|
|
Aboriginal settlers arrived on the continent from Southeast Asia about 40,000 years before the first Europeans began exploration in the 17th century. No formal territorial claims were made until 1770, when Capt. James COOK took possession in the name of Great Britain. Six colonies were created in the late 18th and 19th centuries; they federated and became the Commonwealth of Australia in 1901. The new country took advantage of its natural resources to rapidly develop agricultural and manufacturing industries and to make a major contribution to the British effort in World Wars I and II. In recent decades, Australia has transformed itself into an internationally competitive, advanced market economy. It boasted one of the OECD's fastest growing economies during the 1990s, a performance due in large part to economic reforms adopted in the 1980s. Long-term concerns include climate-change issues such as the depletion of the ozone layer and more frequent droughts, and management and conservation of coastal areas, especially the Great Barrier Reef.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oceania, continent between the Indian Ocean and the South Pacific Ocean
|
|
|
|
|
27 00 S, 133 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 7,741,220 sq km
country comparison to the world: 6
land:
7,682,300 sq km
water:
58,920 sq km
note:
includes Lord Howe Island and Macquarie Island
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than the US contiguous 48 states
|
|
|
|
|
0 km
|
|
|
|
|
25,760 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
continental shelf:
200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
|
|
|
|
|
Current Weather
generally arid to semiarid; temperate in south and east; tropical in north
|
|
|
|
|
mostly low plateau with deserts; fertile plain in southeast
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Lake Eyre -15 m
highest point:
Mount Kosciuszko 2,229 m
|
|
|
|
|
bauxite, coal, iron ore, copper, tin, gold, silver, uranium, nickel, tungsten, mineral sands, lead, zinc, diamonds, natural gas, petroleum
note:
Australia is the world's largest net exporter of coal accounting for 29% of global coal exports
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 6.15% (includes about 27 million hectares of cultivated grassland)
permanent crops:
0.04%
other:
93.81% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
25,450 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
398 cu km (1995)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 24.06 cu km/yr (15%/10%/75%)
per capita:
1,193 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
cyclones along the coast; severe droughts; forest fires
|
|
|
|
|
soil erosion from overgrazing, industrial development, urbanization, and poor farming practices; soil salinity rising due to the use of poor quality water; desertification; clearing for agricultural purposes threatens the natural habitat of many unique animal and plant species; the Great Barrier Reef off the northeast coast, the largest coral reef in the world, is threatened by increased shipping and its popularity as a tourist site; limited natural fresh water resources
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
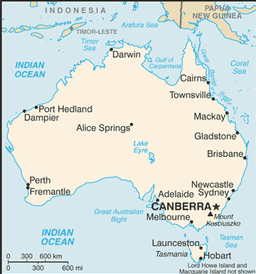
world's smallest continent but sixth-largest country; population concentrated along the eastern and southeastern coasts; the invigorating sea breeze known as the "Fremantle Doctor" affects the city of Perth on the west coast and is one of the most consistent winds in the world
|
|
|
|
|
|
21,515,754 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 18.4% (male 2,033,106/female 1,929,863)
15-64 years:
67.8% (male 7,397,562/female 7,197,829)
65 years and over:
13.7% (male 1,350,248/female 1,607,146) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 37.5 years
male:
36.8 years
female:
38.3 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.171% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
|
|
|
|
|
12.39 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 162
|
|
|
|
|
6.81 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
|
|
|
|
|
6.13 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 89% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
1.2% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.055 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.03 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.84 male(s)/female
total population:
1 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4.67 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 195
male:
5 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
4.33 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 81.72 years
country comparison to the world: 8
male:
79.33 years
female:
84.25 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.78 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|
|
18,000 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 100 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Australian(s)
adjective:
Australian
|
|
|
|
|
white 92%, Asian 7%, aboriginal and other 1%
|
|
|
|
|
Catholic 25.8%, Anglican 18.7%, Uniting Church 5.7%, Presbyterian and Reformed 3%, Eastern Orthodox 2.7%, other Christian 7.9%, Buddhist 2.1%, Muslim 1.7%, other 2.4%, unspecified 11.3%, none 18.7% (2006 Census)
|
|
|
|
|
English 78.5%, Chinese 2.5%, Italian 1.6%, Greek 1.3%, Arabic 1.2%, Vietnamese 1%, other 8.2%, unspecified 5.7% (2006 Census)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
