. Hassan Gouled APTIDON installed an authoritarian one-party state and proceeded to serve as president until 1999. Unrest among the Afars minority during the 1990s led to a civil war that ended in 2001 following the conclusion of a peace accord between Afar rebels and the Issa-dominated government. In 1999, Djibouti's first multi-party presidential elections resulted in the election of Ismail Omar GUELLEH; he was re-elected to a second term in 2005. Djibouti occupies a strategic geographic location at the mouth of the Red Sea and serves as an important transshipment location for goods entering and leaving the east African highlands. The present leadership favors close ties to France, which maintains a significant military presence in the country but also has strong ties with the US. Djibouti hosts the only US military base in sub-Saharan Africa and is a front-line state in the global war on terrorism.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Eastern Africa, bordering the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea, between Eritrea and Somalia
|
|
|
|
|
11 30 N, 43 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 23,200 sq km
country comparison to the world: 150
land:
23,180 sq km
water:
20 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Massachusetts
|
|
|
|
|
total: 516 km
border countries:
Eritrea 109 km, Ethiopia 349 km, Somalia 58 km
|
|
|
|
|
314 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
desert; torrid, dry
|
|
|
|
|
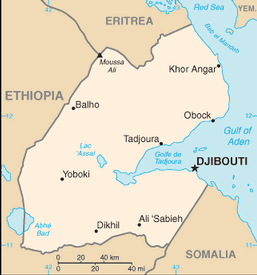
coastal plain and plateau separated by central mountains
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Lac Assal -155 m
highest point:
Moussa Ali 2,028 m
|
|
|
|
|
potential geothermal power, gold, clay, granite, limestone, marble, salt, diatomite, gypsum, pumice, petroleum
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 0.04%
permanent crops:
0%
other:
99.96% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
10 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
0.3 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 0.02 cu km/yr (84%/0%/16%)
per capita:
25 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
earthquakes; droughts; occasional cyclonic disturbances from the Indian Ocean bring heavy rains and flash floods
|
|
|
|
|
inadequate supplies of potable water; limited arable land; desertification; endangered species
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location near world's busiest shipping lanes and close to Arabian oilfields; terminus of rail traffic into Ethiopia; mostly wasteland; Lac Assal (Lake Assal) is the lowest point in Africa
|
|
|
|
|
|
740,528 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 162
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 35.7% (male 132,233/female 131,785)
15-64 years:
61.1% (male 200,282/female 251,965)
65 years and over:
3.3% (male 10,890/female 13,373) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 21.4 years
male:
19.8 years
female:
22.8 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.181% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|
|
25.58 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
|
|
|
|
|
8.37 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 87% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
2.2% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.8 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.81 male(s)/female
total population:
0.86 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 56.65 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 40
male:
64.55 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
48.52 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 60.73 years
country comparison to the world: 184
male:
58.31 years
female:
63.22 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.79 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
3.1% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
16,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|
|
1,100 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne disease:
malaria
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Djiboutian(s)
adjective:
Djiboutian
|
|
|
|
|
Somali 60%, Afar 35%, other 5% (includes French, Arab, Ethiopian, and Italian)
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim 94%, Christian 6%
|
|
|
|
|
French (official), Arabic (official), Somali, Afar
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
67.9%
male:
78%
female:
58.4% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4 years
male:
5 years
female:
4 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
8.4% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Djibouti
conventional short form:
Djibouti
local long form:
Republique de Djibouti/Jumhuriyat Jibuti
local short form:
Djibouti/Jibuti
former:
French Territory of the Afars and Issas, French Somaliland
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Djibouti
geographic coordinates:
