| Introduction ::Costa Rica |
|
|
Although explored by the Spanish early in the 16th century, initial attempts at colonizing Costa Rica proved unsuccessful due to a combination of factors, including: disease from mosquito-infested swamps, brutal heat, resistance by natives, and pirate raids. It was not until 1563 that a permanent settlement of Cartago was established in the cooler, fertile central highlands. The area remained a colony for some two and a half centuries. In 1821, Costa Rica became one of several Central American provinces that jointly declared their independence from Spain. Two years later it joined the United Provinces of Central America, but this federation disintegrated in 1838, at which time Costa Rica proclaimed its sovereignty and independence. Since the late 19th century, only two brief periods of violence have marred the country's democratic development. Although it still maintains a large agricultural sector, Costa Rica has expanded its economy to include strong technology and tourism industries. The standard of living is relatively high. Land ownership is widespread.
|
|
|
|
|
|
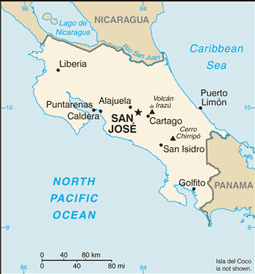
Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Nicaragua and Panama
|
|
|
|
|
10 00 N, 84 00 W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 51,100 sq km
country comparison to the world: 129
land:
51,060 sq km
water:
40 sq km
note:
includes Isla del Coco
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than West Virginia
|
|
|
|
|
total: 639 km
border countries:
Nicaragua 309 km, Panama 330 km
|
|
|
|
|
1,290 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
tropical and subtropical; dry season (December to April); rainy season (May to November); cooler in highlands
|
|
|
|
|
coastal plains separated by rugged mountains including over 100 volcanic cones, of which several are major volcanoes
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Cerro Chirripo 3,810 m
|
|
|
|
|
hydropower
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 4.4%
permanent crops:
5.87%
other:
89.73% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
1,080 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
112.4 cu km (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2.68 cu km/yr (29%/17%/53%)
per capita:
619 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
occasional earthquakes, hurricanes along Atlantic coast; frequent flooding of lowlands at onset of rainy season and landslides; active volcanoes
|
|
|
|
|
deforestation and land use change, largely a result of the clearing of land for cattle ranching and agriculture; soil erosion; coastal marine pollution; fisheries protection; solid waste management; air pollution
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
Marine Life Conservation
|
|
|
|
|
four volcanoes, two of them active, rise near the capital of San Jose in the center of the country; one of the volcanoes, Irazu, erupted destructively in 1963-65
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,516,220 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 25% (male 577,984/female 552,737)
15-64 years:
68.8% (male 1,561,847/female 1,544,528)
65 years and over:
6.2% (male 129,298/female 149,826) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 28.4 years
male:
27.9 years
female:
28.9 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.347% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
16.65 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|
|
4.29 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
|
|
|
|
|
1.11 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 63% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
2.3% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.86 male(s)/female
total population:
1.01 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 9.72 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 154
male:
10.59 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
8.81 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 77.54 years
country comparison to the world: 56
male:
74.93 years
female:
80.28 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.93 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
|
|
|
|
|
0.4% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
9,700 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 200 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: intermediate
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne diseases:
dengue fever (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Costa Rican(s)
adjective:
Costa Rican
|
|
|
|
|
white (including mestizo) 94%, black 3%, Amerindian 1%, Chinese 1%, other 1%
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 76.3%, Evangelical 13.7%, Jehovah's Witnesses 1.3%, other Protestant 0.7%, other 4.8%, none 3.2%
|
|
|
|
|
Spanish (official), English
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
94.9%
male:
94.7%
female:
95.1% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 12 years
male:
12 years
female:
12 years (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
4.9% of GDP (2004)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Costa Rica
conventional short form:
Costa Rica
local long form:
Republica de Costa Rica
local short form:
Costa Rica
|
|
|
|
|
democratic republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: San Jose
geographic coordinates:
9 56 N, 84 05 W
time difference:
UTC-6 (1 hour behind Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
7 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia); Alajuela, Cartago, Guanacaste, Heredia, Limon, Puntarenas, San Jose
|
|
|
|
|
15 September 1821 (from Spain)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 15 September (1821)
|
|
|
|
|
7 November 1949
|
|
|
|
|
based on Spanish civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Court; has accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Laura CHINCHILLA Miranda (since 8 May 2010); First Vice President Alfio PIVA Mesen (since 8 May 2010); Second Vice President Luis LIBERMAN Ginsburg (since 8 May 2010); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Laura CHINCHILLA Miranda (since 8 May 2010); First Vice President Alfio PIVA Mesen (since 8 May 2010); Second Vice President Luis LIBERMAN Ginsburg (since 8 May 2010)