99%
male:
99%
female:
99% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 20 years
male:
20 years
female:
21 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
4.5% of GDP (2005)
country comparison to the world: 85
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Commonwealth of Australia
conventional short form:
Australia
|
|
|
|
|
federal parliamentary democracy and a Commonwealth realm
|
|
|
|
|
name: Canberra
geographic coordinates:
35 17 S, 149 13 E
time difference:
UTC+10 (15 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins first Sunday in October; ends first Sunday in April
note:
Australia is divided into three time zones
|
|
|
|
|
6 states and 2 territories*; Australian Capital Territory*, New South Wales, Northern Territory*, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, Western Australia
|
|
|
|
|
Ashmore and Cartier Islands, Christmas Island, Cocos (Keeling) Islands, Coral Sea Islands, Heard Island and McDonald Islands, Macquarie Island, Norfolk Island
|
|
|
|
|
1 January 1901 (from the federation of UK colonies)
|
|
|
|
|
Australia Day, 26 January (1788); ANZAC Day (commemorated as the anniversary of the landing of troops of the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps during World War I at Gallipoli, Turkey), 25 April (1915)
|
|
|
|
|
9 July 1900; effective on 1 January 1901
|
|
|
|
|
based on English common law; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: Queen of Australia ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor General Quentin BRYCE (since 5 September 2008)
head of government:
Prime Minister Kevin RUDD (since 3 December 2007); Deputy Prime Minister Julia GILLARD (since 3 December 2007)
cabinet:
prime minister nominates, from among members of Parliament, candidates who are subsequently sworn in by the governor general to serve as government ministers
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch on the recommendation of the prime minister; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or leader of a majority coalition is sworn in as prime minister by the governor general
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral Federal Parliament consists of the Senate (76 seats; 12 members from each of the six states and 2 from each of the two mainland territories; one-half of state members are elected every three years by popular vote to serve six-year terms while all territory members are elected every three years) and the House of Representatives (150 seats; members elected by popular preferential vote to serve terms of up to three-years; no state can have fewer than 5 representatives)
elections:
Senate - last held on 24 November 2007 (next to be held no later than 2010); House of Representatives - last held on 24 November 2007 (next to be called no later than 2010)
election results:
Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Liberal Party-National Party coalition 37, Australian Labor Party 32, Australian Greens 5, Family First Party 1, independent 1; House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Australian Labor Party 83, Liberal Party 55, National Party 10, independents 2
|
|
|
|
|
High Court (the chief justice and six other justices are appointed by the governor general)
|
|
|
|
|
Australian Democrats [Julia MELLAND]; Australian Greens [Bob BROWN]; Australian Labor Party [Kevin RUDD]; Country Liberal Party [Terry MILLS]; Family First Party [Steve FIELDING]; Liberal Party [Tony ABBOTT]; The Nationals [Warren TRUSS]
|
|
|
|
|
other: business groups; environmental groups; social groups; trade unions
|
|
|
|
|
ADB, ANZUS, APEC, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, C, CP, EAS, EBRD, FAO, FATF, G-20, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NEA, NSG, OECD, OPCW, Paris Club, PCA, PIF, SAARC (observer), Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNMIS, UNMIT, UNRWA, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Kim Christian BEAZLEY
chancery:
1601 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
telephone:
[1] (202) 797-3000
FAX:
[1] (202) 797-3168
consulate(s) general:
Atlanta, Chicago, Honolulu, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Jeffrey L. BLEICH
embassy:
Moonah Place, Yarralumla, Canberra, Australian Capital Territory 2600
mailing address:
APO AP 96549
telephone:
[61] (02) 6214-5600
FAX:
[61] (02) 6214-5970
consulate(s) general:
Melbourne, Perth, Sydney
|
|
|
|
|
blue with the flag of the UK in the upper hoist-side quadrant and a large seven-pointed star in the lower hoist-side quadrant known as the Commonwealth or Federation Star, representing the federation of the colonies of Australia in 1901; the star depicts one point for each of the six original states and one representing all of Australia's internal and external territories; on the fly half is a representation of the Southern Cross constellation in white with one small five-pointed star and four larger, seven-pointed stars
|
|
|
|
|
|