11 35 N, 43 09 E
time difference:
UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
6 districts (cercles, singular - cercle); Ali Sabieh, Arta, Dikhil, Djibouti, Obock, Tadjourah
|
|
|
|
|
27 June 1977 (from France)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 27 June (1977)
|
|
|
|
|
approved by referendum 4 September 1992; note - constitution allows for multiparties
|
|
|
|
|
based on French civil law system, traditional practices, and Islamic law; accepts ICJ jurisdiction with reservations
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Ismail Omar GUELLEH (since 8 May 1999)
head of government:
Prime Minister Mohamed Dileita DILEITA (since 4 March 2001)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers responsible to the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a six-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 8 April 2005 (next to be held by April 2011); prime minister appointed by the president
election results:
Ismail Omar GUELLEH reelected president; percent of vote - Ismail Omar GUELLEH 100%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Chamber of Deputies or Chambre des Deputes (65 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections:
last held on 8 February 2008 (next to be held in 2013)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats - UMP (coalition of parties associated with President Ismail Omar GUELLAH) 65
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court or Cour Supreme
|
|
|
|
|
Democratic National Party or PND [ADEN Robleh Awaleh]; Democratic Renewal Party or PRD [Abdillahi HAMARITEH]; Djibouti Development Party or PDD [Mohamed Daoud CHEHEM]; Front pour la Restauration de l'Unite Democratique or FRUD [Ali Mohamed DAOUD]; People's Progress Assembly or RPP [Ismail Omar GUELLEH] (governing party); Peoples Social Democratic Party or PPSD [Moumin Bahdon FARAH]; Republican Alliance for Democracy or ARD [Ahmed YOUSSOUF]; Union for a Presidential Majority or UMP [Mohamed Dileita DILEITA] (a coalition of parties including RPP, FRUD, PND, and PPSD); Union for Democracy and Justice or UDJ
|
|
|
|
|
Union for Presidential Majority UMP (coalition includes RPP, FRUD, PPSD and PND); Union for Democratic Changeover or UAD (opposition coalition includes ARD, MRDD, and UDJ)
|
|
|
|
|
ACCT, ACP, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AU, COMESA, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, ITU, ITUC, LAS, MIGA, MINURSO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Roble OLHAYE Oudine
chancery:
Suite 515, 1156 15th Street NW, Washington, DC 20005
telephone:
[1] (202) 331-0270
FAX:
[1] (202) 331-0302
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador James C. SWAN
embassy:
Plateau du Serpent, Boulevard Marechal Joffre, Djibouti
mailing address:
B. P. 185, Djibouti
telephone:
[253] 35 39 95
FAX:
[253] 35 39 40
|
|
|
|
|
two equal horizontal bands of light blue (top) and light green with a white isosceles triangle based on the hoist side bearing a red five-pointed star in the center
|
|
|
|
|
|
The economy is based on service activities connected with the country's strategic location and status as a free trade zone in the Horn of Africa. Two-thirds of Djibouti's inhabitants live in the capital city; the remainder are mostly nomadic herders. Scanty rainfall limits crop production to fruits and vegetables, and most food must be imported. Djibouti provides services as both a transit port for the region and an international transshipment and refueling center. Imports and exports from landlocked neighbor Ethiopia represent 70% of port activity at Djibouti's container terminal. Djibouti has few natural resources and little industry. The nation is, therefore, heavily dependent on foreign assistance to help support its balance of payments and to finance development projects. An unemployment rate of nearly 60% in urban areas continues to be a major problem. While inflation is not a concern, due to the fixed tie of the Djiboutian franc to the US dollar, the artificially high value of the Djiboutian franc adversely affects Djibouti's balance of payments. Per capita consumption dropped an estimated 35% between 1999 and 2006 because of recession, civil war, and a high population growth rate (including immigrants and refugees). Djibouti has experienced relatively minimal impact from the global economic downturn, but its reliance on diesel-generated electricity and imported food leave average consumers vulnerable to global price shocks.
|
|
|
|
|
$2.011 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183
$1.89 billion (2008 est.)
$1.785 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$1.102 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.4% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
5.9% (2008 est.)
4% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2,800 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
$2,700 (2008 est.)
