

| The World Factbook | ||


|
United States |

|
|
| Introduction | United States |
|
Background:
|
Britain's American colonies broke with the mother country in 1776 and were recognized as the new nation of the United States of America following the Treaty of Paris in 1783. During the 19th and 20th centuries, 37 new states were added to the original 13 as the nation expanded across the North American continent and acquired a number of overseas possessions. The two most traumatic experiences in the nation's history were the Civil War (1861-65), in which a northern Union of states defeated a secessionist Confederacy of 11 southern slave states, and the Great Depression of the 1930s, an economic downturn during which about a quarter of the labor force lost its jobs. Buoyed by victories in World Wars I and II and the end of the Cold War in 1991, the US remains the world's most powerful nation state. The economy is marked by steady growth, low unemployment and inflation, and rapid advances in technology. |
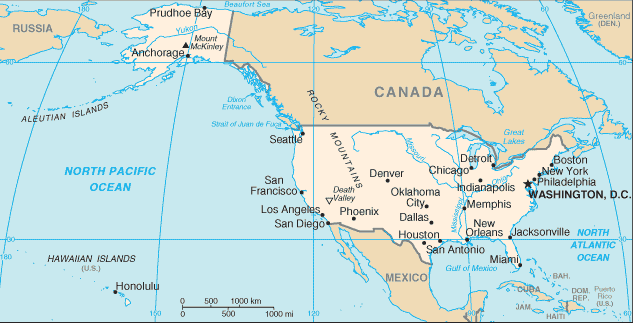
| Geography | United States |
|
Location:
|
North America, bordering both the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Pacific Ocean, between Canada and Mexico |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
38 00 N, 97 00 W |
|
Map references:
|
North America |
|
Area:
|
total: 9,826,630 sq km
land: 9,161,923 sq km water: 664,707 sq km note: includes only the 50 states and District of Columbia |
|
Area - comparative:
|
about half the size of Russia; about three-tenths the size of Africa; about half the size of South America (or slightly larger than Brazil); slightly larger than China; more than twice the size of the European Union |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 12,034 km
border countries: Canada 8,893 km (including 2,477 km with Alaska), Mexico 3,141 km note: US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay, Cuba is leased by the US and is part of Cuba; the base boundary is 28 km |
|
Coastline:
|
19,924 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm exclusive economic zone: 200 nm continental shelf: not specified |
|
Climate:
|
mostly temperate, but tropical in Hawaii and Florida, arctic in Alaska, semiarid in the great plains west of the Mississippi River, and arid in the Great Basin of the southwest; low winter temperatures in the northwest are ameliorated occasionally in January and February by warm chinook winds from the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains |
|
Terrain:
|
vast central plain, mountains in west, hills and low mountains in east; rugged mountains and broad river valleys in Alaska; rugged, volcanic topography in Hawaii |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Death Valley -86 m
highest point: Mount McKinley 6,198 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
coal, copper, lead, molybdenum, phosphates, uranium, bauxite, gold, iron, mercury, nickel, potash, silver, tungsten, zinc, petroleum, natural gas, timber
note: the US has the world's largest coal reserves with 491 billion short tons accounting for 27% of the world's total |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 18.01%
permanent crops: 0.21% other: 81.78% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
223,850 sq km (2003) |
|
Total renewable water resources:
|
3,069 cu km (1985) |
|
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
|
total: 477 cu km/yr (13%/46%/41%)
per capita: 1,600 cu m/yr (2000) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
tsunamis; volcanoes; earthquake activity around Pacific Basin; hurricanes along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts; tornadoes in the midwest and southeast; mud slides in California; forest fires in the west; flooding; permafrost in northern Alaska, a major impediment to development |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
air pollution resulting in acid rain in both the US and Canada; the US is the largest single emitter of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels; water pollution from runoff of pesticides and fertilizers; limited natural fresh water resources in much of the western part of the country require careful management; desertification |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Hazardous Wastes |
|
Geography - note:
|
world's third-largest country by size (after Russia and Canada) and by population (after China and India); Mt. McKinley is highest point in North America and Death Valley the lowest point on the continent |
| People | United States |
|
Population:
|
307,212,123 (July 2009 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 20.2% (male 31,639,127/female 30,305,704)
15-64 years: 67% (male 102,665,043/female 103,129,321) 65 years and over: 12.8% (male 16,901,232/female 22,571,696) (2009 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 36.7 years
male: 35.4 years female: 38 years (2009 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
0.975% (2009 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
13.82 births/1,000 population (2009 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
8.27 deaths/1,000 population (2008 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
4.31 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2009 est.) |
|
Urbanization:
|
