|
|
For centuries China stood as a leading civilization, outpacing the rest of the world in the arts and sciences, but in the 19th and early 20th centuries, the country was beset by civil unrest, major famines, military defeats, and foreign occupation. After World War II, the Communists under MAO Zedong established an autocratic socialist system that, while ensuring China's sovereignty, imposed strict controls over everyday life and cost the lives of tens of millions of people. After 1978, MAO's successor DENG Xiaoping and other leaders focused on market-oriented economic development and by 2000 output had quadrupled. For much of the population, living standards have improved dramatically and the room for personal choice has expanded, yet political controls remain tight. China since the early 1990s has increased its global outreach and participation in international organizations.
|
|
|
|
|
|
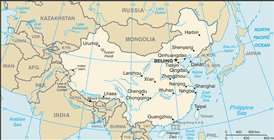
Eastern Asia, bordering the East China Sea, Korea Bay, Yellow Sea, and South China Sea, between North Korea and Vietnam
|
|
|
|
|
35 00 N, 105 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 9,596,961 sq km
country comparison to the world: 4
land:
9,569,901 sq km
water:
27,060 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than the US
|
|
|
|
|
total: 22,117 km
border countries:
Afghanistan 76 km, Bhutan 470 km, Burma 2,185 km, India 3,380 km, Kazakhstan 1,533 km, North Korea 1,416 km, Kyrgyzstan 858 km, Laos 423 km, Mongolia 4,677 km, Nepal 1,236 km, Pakistan 523 km, Russia (northeast) 3,605 km, Russia (northwest) 40 km, Tajikistan 414 km, Vietnam 1,281 km
regional borders:
Hong Kong 30 km, Macau 0.34 km
|
|
|
|
|
14,500 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
extremely diverse; tropical in south to subarctic in north
|
|
|
|
|
mostly mountains, high plateaus, deserts in west; plains, deltas, and hills in east
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Turpan Pendi -154 m
highest point:
Mount Everest 8,850 m
|
|
|
|
|
coal, iron ore, petroleum, natural gas, mercury, tin, tungsten, antimony, manganese, molybdenum, vanadium, magnetite, aluminum, lead, zinc, uranium, hydropower potential (world's largest)
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 14.86%
permanent crops:
1.27%
other:
83.87% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
545,960 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
2,829.6 cu km (1999)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 549.76 cu km/yr (7%/26%/68%)
per capita:
415 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
frequent typhoons (about five per year along southern and eastern coasts); damaging floods; tsunamis; earthquakes; droughts; land subsidence
|
|
|
|
|
air pollution (greenhouse gases, sulfur dioxide particulates) from reliance on coal produces acid rain; water shortages, particularly in the north; water pollution from untreated wastes; deforestation; estimated loss of one-fifth of agricultural land since 1949 to soil erosion and economic development; desertification; trade in endangered species
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
world's fourth largest country (after Russia, Canada, and US); Mount Everest on the border with Nepal is the world's tallest peak
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,330,141,295 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 17.9% (male 128,363,812/female 109,917,641)
15-64 years:
73.4% (male 501,987,034/female 474,871,442)
65 years and over:
8.6% (male 55,287,997/female 59,713,369) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 35.2 years
male:
34.5 years
female:
35.8 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.494% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|
|
12.17 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 164
|
|
|
|
|
6.89 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
|
|
|
|
|
-0.34 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 43% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
2.7% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.14 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.17 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.06 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.93 male(s)/female
total population:
1.06 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 16.51 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 115
male:
15.84 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
17.27 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 74.51 years
country comparison to the world: 92
male:
72.54 years
female:
76.77 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.54 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
|
|
|
|
|
0.1% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
|
|
|
|
|
700,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
39,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: intermediate
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
Japanese encephalitis and dengue fever
soil contact disease:
hantaviral hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS)
animal contact disease:
rabies
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds
(2009)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Chinese (singular and plural)
adjective:
Chinese
|
|
|
|
|