$2,600 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 3.2%
industry:
14.9%
services:
81.9% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
351,700 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 160
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: NA%
industry:
NA%
services:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
59% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 194
note:
data are for urban areas, 83% in rural areas
|
|
|
|
|
42% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 2.4%
highest 10%:
30.9%
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $135 million
expenditures:
$182 million (1999 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
|
|
|
|
|
11.56% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$462.7 million (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 104
$380 million (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$338 million (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 120
$284.1 million (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$269.9 million (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 128
$224.7 million (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
fruits, vegetables; goats, sheep, camels, animal hides
|
|
|
|
|
construction, agricultural processing
|
|
|
|
|
280 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
|
|
|
|
|
260.4 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 171
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183
|
|
|
|
|
13,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
|
|
|
|
|
19 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
|
|
|
|
|
8,476 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 177
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 187
|
|
|
|
|
-$212 million (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
$340 million (2006)
country comparison to the world: 173
|
|
|
|
|
reexports, hides and skins, coffee (in transit)
|
|
|
|
|
Somalia 79.9%, UAE 4.1%, Yemen 4.1% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.555 billion (2006)
country comparison to the world: 161
|
|
|
|
|
foods, beverages, transport equipment, chemicals, petroleum products
|
|
|
|
|
Saudi Arabia 21.4%, India 16.8%, China 11.1%, US 6.3%, Malaysia 6.3% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$428 million (2006)
country comparison to the world: 160
|
|
|
|
|
Djiboutian francs (DJF) per US dollar - 177.71 (2007), 174.75 (2006), 177.72 (2005), 177.72 (2004), 177.72 (2003)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Djibouti |
|
|
10,800 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 201
|
|
|
|
|
44,100 (2005)
country comparison to the world: 196
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: telephone facilities in the city of Djibouti are adequate, as are the microwave radio relay connections to outlying areas of the country
domestic:
Djibouti Telecom is the sole provider of telecommunications services and utilizes mostly a microwave radio relay network; fiber-optic cable is installed in the capital; rural areas connected via wireless local loop radio systems; mobile cellular coverage is primarily limited to the area in and around Djibouti city
international:
country code - 253; landing point for the SEA-ME-WE-3 optical telecommunications submarine cable with links to Asia, the Middle East, and Europe; satellite earth stations - 2 (1 Intelsat - Indian Ocean and 1 Arabsat); Medarabtel regional microwave radio relay telephone network (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 1, FM 2, shortwave 0 (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
.dj
|
|
|
|
|
199 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 188
|
|
|
|
|
13,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 197
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Djibouti |
|
|
13 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 152
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10
1,524 to 2,437 m:
2
914 to 1,523 m:
5
under 914 m:
3 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 100 km (Djibouti segment of the 781 km Addis Ababa-Djibouti railway)
country comparison to the world: 127
narrow gauge:
100 km 1.000-m gauge
note:
railway is under joint control of Djibouti and Ethiopia but is largely inoperable (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,065 km
country comparison to the world: 164
paved:
1,226 km
unpaved:
1,839 km (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
Djibouti
|
|
|
|
|
the International Maritime Bureau reports offshore waters in the Gulf of Aden are high risk for piracy; numerous vessels, including commercial shipping and pleasure craft, have been attacked and hijacked both at anchor and while underway; crew, passengers, and cargo are held for ransom
|
|
|
|
|
|
Djibouti National Army (includes Navy and Air Force)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age for voluntary military service; 16-25 years of age for voluntary military training; no conscription (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 165,000
females age 16-49:
213,894 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 110,441
females age 16-49:
147,939 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 8,260
female:
8,503 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.8% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 31
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Djibouti |
|
|
Djibouti maintains economic ties and border accords with "Somaliland" leadership while maintaining some political ties to various factions in Somalia; Kuwait is chief investor in the 2008 restoration and upgrade of the Ethiopian-Djibouti rail link; in 2008, Eritrean troops move across the border on Ras Doumera peninsula and occupy Doumera Island with undefined sovereignty in the Red Sea
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 8,642 (Somalia) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: Djibouti is a source, transit, and destination country for women and children trafficked for the purposes of commercial sexual exploitation and domestic servitude; large numbers of voluntary economic migrants from Ethiopia and Somalia pass illegally through Djibouti en route to Yemen and other locations in the Middle East; Djibouti's large refugee population - comprised of Somalis, Ethiopians, and Eritreans - remains vulnerable to various forms of exploitation, including human trafficking
tier rating:
Djibouti is placed on Tier 2 Watch List because it does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking, but it is making significant efforts to do so; the government made nascent efforts to bring trafficking offenders and migrant smugglers to justice during the reporting period, but the government showed only limited evidence of progress in prosecuting specific human trafficking offenses and in raising public awareness of the crime (2009)
|
|
|
|
|