urban population: 82% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization: 1.3% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/female total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2009 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 6.26 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 6.94 deaths/1,000 live births female: 5.55 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 78.11 years
male: 75.65 years female: 80.69 years (2009 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
2.05 children born/woman (2009 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
0.6% (2007 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
1.2 million (2007 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
22,000 (2007 est.) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: American(s)
adjective: American |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
white 79.96%, black 12.85%, Asian 4.43%, Amerindian and Alaska native 0.97%, native Hawaiian and other Pacific islander 0.18%, two or more races 1.61% (July 2007 estimate)
note: a separate listing for Hispanic is not included because the US Census Bureau considers Hispanic to mean a person of Latin American descent (including persons of Cuban, Mexican, or Puerto Rican origin) living in the US who may be of any race or ethnic group (white, black, Asian, etc.); about 15.1% of the total US population is Hispanic |
|
Religions:
|
Protestant 51.3%, Roman Catholic 23.9%, Mormon 1.7%, other Christian 1.6%, Jewish 1.7%, Buddhist 0.7%, Muslim 0.6%, other or unspecified 2.5%, unaffiliated 12.1%, none 4% (2007 est.) |
|
Languages:
|
English 82.1%, Spanish 10.7%, other Indo-European 3.8%, Asian and Pacific island 2.7%, other 0.7% (2000 census)
note: Hawaiian is an official language in the state of Hawaii |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99% male: 99% female: 99% (2003 est.) |
|
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
|
total: 16 years
male: 15 years female: 16 years (2006) |
|
Education expenditures:
|
5.3% of GDP (2005) |
| Government | United States |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: United States of America
conventional short form: United States abbreviation: US or USA |
|
Government type:
|
Constitution-based federal republic; strong democratic tradition |
|
Capital:
|
name: Washington, DC
geographic coordinates: 38 53 N, 77 02 W time difference: UTC-5 (during Standard Time) daylight saving time: +1hr, begins second Sunday in March; ends first Sunday in November note: the 50 United States cover six time zones |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
50 states and 1 district*; Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, District of Columbia*, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin, Wyoming |
|
Dependent areas:
|
American Samoa, Baker Island, Guam, Howland Island, Jarvis Island, Johnston Atoll, Kingman Reef, Midway Islands, Navassa Island, Northern Mariana Islands, Palmyra Atoll, Puerto Rico, Virgin Islands, Wake Island
note: from 18 July 1947 until 1 October 1994, the US administered the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands; it entered into a political relationship with all four political units: the Northern Mariana Islands is a commonwealth in political union with the US (effective 3 November 1986); the Republic of the Marshall Islands signed a Compact of Free Association with the US (effective 21 October 1986); the Federated States of Micronesia signed a Compact of Free Association with the US (effective 3 November 1986); Palau concluded a Compact of Free Association with the US (effective 1 October 1994) |
|
Independence:
|
4 July 1776 (from Great Britain) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 4 July (1776) |
|
Constitution:
|
17 September 1787, effective 4 March 1789 |
|
Legal system:
|
federal court system based on English common law; each state has its own unique legal system, of which all but one (Louisiana, which is still influenced by the Napoleonic Code) is based on English common law; judicial review of legislative acts; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Barack H. OBAMA (since 20 January 2009); Vice President Joseph R. BIDEN (since 20 January 2009); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Barack H. OBAMA (since 20 January 2009); Vice President Joseph BIDEN (since 20 January 2009) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president with Senate approval elections: president and vice president elected on the same ticket by a college of representatives who are elected directly from each state; president and vice president serve four-year terms (eligible for a second term); election last held 4 November 2008 (next to be held on 6 November 2012) election results: Barack H. OBAMA elected president; percent of popular vote - Barack H. OBAMA 52.4%, John MCCAIN 46.3%, other 1.3%; |
|
Legislative branch:
|
bicameral Congress consists of the Senate (100 seats, 2 members are elected from each state by popular vote to serve six-year terms; one-third are elected every two years) and the House of Representatives (435 seats; members are directly elected by popular vote to serve two-year terms)