cabinet:
Cabinet selected by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president and vice presidents elected on the same ticket by popular vote for a single four-year term; election last held on 7 February 2010 (next to be held in February 2014)
election results:
Laura CHINCHILLA Miranda elected president; percent of vote - Laura CHINCHILLA Miranda (PLN) 46.7%; Otton SOLIS (PAC) 25.1%, Otto GUEVARA Guth (ML) 20.8%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Legislative Assembly or Asamblea Legislativa (57 seats; members elected by direct, popular vote to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 7 February 2010 (next to be held in February 2014)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PLN 23, PAC 10, ML 9, PUSC 6, PASE 4, other 5
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court or Corte Suprema (22 justices are elected for renewable eight-year terms by the Legislative Assembly)
|
|
|
|
|
Accessibility Without Exclusion or PASE [Oscar Andres LOPEZ Arias]; Citizen Action Party or PAC [Alberto CANAS Escalante]; Costa Rican Renovation Party or PRC [Gerardo Justo OROZCO Alvarez]; Democratic Force Party or PFD [Marco GONZALEZ Nunez]; Frente Amplio [Jose MERINO del Rio]; Homeland First or PP (Patria Primero) [Juan Jose VARGAS Fallas]; Libertarian Movement Party or PML [Otto GUEVARA Guth]; National Democratic Alliance or ADN [Jose Miguel VILLALOBOS Umana]; National Integration Party or PIN [Walter MUNOZ Cespedes]; National Liberation Party or PLN [Francisco Antonio PACHECO Fernandez]; National Rescue Party or PRN [Fabio Enrique DELGADO Hernandez]; National Union Party or PUN [Arturo ACOSTA Mora]; Patriotic Alliance [Mariano FIGUERES Olsen]; Patriotic Union or UP [Jose Miguel CORRALES Bolanos]; Popular Vanguard [Trino BARRANTES Araya]; Social Christian Unity Party or PUSC [Luis FISHMAN Zonzinski]; Union for Change Party or UPC [Antonio ALVAREZ Desanti]
|
|
|
|
|
Authentic Confederation of Democratic Workers or CATD (Communist Party affiliate); Chamber of Coffee Growers; Confederated Union of Workers or CUT (Communist Party affiliate); Costa Rican Confederation of Democratic Workers or CCTD (Liberation Party affiliate); Costa Rican Exporter's Chamber or CADEXCO; Costa Rican Solidarity Movement; Costa Rican Union of Private Sector Enterprises or UCCAEP [Rafael CARRILLO]; Federation of Public Service Workers or FTSP; National Association for Economic Development or ANFE; National Association of Educators or ANDE; National Association of Public and Private Employees or ANEP [Albino VARGAS]; Rerum Novarum or CTRN (PLN affiliate) [Gilbert BROWN]
|
|
|
|
|
BCIE, CACM, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, LAES, LAIA (observer), MIGA, NAM (observer), OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, RG, SICA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Ana Lorena VILLALOBOS
chancery:
2114 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 234-2945 or 2946
FAX:
[1] (202) 265-4795
consulate(s) general:
Atlanta, Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New Orleans, New York, San Francisco, San Juan (Puerto Rico)
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Anne Slaughter ANDREW
embassy:
Calle 120 Avenida O, Pavas, San Jose
mailing address:
APO AA 34020
telephone:
[506] 2519-2000
FAX:
[506] 2519-2305
|
|
|
|
|
five horizontal bands of blue (top), white, red (double width), white, and blue, with the coat of arms in a white elliptical disk on the hoist side of the red band; above the coat of arms a light blue ribbon contains the words, AMERICA CENTRAL, and just below it near the top of the coat of arms is a white ribbon with the words, REPUBLICA COSTA RICA
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prior to the global economic crisis, Costa Rica enjoyed stable economic growth. The economy contracted by about 2% in 2009. While the traditional agricultural exports of bananas, coffee, sugar, and beef are still the backbone of commodity export trade, a variety of industrial and specialized agricultural products have broadened export trade in recent years. High value added goods and services, including microchips, have further bolstered exports. Tourism continues to bring in foreign exchange, as Costa Rica's impressive biodiversity makes it a key destination for ecotourism. Foreign investors remain attracted by the country's political stability and relatively high education levels, as well as the fiscal incentives offered in the free-trade zones; and Costa Rica has attracted one of the highest levels of foreign direct investment per capita in Latin America. However, many business impediments, such as high levels of bureaucracy, difficulty of enforcing contracts, and weak investor protection, remain. Poverty has remained around 20% for nearly 20 years, and the strong social safety net that had been put into place by the government has eroded due to increased financial constraints on government expenditures. Unlike the rest of Central America, Costa Rica is not highly dependent on remittances as they only represent about 2% of GDP. Immigration from Nicaragua has increasingly become a concern for the government. The estimated 300,000-500,000 Nicaraguans in Costa Rica legally and illegally are an important source of - mostly unskilled - labor, but also place heavy demands on the social welfare system. Under the ARIAS administration, the government has made strides in reducing internal and external debt - in 2007, Costa Rica had its first budget surplus in 50 years. The US-Central American-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR) entered into force on 1 January 2009, after significant delays within the Costa Rican legislature.
|
|
|
|
|
$48.63 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
$49.42 billion (2008 est.)