Australia's abundant and diverse natural resources attract high levels of foreign investment and include extensive reserves of coal, iron ore, copper, gold, natural gas, uranium, and renewable energy sources. A series of major investments, such as the US$40 billion Gorgon Liquid Natural Gas project, will significantly expand the resources sector. Australia also has a large services sector and is a significant exporter of natural resources, energy, and food. Key tenets of Australia's trade policy include support for open trade and the successful culmination of the Doha Round of multilateral trade negotiations, particularly for agriculture and services. The Australian economy grew for 17 consecutive years before the global financial crisis. Subsequently, the Rudd government introduced a fiscal stimulus package worth over US$50 billion to offset the effect of the slowing world economy, while the Reserve Bank of Australia cut interest rates to historic lows. These policies - and continued demand for commodities, especially from China - helped the Australian economy rebound after just one quarter of negative growth. The economy grew by 1.5% during the first three quarters of 2009 - the best performance in the OECD. Unemployment, originally expected to reach 8-10%, peaked at 5.7% in late 2009 and fell to 5.3% by February 2010. As a result of an improved economy, the budget deficit is expected to peak below 4.2% of GDP and the government could return to budget surpluses as early as 2015. The Australian financial system remained resilient throughout the financial crisis and Australian banks have rebounded. Australia was one of the first advanced economies to raise interest rates - three times since October 2009 - and the government removed the wholesale funding guarantee for financial institutions in March 2010. During 2010, the government will focus on raising Australia's economic productivity, managing the symbiotic, but sometimes tense, economic relationship with China, passing emissions trading legislation, and dealing with other climate-related issues such as drought and devastating bushfires. Australia is engaged in the Trans-Pacific Partnership talks and ongoing free trade agreement negotiations with China and Japan.
|
|
|
|
|
$824.3 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
$816.2 billion (2008 est.)
$798.6 billion (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$930.8 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
2.2% (2008 est.)
4.8% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$38,800 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
$38,900 (2008 est.)
$38,500 (2007 est.)
note:
data are in 2009 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 3.8%
industry:
24.9%
services:
71.3% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
11.44 million (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 3.6%
industry:
21.1%
services:
75% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.7% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
4.2% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 2%
highest 10%:
25.4% (1994)
|
|
|
|
|
30.5 (2006)
country comparison to the world: 110
35.2 (1994)
|
|
|
|
|
27.3% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $323.6 billion
expenditures:
$358.4 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
18.6% of GDP (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
14.7% of GDP (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.9% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
4.4% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.75% (31 March 2010)
country comparison to the world: 110
4.25% (3 December 2008)
note:
this is the Reserve Bank of Australia's "cash rate target," or policy rate
|
|
|
|
|
8.91% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 90
10.02% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$298.5 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$667.2 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$1.312 trillion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 12
$1.298 trillion (31 December 2007)
$1.096 trillion (31 December 2006)
|
|
|
|
|
wheat, barley, sugarcane, fruits; cattle, sheep, poultry
|
|
|
|
|
mining, industrial and transportation equipment, food processing, chemicals, steel
|
|
|
|
|
-5.8% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
|
|
|
|
|
239.9 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
222 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
586,400 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
|
|
|
|
|
953,700 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|
|
332,400 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
|
|
|
|
|
687,200 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 billion bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
|
|
|
|
|
45.22 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
34.2 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
19.48 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
5.377 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
|
|
|
|
|
849.5 billion cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|
|
-$33.31 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
-$44.04 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$161.5 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
$189.9 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
coal, iron ore, gold, meat, wool, alumina, wheat, machinery and transport equipment
|
|
|
|
|
Japan 22.2%, China 14.6%, South Korea 8.2%, India 6.1%, US 5.5%, NZ 4.3%, UK 4.2% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$160.9 billion (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
$194.2 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and transport equipment, computers and office machines, telecommunication equipment and parts; crude oil and petroleum products
