


| The World Factbook | ||


|
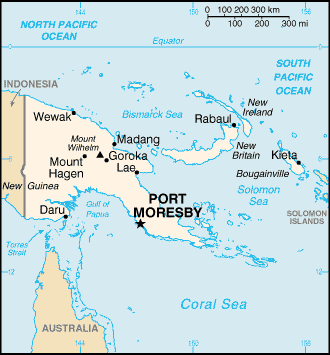
Papua New Guinea |

|
|
| Introduction | Papua New Guinea |
|
Background:
|
The eastern half of the island of New Guinea - second largest in the world - was divided between Germany (north) and the UK (south) in 1885. The latter area was transferred to Australia in 1902, which occupied the northern portion during World War I and continued to administer the combined areas until independence in 1975. A nine-year secessionist revolt on the island of Bougainville ended in 1997 after claiming some 20,000 lives. |
| Geography | Papua New Guinea |
|
Location:
|
Oceania, group of islands including the eastern half of the island of New Guinea between the Coral Sea and the South Pacific Ocean, east of Indonesia |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
6 00 S, 147 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Oceania |
|
Area:
|
total: 462,840 sq km
land: 452,860 sq km water: 9,980 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly larger than California |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 820 km
border countries: Indonesia 820 km |
|
Coastline:
|
5,152 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
measured from claimed archipelagic baselines
territorial sea: 12 nm continental shelf: 200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation exclusive fishing zone: 200 nm |
|
Climate:
|
tropical; northwest monsoon (December to March), southeast monsoon (May to October); slight seasonal temperature variation |
|
Terrain:
|
mostly mountains with coastal lowlands and rolling foothills |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: Mount Wilhelm 4,509 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
gold, copper, silver, natural gas, timber, oil, fisheries |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 0.49%
permanent crops: 1.4% other: 98.11% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
NA |
|
Total renewable water resources:
|
801 cu km (1987) |
|
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
|
total: 0.1 cu km/yr (56%/43%/1%)
per capita: 17 cu m/yr (1987) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
active volcanism; situated along the Pacific "Ring of Fire"; the country is subject to frequent and sometimes severe earthquakes; mud slides; tsunamis |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
rain forest subject to deforestation as a result of growing commercial demand for tropical timber; pollution from mining projects; severe drought |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
|
Geography - note:
|
shares island of New Guinea with Indonesia; one of world's largest swamps along southwest coast |
| People | Papua New Guinea |
|
Population:
|
6,057,263 (July 2009 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 36.9% (male 1,137,796/female 1,099,365)
15-64 years: 59% (male 1,836,272/female 1,735,298) 65 years and over: 4.1% (male 114,789/female 133,743) (2009 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 21.7 years
male: 21.8 years female: 21.6 years (2009 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
2.069% (2009 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
27.55 births/1,000 population (2009 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
6.96 deaths/1,000 population (2008 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
NA (2009 est.) |
|
Urbanization:
|
urban population: 12% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization: 1.9% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.03 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.06 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/female total population: 1.04 male(s)/female (2009 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 45.23 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 49.17 deaths/1,000 live births female: 41.09 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 66.34 years
male: 64.08 years female: 68.72 years (2009 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
3.62 children born/woman (2009 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
1.5% (2007 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
54,000 (2007 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
fewer than 1,000 (2007 est.) |
|
Major infectious diseases:
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria (2009) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Papua New Guinean(s)
adjective: Papua New Guinean |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Melanesian, Papuan, Negrito, Micronesian, Polynesian |
|
Religions:
|
Roman Catholic 27%, Evangelical Lutheran 19.5%, United Church 11.5%, Seventh-Day Adventist 10%, Pentecostal 8.6%, Evangelical Alliance 5.2%, Anglican 3.2%, Baptist 2.5%, other Protestant 8.9%, Bahai 0.3%, indigenous beliefs and other 3.3% (2000 census) |
|
Languages:
|