$48.16 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$29.64 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-1.6% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
2.6% (2008 est.)
7.8% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$10,900 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$11,200 (2008 est.)
$11,100 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 6.5%
industry:
25.5%
services:
68% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.09 million
country comparison to the world: 118
note:
this official estimate excludes Nicaraguans living in Costa Rica (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 14%
industry:
22%
services:
64% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.4% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
4.9% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
16% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 1.5%
highest 10%:
35.5% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
48 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 30
45.9 (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
20.5% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $3.795 billion
expenditures:
$4.908 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
49.3% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
42.2% of GDP (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
8.3% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
13.4% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
25% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 12
17% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
15.83% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 70
12.8% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.209 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 65
$4.504 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$3.143 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 88
$2.87 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$15.15 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 71
$12.91 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 98
$2.035 billion (31 December 2007)
$1.944 billion (31 December 2006)
|
|
|
|
|
bananas, pineapples, coffee, melons, ornamental plants, sugar, corn, rice, beans, potatoes; beef, poultry, dairy; timber
|
|
|
|
|
microprocessors, food processing, medical equipment, textiles and clothing, construction materials, fertilizer, plastic products
|
|
|
|
|
-5% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|
|
8.808 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
|
|
|
|
|
8.064 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
77.16 million kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
203.2 million kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
|
|
|
|
|
45,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
|
|
|
|
|
2,117 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|
|
47,860 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl
country comparison to the world: 191
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
|
|
|
|
|
-$662 million (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
-$2.648 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$8.096 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
$9.738 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
bananas, pineapples, coffee, melons, ornamental plants, sugar; beef; seafood; electronic components, medical equipment
|
|
|
|
|
US 23.9%, Netherlands 13.3%, China 13%, UK 5%, Mexico 4.9% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$10.53 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
$14.55 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
raw materials, consumer goods, capital equipment, petroleum, construction materials
|
|
|
|
|
US 42.7%, Mexico 6.9%, Venezuela 6.3%, Japan 5.4%, China 4.6%, Brazil 4.5% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.089 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
$3.799 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$8.057 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
$9.249 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$11.64 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
$18.96 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$540 million (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
$532 million (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Costa Rican colones (CRC) per US dollar - 580.01 (2009), 530.41 (2008), 519.53 (2007), 511.3 (2006), 477.79 (2005)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Costa Rica |
|
|
1.438 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
1.887 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: good domestic telephone service in terms of breadth of coverage; under the terms of CAFTA-DR, the state-run telecommunications provider is losing its monopoly position and competitors are entering the market
domestic:
point-to-point and point-to-multi-point microwave, fiber-optic, and coaxial cable link rural areas; Internet service is available
international:
country code - 506; landing points for the Americas Region Caribbean Ring System (ARCOS-1), MAYA-1, and the Pan American Crossing submarine cables that provide links to South and Central America, parts of the Caribbean, and the US; connected to Central American Microwave System; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 65, FM 51, shortwave 19 (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
20 (plus 43 repeaters) (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
.cr
|
|
|
|
|
34,066 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 89
|
|
|
|
|
1.46 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Costa Rica |
|
|
151 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 36
|
|
|
|
|
total: 38
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
1,524 to 2,437 m:
2
914 to 1,523 m:
22
under 914 m:
12 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 113
914 to 1,523 m:
19
under 914 m:
94 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
refined products 796 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 278 km
country comparison to the world: 124
narrow gauge:
278 km 1.067-m gauge
note:
none of the railway network is in use (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 35,330 km
country comparison to the world: 94
paved:
8,621 km
unpaved:
26,709 km (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
730 km (seasonally navigable by small craft) (2008)
country comparison to the world: 75
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1
country comparison to the world: 161
by type:
passenger/cargo 1 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Caldera, Puerto Limon
|
|
|
|
|
|
no regular military forces; Ministry of Public Security, Government, and Police (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,241,183
females age 16-49:
1,217,037 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,044,923
females age 16-49:
1,026,432 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 42,486
female:
40,745 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.6% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 155
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Costa Rica |
|
|
the ICJ has given Costa Rica until January 2008 to reply and Nicaragua until July 2008 to rejoin before rendering its decision on the navigation, security, and commercial rights of Costa Rican vessels on the Río San Juan over which Nicaragua retains sovereignty
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 9,699-11,500 (Colombia) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
transshipment country for cocaine and heroin from South America; illicit production of cannabis in remote areas; domestic cocaine consumption, particularly crack cocaine, is rising; significant consumption of amphetamines; seizures of smuggled cash in Costa Rica and at the main border crossing to enter Costa Rica from Nicaragua have risen in recent years (2008)
|
|
|
|
|