Han Chinese 91.5%, Zhuang, Manchu, Hui, Miao, Uyghur, Tujia, Yi, Mongol, Tibetan, Buyi, Dong, Yao, Korean, and other nationalities 8.5% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Daoist (Taoist), Buddhist, Christian 3%-4%, Muslim 1%-2%
note:
officially atheist (2002 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Standard Chinese or Mandarin (Putonghua, based on the Beijing dialect), Yue (Cantonese), Wu (Shanghainese), Minbei (Fuzhou), Minnan (Hokkien-Taiwanese), Xiang, Gan, Hakka dialects, minority languages (see Ethnic groups entry)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
90.9%
male:
95.1%
female:
86.5% (2000 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 11 years
male:
11 years
female:
11 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
1.9% of GDP (1999)
country comparison to the world: 170
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: People's Republic of China
conventional short form:
China
local long form:
Zhonghua Renmin Gongheguo
local short form:
Zhongguo
abbreviation:
PRC
|
|
|
|
|
Communist state
|
|
|
|
|
name: Beijing
geographic coordinates:
39 55 N, 116 23 E
time difference:
UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
note:
despite its size, all of China falls within one time zone; many people in Xinjiang Province observe an unofficial "Xinjiang timezone" of UTC+6, two hours behind Beijing
|
|
|
|
|
23 provinces (sheng, singular and plural), 5 autonomous regions (zizhiqu, singular and plural), and 4 municipalities (shi, singular and plural)
provinces:
Anhui, Fujian, Gansu, Guangdong, Guizhou, Hainan, Hebei, Heilongjiang, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangsu, Jiangxi, Jilin, Liaoning, Qinghai, Shaanxi, Shandong, Shanxi, Sichuan, Yunnan, Zhejiang; (see note on Taiwan)
autonomous regions:
Guangxi, Nei Mongol, Ningxia, Xinjiang Uygur, Xizang (Tibet)
municipalities:
Beijing, Chongqing, Shanghai, Tianjin
note:
China considers Taiwan its 23rd province; see separate entries for the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau
|
|
|
|
|
221 BC (unification under the Qin Dynasty); 1 January 1912 (Qing Dynasty replaced by the Republic of China); 1 October 1949 (People's Republic of China established)
|
|
|
|
|
Anniversary of the founding of the People's Republic of China, 1 October (1949)
|
|
|
|
|
most recent promulgation 4 December 1982 with amendments in 1988, 1993, 2004
|
|
|
|
|
based on civil law system; derived from Soviet and continental civil code legal principles; legislature retains power to interpret statutes; constitution ambiguous on judicial review of legislation; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President HU Jintao (since 15 March 2003); Vice President XI Jinping (since 15 March 2008)
head of government:
Premier WEN Jiabao (since 16 March 2003); Executive Vice Premier LI Keqiang (17 March 2008), Vice Premier HUI Liangyu (since 17 March 2003), Vice Premier ZHANG Deijiang (since 17 March 2008), and Vice Premier WANG Qishan (since 17 March 2008)
cabinet:
State Council appointed by National People's Congress
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president and vice president elected by National People's Congress for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); elections last held on 15-17 March 2008 (next to be held in mid-March 2013); premier nominated by president, confirmed by National People's Congress
election results:
HU Jintao elected president by National People's Congress with a total of 2,963 votes; XI Jinping elected vice president with a total of 2,919 votes
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National People's Congress or Quanguo Renmin Daibiao Dahui (2,987 seats; members elected by municipal, regional, and provincial people's congresses, and People's Liberation Army to serve five-year terms)
elections:
last held in December 2007-February 2008 (date of next election to be held in late 2012 to early 2013)
election results:
percent of vote - NA; seats - 2,987
note:
only members of the CCP, its eight allied parties, and sympathetic independent candidates are elected
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme People's Court (judges appointed by the National People's Congress); Local People's Courts (comprise higher, intermediate, and basic courts); Special People's Courts (primarily military, maritime, railway transportation, and forestry courts)
|
|
|
|
|
Chinese Communist Party or CCP [HU Jintao]; eight registered small parties controlled by CCP
|
|
|
|
|
no substantial political opposition groups exist
|
|
|
|
|
ADB, AfDB (nonregional member), APEC, APT, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), BIS, CDB, CICA, EAS, FAO, FATF, G-20, G-24 (observer), G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAIA (observer), MIGA, MINURSO, MONUC, NAM (observer), NSG, OAS (observer), OPCW, PCA, PIF (partner), SAARC (observer), SCO, SICA (observer), UN, UN Security Council, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNITAR, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNMIT, UNOCI, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador ZHANG Yesui
chancery:
3505 International Place NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 495-2000
FAX:
[1] (202) 495-2190
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Jon M. HUNTSMAN, Jr.