elections: Senate - last held 4 November 2008 (next to be held November 2010); House of Representatives - last held 4 November 2008 (next to be held in November 2010) election results: Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Democratic Party 57, Republican Party 41, independent 2; House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Democratic Party 257, Republican Party 178 |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court (nine justices; nominated by the president and confirmed with the advice and consent of the Senate; appointed to serve for life); United States Courts of Appeal; United States District Courts; State and County Courts |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Democratic Party [Timothy KAINE]; Green Party; Libertarian Party [William (Bill) REDPATH]; Republican Party [Michael STEELE] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
environmentalists; business groups; labor unions; churches; ethnic groups; political action committees or PAC; health groups; education groups; civic groups; youth groups; transportation groups; agricultural groups; veterans groups; women's groups; reform lobbies |
|
International organization participation:
|
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), ANZUS, APEC, Arctic Council, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CBSS (observer), CE (observer), CERN (observer), CP, EAPC, EBRD, FAO, G-20, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt (signatory), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MINUSTAH, NAFTA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS, OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PIF (partner), SAARC (observer), SECI (observer), SPC, UN, UN Security Council, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNITAR, UNMIL, UNOMIG, UNRWA, UNTSO, UPU, WCL, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC |
|
Flag description:
|
13 equal horizontal stripes of red (top and bottom) alternating with white; there is a blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing 50 small, white, five-pointed stars arranged in nine offset horizontal rows of six stars (top and bottom) alternating with rows of five stars; the 50 stars represent the 50 states, the 13 stripes represent the 13 original colonies; known as Old Glory; the design and colors have been the basis for a number of other flags, including Chile, Liberia, Malaysia, and Puerto Rico |
| Economy | United States |
|
Economy - overview:
|
The US has the largest and most technologically powerful economy in the world, with a per capita GDP of $48,000. In this market-oriented economy, private individuals and business firms make most of the decisions, and the federal and state governments buy needed goods and services predominantly in the private marketplace. US business firms enjoy greater flexibility than their counterparts in Western Europe and Japan in decisions to expand capital plant, to lay off surplus workers, and to develop new products. At the same time, they face higher barriers to enter their rivals' home markets than foreign firms face entering US markets. US firms are at or near the forefront in technological advances, especially in computers and in medical, aerospace, and military equipment; their advantage has narrowed since the end of World War II. The onrush of technology largely explains the gradual development of a "two-tier labor market" in which those at the bottom lack the education and the professional/technical skills of those at the top and, more and more, fail to get comparable pay raises, health insurance coverage, and other benefits. Since 1975, practically all the gains in household income have gone to the top 20% of households. The war in March-April 2003 between a US-led coalition and Iraq, and the subsequent occupation of Iraq, required major shifts in national resources to the military. Hurricane Katrina caused extensive damage in the Gulf Coast region in August 2005, but had a small impact on overall GDP growth for the year. Soaring oil prices between 2005 and the first half of 2008 threatened inflation and unemployment, as higher gasoline prices ate into consumers' budgets. Imported oil accounts for about two-thirds of US consumption. Long-term problems include inadequate investment in economic infrastructure, rapidly rising medical and pension costs of an aging population, sizable trade and budget deficits, and stagnation of family income in the lower economic groups. The merchandise trade deficit reached a record $847 billion in 2007, but declined to $810 billion in 2008, as a depreciating exchange rate for the dollar against most major currencies discouraged US imports and made US exports more competitive abroad. The global economic downturn, the sub-prime mortgage crisis, investment bank failures, falling home prices, and tight credit pushed the United States into a recession by mid-2008. To help stabilize financial markets, the US Congress established a $700 billion Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) in October 2008. The government used some of these funds to purchase equity in US banks and other industrial corporations. In January 2009 the US Congress passed and President Barack OBAMA signed a bill providing an additional $787 billion fiscal stimulus - two-thirds on additional spending and one-third on tax cuts - to create jobs and to help the economy recover. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$14.29 trillion (2008 est.)
$14.11 trillion (2007) $13.83 trillion (2006) note: data are in 2008 US dollars |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$14.33 trillion (2008 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
1.3% (2008 est.)
2% (2007 est.) 2.8% (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$47,000 (2008 est.)