|
|
|
|
|
China 15.4%, US 12.1%, Japan 9.1%, Singapore 7%, Germany 5.1%, Thailand 4.5%, UK 4.4%, Malaysia 4.1% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$44.98 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
$32.92 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$920 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
$799.8 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$282.3 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
$366.5 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$209.4 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
$197.2 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Australian dollars (AUD) per US dollar - 1.2894 (2009), 1.2059 (2008), 1.2137 (2007), 1.3285 (2006), 1.3095 (2005)
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Australia |
|
|
9.37 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|
|
22.12 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 36
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: excellent domestic and international service
domestic:
domestic satellite system; significant use of radiotelephone in areas of low population density; rapid growth of mobile telephones
international:
country code - 61; landing point for the SEA-ME-WE-3 optical telecommunications submarine cable with links to Asia, the Middle East, and Europe; the Southern Cross fiber optic submarine cable provides links to New Zealand and the United States; satellite earth stations - 19 (10 Intelsat - 4 Indian Ocean and 6 Pacific Ocean, 2 Inmarsat - Indian and Pacific Ocean regions, 2 Globalstar, 5 other) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 262, FM 345, shortwave 1 (1998)
|
|
|
|
|
104 (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
.au
|
|
|
|
|
11.756 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 10
|
|
|
|
|
15.17 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Australia |
|
|
464 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
total: 325
over 3,047 m:
11
2,438 to 3,047 m:
13
1,524 to 2,437 m:
145
914 to 1,523 m:
142
under 914 m:
14 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 139
1,524 to 2,437 m:
17
914 to 1,523 m:
110
under 914 m:
12 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 27,105 km; liquid petroleum gas 240 km; oil 3,258 km; oil/gas/water 1 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 37,855 km
country comparison to the world: 7
broad gauge:
142 km 1.600-m gauge
standard gauge:
24,409 km 1.435-m gauge (1,094 km electrified)
narrow gauge:
13,304 km 1.067-m gauge (1,193 km electrified) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 812,972 km
country comparison to the world: 9
paved:
341,448 km
unpaved:
471,524 km (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
2,000 km (mainly used for recreation on Murray and Murray-Darling river systems) (2006)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|
|
total: 50
country comparison to the world: 71
by type:
bulk carrier 12, cargo 5, chemical tanker 1, container 1, liquefied gas 4, passenger 7, passenger/cargo 7, petroleum tanker 8, roll on/roll off 5
foreign-owned:
24 (Canada 9, France 1, Germany 2, Japan 1, Netherlands 2, Norway 1, Singapore 1, UK 5, US 2)
registered in other countries:
28 (Antigua and Barbuda 1, Belize 1, Bermuda 1, Dominica 2, Fiji 1, Marshall Islands 1, NZ 1, Panama 4, Singapore 12, Tonga 1, US 1, Vanuatu 2) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Brisbane, Dampier, Fremantle, Gladstone, Hay Point, Melbourne, Newcastle, Port Hedland, Port Kembla, Port Walcott, Sydney
|
|
|
|
|
|
Australian Defense Force (ADF): Australian Army, Royal Australian Navy, Royal Australian Air Force, Special Operations Command (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
17 years of age for voluntary military service (with parental consent); no conscription; women allowed to serve in Army combat units in non-combat support roles (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 5,275,667
females age 16-49:
5,082,543 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 4,377,411
females age 16-49:
4,210,442 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 144,232
female:
136,525 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 43
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Australia |
|
|
In 2007 Australia and Timor-Leste signed a 50-year development zone and revenue sharing agreement in lieu of a maritime boundary; dispute with Timor-Leste hampers creation of a revised maritime boundary with Indonesia in the Timor Sea; regional states continue to express concern over Australia's 2004 declaration of a 1,000-nautical mile-wide maritime identification zone; Australia asserts land and maritime claims to Antarctica; in 2004 Australia submitted its claims to Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS) to extend its continental margins covering over 3.37 million square kilometers, expanding its seabed roughly 30 percent more than its claimed exclusive economic zone; since 2003, Australia has led the Regional Assistance Mission to the Solomon Islands (RAMSI) to maintain civil and political order and reinforce regional security
|
|
|
|
|
Tasmania is one of the world's major suppliers of licit opiate products; government maintains strict controls over areas of opium poppy cultivation and output of poppy straw concentrate; major consumer of cocaine and amphetamines
|
|
|
|
|