embassy:
55 An Jia Lou Lu, 100600 Beijing
mailing address:
PSC 461, Box 50, FPO AP 96521-0002
telephone:
[86] (10) 8531-3000
FAX:
[86] (10) 8531-3300
consulate(s) general:
Chengdu, Guangzhou, Shanghai, Shenyang, Wuhan
|
|
|
|
|
red with a large yellow five-pointed star and four smaller yellow five-pointed stars (arranged in a vertical arc toward the middle of the flag) in the upper hoist-side corner; the color red represents revolution, while the stars symbolize the four social classes - the working class, the peasantry, the urban petty bourgeoisie, and the national bourgeoisie (capitalists) - united under the Communist Party of China
|
|
|
|
|
|
China's economy during the past 30 years has changed from a centrally planned system that was largely closed to international trade to a more market-oriented economy that has a rapidly growing private sector and is a major player in the global economy. Reforms started in the late 1970s with the phasing out of collectivized agriculture, and expanded to include the gradual liberalization of prices, fiscal decentralization, increased autonomy for state enterprises, the foundation of a diversified banking system, the development of stock markets, the rapid growth of the non-state sector, and the opening to foreign trade and investment. Annual inflows of foreign direct investment rose to nearly $108 billion in 2008. China has generally implemented reforms in a gradualist or piecemeal fashion. In recent years, China has re-invigorated its support for leading state-owned enterprises in sectors it considers important to "economic security," explicitly looking to foster globally competitive national champions. After keeping its currency tightly linked to the US dollar for years, China in July 2005 revalued its currency by 2.1% against the US dollar and moved to an exchange rate system that references a basket of currencies. Cumulative appreciation of the renminbi against the US dollar since the end of the dollar peg was more than 20% by late 2008, but the exchange rate has remained virtually pegged since the onset of the global financial crisis. The restructuring of the economy and resulting efficiency gains have contributed to a more than tenfold increase in GDP since 1978. Measured on a purchasing power parity (PPP) basis that adjusts for price differences, China in 2009 stood as the second-largest economy in the world after the US, although in per capita terms the country is still lower middle-income. The Chinese government faces numerous economic development challenges, including: (a) reducing its high domestic savings rate and correspondingly low domestic demand through increased corporate transfers and a strengthened social safety net; (b) sustaining adequate job growth for tens of millions of migrants and new entrants to the work force; (c) reducing corruption and other economic crimes; and (d) containing environmental damage and social strife related to the economy's rapid transformation. Economic development has been more rapid in coastal provinces than in the interior, and approximately 200 million rural laborers and their dependents have relocated to urban areas to find work. One demographic consequence of the "one child" policy is that China is now one of the most rapidly aging countries in the world. Deterioration in the environment - notably air pollution, soil erosion, and the steady fall of the water table, especially in the north - is another long-term problem. China continues to lose arable land because of erosion and economic development. In 2006, China announced that by 2010 it would decrease energy intensity 20% from 2005 levels. In 2009, China announced that by 2020 it would reduce carbon intensity 40% from 2005 levels. The Chinese government seeks to add energy production capacity from sources other than coal and oil, and is focusing on nuclear and other alternative energy development. In 2009, the global economic downturn reduced foreign demand for Chinese exports for the first time in many years. The government vowed to continue reforming the economy and emphasized the need to increase domestic consumption in order to make China less dependent on foreign exports for GDP growth in the future.
|
|
|
|
|
$8.789 trillion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
$8.086 trillion (2008 est.)