$46,800 (2007 est.) $46,300 (2006 est.) note: data are in 2008 US dollars |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 1.2%
industry: 19.6% services: 79.2% (2008 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
155.2 million (includes unemployed) (2008 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
farming, forestry, and fishing 0.6%, manufacturing, extraction, transportation, and crafts 22.6%, managerial, professional, and technical 35.5%, sales and office 24.8%, other services 16.5%
note: figures exclude the unemployed (2007) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
7.2% (December 2008 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
12% (2004 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 2%
highest 10%: 30% (2007 est.) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
45 (2007) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
14.6% of GDP (2008 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $2.524 trillion
expenditures: $2.979 trillion (2008 est.) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
1 October - 30 September |
|
Public debt:
|
60.8% of GDP (2007 est.) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
4.2% (2008 est.) |
|
Central bank discount rate:
|
0.5% (31 March 2009) |
|
Commercial bank prime lending rate:
|
3.25% (31 March 2009) |
|
Stock of money:
|
$1.596 trillion (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of quasi money:
|
$8.154 trillion (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of domestic credit:
|
$14.15 trillion (31 December 2007) |
|
Market value of publicly traded shares:
|
$19.95 trillion (31 December 2007) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
wheat, corn, other grains, fruits, vegetables, cotton; beef, pork, poultry, dairy products; fish; forest products |
|
Industries:
|
leading industrial power in the world, highly diversified and technologically advanced; petroleum, steel, motor vehicles, aerospace, telecommunications, chemicals, electronics, food processing, consumer goods, lumber, mining |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
0.2% (2008 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
4.167 trillion kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
3.892 trillion kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
20.14 billion kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
51.4 billion kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 71.4%
hydro: 5.6% nuclear: 20.7% other: 2.3% (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
8.457 million bbl/day (2007 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
20.68 million bbl/day (2007 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
1.165 million bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
13.71 million bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
20.97 billion bbl (1 January 2008 est.) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
545.9 billion cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
652.9 billion cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
23.28 billion cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
130.3 billion cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
5.977 trillion cu m (1 January 2008 est.) |
|
Current account balance:
|
-$568.8 billion (2008 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$1.377 trillion f.o.b. (2008 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
agricultural products (soybeans, fruit, corn) 9.2%, industrial supplies (organic chemicals) 26.8%, capital goods (transistors, aircraft, motor vehicle parts, computers, telecommunications equipment) 49.0%, consumer goods (automobiles, medicines) 15.0% (2003) |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Canada 21.4%, Mexico 11.7%, China 5.6%, Japan 5.4%, UK 4.3%, Germany 4.3% (2007) |
|
Imports:
|
$2.19 trillion f.o.b. (2008 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
agricultural products 4.9%, industrial supplies 32.9% (crude oil 8.2%), capital goods 30.4% (computers, telecommunications equipment, motor vehicle parts, office machines, electric power machinery), consumer goods 31.8% (automobiles, clothing, medicines, furniture, toys) (2003) |
|
Imports - partners:
|
China 16.9%, Canada 15.7%, Mexico 10.6%, Japan 7.4%, Germany 4.8% (2007) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$70.57 billion (31 December 2007 est.) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$12.25 trillion (30 June 2007) |
|
Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:
|
$2.22 trillion (2008 est.) |
|
Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:
|
$2.751 trillion (2008 est.) |
|
Currency (code):
|
US dollar (USD) |
|
Currency code:
|
USD |
|
Exchange rates:
|
British pounds per US dollar: 0.5302 (2008), 0.4993 (2007), 0.5418 (2006), 0.5493 (2005), 0.5462 (2004)
Canadian dollars per US dollar: 1.0364 (2008), 1.0724 (2007), 1.1334 (2006), 1.2118 (2005), 1.3010 (2004) Chinese yuan per US dollar: 6.9385 (2008), 7.61 (2007), 7.97 (2006), 8.1943 (2005), 8.2768 (2004) euros per US dollar: 0.6827 (2008), 0.7345 (2007), 0.7964 (2006), 0.8041 (2005), 0.8054 (2004) Japanese yen per US dollar: 103.58 (2008), 117.99 (2007), 116.18 (2006) 110.22 (2005), 108.19 (2004) |
| Communications | United States |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
163.2 million (2007) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
255 million (2007) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: a large, technologically advanced, multipurpose communications system