$7.418 trillion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$4.814 trillion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
8.7% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
9% (2008 est.)
13% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$6,600 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
$6,100 (2008 est.)
$5,700 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 10.9%
industry:
48.6%
services:
40.5% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
812.7 million (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 39.5%
industry:
27.2%
services:
33.2% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.3% (September 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
4.2% (December 2008 est.)
note:
official data for urban areas only; including migrants may boost total unemployment to 9%; substantial unemployment and underemployment in rural areas
|
|
|
|
|
2.8% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3.5%
highest 10%:
15%
note:
data are for urban households only (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
41.5 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 54
40 (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
42.6% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $972.3 billion
expenditures:
$1.137 trillion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
18.2% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
15.6% of GDP (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-0.8% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
5.9% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.79% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 125
3.33% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
5.31% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 142
5.58% (17 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.434 trillion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 3
$2.09 trillion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.523 trillion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 4
$3.437 trillion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$5.555 trillion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 4
$4.653 trillion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.794 trillion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
$6.226 trillion (31 December 2007)
$2.426 trillion (31 December 2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
rice, wheat, potatoes, corn, peanuts, tea, millet, barley, apples, cotton, oilseed; pork; fish
|
|
|
|
|
mining and ore processing, iron, steel, aluminum, and other metals, coal; machine building; armaments; textiles and apparel; petroleum; cement; chemicals; fertilizers; consumer products, including footwear, toys, and electronics; food processing; transportation equipment, including automobiles, rail cars and locomotives, ships, and aircraft; telecommunications equipment, commercial space launch vehicles, satellites
|
|
|
|
|
8.1% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|
|
3.451 trillion kWh (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
3.438 trillion kWh (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
16.64 billion kWh (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
3.842 billion kWh (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
3.795 million bbl/day (2008)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|
|
7.999 million bbl/day (2008)
country comparison to the world: 3
|
|
|
|
|
388,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
|
|
|
|
|
4.393 million bbl/day (2008)
country comparison to the world: 4
|
|
|
|
|
15.55 billion bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
76.1 billion cu m (2008)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
80.7 billion cu m (2008)
country comparison to the world: 10
|
|
|
|
|
3.34 billion cu m (2008)
country comparison to the world: 30
|
|
|
|
|
4.44 billion cu m (2008)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
2.46 trillion cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
$296.2 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
$426.1 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.194 trillion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
$1.429 trillion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
electrical and other machinery, including data processing equipment, apparel, textiles, iron and steel, optical and medical equipment
|
|
|
|
|
US 17.7%, Hong Kong 13.3%, Japan 8.1%, South Korea 5.2%, Germany 4.1% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$921.5 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
$1.131 trillion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
electrical and other machinery, oil and mineral fuels, optical and medical equipment, metal ores, plastics, organic chemicals
|
|
|
|
|
Japan 13.3%, South Korea 9.9%, Taiwan 9.2%, US 7.2%, Germany 4.9% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.206 trillion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
$1.955 trillion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$347.1 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
$400.6 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$576.1 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
$758.9 billion (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$227.3 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
$184 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Renminbi yuan (RMB) per US dollar - 6.8249 (2009), 6.9385 (2008), 7.61 (2007), 7.97 (2006), 8.1943 (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
|
365.6 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
634 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: domestic and international services are increasingly available for private use; unevenly distributed domestic system serves principal cities, industrial centers, and many towns; China continues to develop its telecommunications infrastructure, and is partnering with foreign providers to expand its global reach; China in the summer of 2008 began a major restructuring of its telecommunications industry, resulting in the consolidation of its six telecom service operators to three, China Telecom, China Mobile and China Unicom, each providing both fixed-line and mobile services
domestic:
interprovincial fiber-optic trunk lines and cellular telephone systems have been installed; mobile-cellular subscribership is increasing rapidly; the number of Internet users exceeded 250 million by summer 2008; a domestic satellite system with 55 earth stations is in place
international:
country code - 86; a number of submarine cables provide connectivity to Asia, the Middle East, Europe, and the US; satellite earth stations - 7 (5 Intelsat - 4 Pacific Ocean and 1 Indian Ocean; 1 Intersputnik - Indian Ocean region; and 1 Inmarsat - Pacific and Indian Ocean regions) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 369, FM 259, shortwave 45 (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
3,240 (of which 209 are operated by China Central Television, 31 are provincial TV stations, and nearly 3,000 are local city stations) (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
.cn
|
|
|
|
|
14.156 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
298 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
|
482 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 15
|
|
|
|
|
total: 425
over 3,047 m:
63
2,438 to 3,047 m:
132
1,524 to 2,437 m:
133
914 to 1,523 m:
25
under 914 m:
72 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 57
over 3,047 m:
3
2,438 to 3,047 m:
5
1,524 to 2,437 m:
10
914 to 1,523 m:
13
under 914 m:
26 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
45 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 32,545 km; oil 20,097 km; refined products 10,915 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 77,834 km
country comparison to the world: 3
standard gauge:
77,084 km 1.435-m gauge (24,433 km electrified)
narrow gauge:
750 km 0.750-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,583,715 km (includes 53,913 km of expressways) (2007)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
110,000 km navigable (2008)
country comparison to the world: 1
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,826
country comparison to the world: 3
by type:
barge carrier 4, bulk carrier 451, cargo 689, carrier 2, chemical tanker 69, combination ore/oil 1, container 162, liquefied gas 44, passenger 8, passenger/cargo 83, petroleum tanker 244, refrigerated cargo 33, roll on/roll off 10, specialized tanker 9, vehicle carrier 17
foreign-owned:
20 (Ecuador 1, Greece 2, Hong Kong 12, Indonesia 1, Japan 2, South Korea 1, Norway 1)
registered in other countries:
1,441 (Bahamas 10, Bangladesh 1, Belize 71, Bermuda 10, Bolivia 1, Cambodia 193, Cyprus 10, France 5, Georgia 10, Germany 2, Honduras 3, Hong Kong 324, India 1, Indonesia 2, Kiribati 15, South Korea 1, Liberia 11, Malta 12, Marshall Islands 7, Mongolia 1, Norway 36, Panama 532, Philippines 4, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 94, Sierra Leone 15, Singapore 14, Thailand 1, Tuvalu 16, unknown 39) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Dalian, Guangzhou, Ningbo, Qingdao, Qinhuangdao, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Tianjin
|
|
|
|
|
|
People's Liberation Army (PLA): Ground Forces, Navy (includes marines and naval aviation), Air Force (includes airborne forces), and Second Artillery Corps (strategic missile force); People's Armed Police (PAP); PLA Reserve Force (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
18-22 years of age for selective compulsory military service, with 24-month service obligation; no minimum age for voluntary service (all officers are volunteers); 18-19 years of age for women high school graduates who meet requirements for specific military jobs (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 381,747,145
females age 16-49:
360,385,629 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 314,668,817
females age 16-49:
298,745,786 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 10,699,186
female:
9,460,217 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.3% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 23
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::China |
|
|