domestic: a large system of fiber-optic cable, microwave radio relay, coaxial cable, and domestic satellites carries every form of telephone traffic; a rapidly growing cellular system carries mobile telephone traffic throughout the country international: country code - 1; multiple ocean cable systems provide international connectivity; satellite earth stations - 61 Intelsat (45 Atlantic Ocean and 16 Pacific Ocean), 5 Intersputnik (Atlantic Ocean region), and 4 Inmarsat (Pacific and Atlantic Ocean regions) (2000) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 4,789, FM 8,961, shortwave 19 (2006) |
|
Radios:
|
575 million (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
2,218 (2006) |
|
Televisions:
|
219 million (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.us |
|
Internet hosts:
|
316 million (2008); note - the US Internet total host count includes the following top level domain host addresses: .us, .com, .edu, .gov, .mil, .net, and .org |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
7,000 (2002 est.) |
|
Internet users:
|
223 million (2008) |
| Transportation | United States |
|
Airports:
|
14,951 (2008) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 5,146
over 3,047 m: 190 2,438 to 3,047 m: 227 1,524 to 2,437 m: 1,464 914 to 1,523 m: 2,307 under 914 m: 958 (2008) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 9,805
2,438 to 3,047 m: 6 1,524 to 2,437 m: 156 914 to 1,523 m: 1,734 under 914 m: 7,909 (2008) |
|
Heliports:
|
146 (2007) |
|
Pipelines:
|
petroleum products 244,620 km; natural gas 548,665 km (2006) |
|
Railways:
|
total: 226,612 km
standard gauge: 226,612 km 1.435-m gauge (2005) |
|
Roadways:
|
total: 6,465,799 km
paved: 4,209,835 km (includes 75,040 km of expressways) unpaved: 2,255,964 km (2007) |
|
Waterways:
|
41,009 km (19,312 km used for commerce)
note: Saint Lawrence Seaway of 3,769 km, including the Saint Lawrence River of 3,058 km, shared with Canada (2008) |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 422
by type: barge carrier 6, bulk carrier 61, cargo 69, carrier 2, chemical tanker 22, container 81, passenger 19, passenger/cargo 59, petroleum tanker 53, refrigerated cargo 3, roll on/roll off 25, vehicle carrier 22 foreign-owned: 74 (Australia 1, Denmark 31, Germany 5, Japan 7, Malaysia 2, Netherlands 1, Norway 9, Singapore 12, Sweden 5, UK 1) registered in other countries: 732 (Antigua and Barbuda 8, Australia 2, Bahamas 106, Bermuda 23, Cambodia 6, Canada 10, Cayman Islands 42, Comoros 2, Cyprus 5, Ecuador 1, Greece 8, Hong Kong 29, Ireland 2, Isle of Man 4, Italy 17, South Korea 7, Liberia 98, Luxembourg 4, Malta 23, Marshall Islands 123, Netherlands 14, Netherlands Antilles 1, Norway 8, Panama 126, Portugal 1, Puerto Rico 3, Russia 1, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 18, Sierra Leone 1, Singapore 22, Trinidad and Tobago 1, Tuvalu 1, UK 12, Vanuatu 1, unknown 2) (2008) |
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Corpus Christi, Duluth, Hampton Roads, Houston, Long Beach, Los Angeles, New York, Philadelphia, Tampa, Texas City |
| Military | United States |
|
Military branches:
|
United States Armed Forces: US Army, US Navy (includes Marine Corps), US Air Force, US Coast Guard; note - Coast Guard administered in peacetime by the Department of Homeland Security, but in wartime reports to the Department of the Navy (2009) |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
18 years of age (17 years of age with parental consent) for male and female voluntary service; maximum enlistment age 42 (Army), 27 (Air Force), 34 (Navy), 28 (Marines); service obligation 8 years, including 2-5 years active duty (Army), 2 years active (Navy), 4 years active (Air Force, Marines) (2008) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 72,715,332
females age 16-49: 71,638,785 (2008 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 59,764,677
females age 16-49: 59,437,663 (2009 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:
|
male: 2,196,124
female: 2,085,085 (2009 est.) |
|
Military expenditures:
|
4.06% of GDP (2005 est.) |
| Transnational Issues | United States |
|
Disputes - international:
|
the U.S. has intensified domestic security measures and is collaborating closely with its neighbors, Canada and Mexico, to monitor and control legal and illegal personnel, transport, and commodities across the international borders; abundant rainfall in recent years along much of the Mexico-US border region has ameliorated periodically strained water-sharing arrangements; 1990 Maritime Boundary Agreement in the Bering Sea still awaits Russian Duma ratification; managed maritime boundary disputes with Canada at Dixon Entrance, Beaufort Sea, Strait of Juan de Fuca, and around the disputed Machias Seal Island and North Rock; The Bahamas and US have not been able to agree on a maritime boundary; US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay is leased from Cuba and only mutual agreement or US abandonment of the area can terminate the lease; Haiti claims US-administered Navassa Island; US has made no territorial claim in Antarctica (but has reserved the right to do so) and does not recognize the claims of any other states; Marshall Islands claims Wake Island; Tokelau included American Samoa's Swains Island among the islands listed in its 2006 draft constitution |
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
refugees (country of origin): the US admitted 62,643 refugees during FY04/05 including; 10,586 (Somalia); 8,549 (Laos); 6,666 (Russia); 6,479 (Cuba); 3,100 (Haiti); 2,136 (Iran) (2006) |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
world's largest consumer of cocaine (shipped from Colombia through Mexico and the Caribbean), Colombian heroin, and Mexican heroin and marijuana; major consumer of ecstasy and Mexican methamphetamine; minor consumer of high-quality Southeast Asian heroin; illicit producer of cannabis, marijuana, depressants, stimulants, hallucinogens, and methamphetamine; money-laundering center |
|
This page was last updated on 14 May, 2009 |