continuing talks and confidence-building measures work toward reducing tensions over Kashmir that nonetheless remains militarized with portions under the de facto administration of China (Aksai Chin), India (Jammu and Kashmir), and Pakistan (Azad Kashmir and Northern Areas); India does not recognize Pakistan's ceding historic Kashmir lands to China in 1964; China and India continue their security and foreign policy dialogue started in 2005 related to the dispute over most of their rugged, militarized boundary, regional nuclear proliferation, and other matters; China claims most of India's Arunachal Pradesh to the base of the Himalayas; lacking any treaty describing the boundary, Bhutan and China continue negotiations to establish a common boundary alignment to resolve territorial disputes due to cartographic discrepancies; Chinese maps show an international boundary symbol off the coasts of the littoral states of the South China Seas, where China has interrupted Vietnamese hydrocarbon exploration; China asserts sovereignty over Scarborough Reef along with the Philippines and Taiwan, and over the Spratly Islands together with Malaysia, the Philippines, Taiwan, Vietnam, and Brunei; the 2002 "Declaration on the Conduct of Parties in the South China Sea" eased tensions in the Spratly's but is not the legally binding "code of conduct" sought by some parties; Vietnam and China continue to expand construction of facilities in the Spratly's and in March 2005, the national oil companies of China, the Philippines, and Vietnam signed a joint accord on marine seismic activities in the Spratly Islands; China occupies some of the Paracel Islands also claimed by Vietnam and Taiwan; China and Taiwan continue to reject both Japan's claims to the uninhabited islands of Senkaku-shoto (Diaoyu Tai) and Japan's unilaterally declared equidistance line in the East China Sea, the site of intensive hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation; certain islands in the Yalu and Tumen rivers are in dispute with North Korea; North Korea and China seek to stem illegal migration to China by North Koreans, fleeing privations and oppression, by building a fence along portions of the border and imprisoning North Koreans deported by China; China and Russia have demarcated the once disputed islands at the Amur and Ussuri confluence and in the Argun River in accordance with their 2004 Agreement; China and Tajikistan have begun demarcating the revised boundary agreed to in the delimitation of 2002; the decade-long demarcation of the China-Vietnam land boundary was completed in 2009; citing environmental, cultural, and social concerns, China has reconsidered construction of 13 dams on the Salween River, but energy-starved Burma, with backing from Thailand, remains intent on building five hydro-electric dams downstream despite regional and international protests; Chinese and Hong Kong authorities met in March 2008 to resolve ownership and use of lands recovered in Shenzhen River channelization, including 96-hectare Lok Ma Chau Loop; Hong Kong developing plans to reduce 2,000 out of 2,800 hectares of its restricted Closed Area by 2010
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 300,897 (Vietnam); estimated 30,000-50,000 (North Korea)
IDPs:
90,000 (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: China is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children trafficked for the purposes of sexual exploitation and forced labor; the majority of trafficking in China occurs within the country's borders, but there is also considerable international trafficking of Chinese citizens to Africa, Asia, Europe, Latin America, the Middle East, and North America; Chinese women are lured abroad through false promises of legitimate employment, only to be forced into commercial sexual exploitation, largely in Taiwan, Thailand, Malaysia, and Japan; women and children are trafficked to China from Mongolia, Burma, North Korea, Russia, and Vietnam for forced labor, marriage, and prostitution; some North Korean women and children seeking to leave their country voluntarily cross the border into China and are then sold into prostitution, marriage, or forced labor
tier rating:
Tier 2 Watch List - China is on the Tier 2 Watch List for the fourth consecutive year for its failure to provide evidence of increasing efforts to combat human trafficking, particularly in terms of punishment of trafficking crimes and the protection of Chinese and foreign victims of trafficking; victims are sometimes punished for unlawful acts that were committed as a direct result of their being trafficked, such as violations of prostitution or immigration/emigration controls; the Chinese Government continued to treat North Korean victims of trafficking solely as economic migrants, routinely deporting them back to horrendous conditions in North Korea; additional challenges facing the Chinese Government include the enormous size of its trafficking problem and the significant level of corruption and complicity in trafficking by some local government officials (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
major transshipment point for heroin produced in the Golden Triangle region of Southeast Asia; growing domestic consumption of synthetic drugs, and heroin from Southeast and Southwest Asia; source country for methamphetamine and heroin chemical precursors, despite new regulations on its large chemical industry
(2008)
|
|
|
|
|