The three official languages are English, Tok Pisin, and Motu; there are approximately 860 other languages |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 57.3% male: 63.4% female: 50.9% (2000 census) |
|
Education expenditures:
|
NA |
|
People - note:
|
the indigenous population of Papua New Guinea is one of the most heterogeneous in the world; PNG has several thousand separate communities, most with only a few hundred people; divided by language, customs, and tradition, some of these communities have engaged in low-scale tribal conflict with their neighbors for millennia; the advent of modern weapons and modern migrants into urban areas has greatly magnified the impact of this lawlessness |
| Government | Papua New Guinea |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Independent State of Papua New Guinea
conventional short form: Papua New Guinea local short form: Papuaniugini former: Territory of Papua and New Guinea abbreviation: PNG |
|
Government type:
|
constitutional parliamentary democracy and a Commonwealth realm |
|
Capital:
|
name: Port Moresby
geographic coordinates: 9 30 S, 147 10 E time difference: UTC+10 (15 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time) |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
20 provinces; Bougainville (autonomous region), Central, Chimbu, Eastern Highlands, East New Britain, East Sepik, Enga, Gulf, Madang, Manus, Milne Bay, Morobe, National Capital, New Ireland, Northern, Sandaun, Southern Highlands, Western, Western Highlands, West New Britain |
|
Independence:
|
16 September 1975 (from the Australian-administered UN trusteeship) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 16 September (1975) |
|
Constitution:
|
16 September 1975 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on English common law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by governor general Sir Paulius MATANE (since 29 June 2004)
head of government: Prime Minister Sir Michael SOMARE (since 2 August 2002); Deputy Prime Minister Puka TEMU (since 29 August 2007) cabinet: National Executive Council appointed by the governor general on the recommendation of the prime minister elections: the monarch is hereditary; the governor general is nominated by parliament and appointed by the chief of state; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or leader of the majority coalition usually is appointed prime minister by the governor general acting in accordance with a decision of the parliament |
|
Legislative branch:
|
unicameral National Parliament (109 seats, 89 filled from open electorates and 20 from provinces and national capital district; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms); constitution allows up to 126 seats
elections: last held from 30 June to 10 July 2007; next to be held in June 2012 election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - National Alliance 27, PNGP 8, PAP 6, URP 6, PANGU 5, PDM 5, independents 19, others 33; note - election to 1 seat was nullified note: 15 other parties won 4 or fewer seats; association with political parties is fluid |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court (the chief justice is appointed by the governor general on the proposal of the National Executive Council after consultation with the minister responsible for justice; other judges are appointed by the Judicial and Legal Services Commission) |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
National Alliance Party or NA [Michael SOMARE]; Papua and Niugini Union Party or PANGU PATI [Andrew KUMBAKOR]; Papua New Guinea Party or PNGP [Sir Mekere MORAUTA]; People's Democratic Movement or PDM [Michael OGIO]; People's Action Party or PAP [Gabriel KAPRIS]; United Resources Party or URP [William DUMA] (2007) |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
Ahora [Andrew MAMOKO] (represents local tribes); Centre for Environment Law and Community Rights or Celcor [Damien ASE]; Community Coalition Against Corruption |
|
International organization participation:
|
ACP, ADB, APEC, ARF, ASEAN (observer), C, CP, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Evan Jeremy PAKI
chancery: 1779 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Suite 805, Washington, DC 20036 telephone: [1] (202) 745-3680 FAX: [1] (202) 745-3679 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Leslie V. ROWE
embassy: Douglas Street, Port Moresby, N.C.D. mailing address: 4240 Port Moresby PI, US Department of State, Washington DC 20521-4240 telephone: [675] 321-1455 FAX: [675] 321-3423 |
|
Flag description:
|
divided diagonally from upper hoist-side corner; the upper triangle is red with a soaring yellow bird of paradise centered; the lower triangle is black with five, white, five-pointed stars of the Southern Cross constellation centered |
| Economy | Papua New Guinea |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Papua New Guinea is richly endowed with natural resources, but exploitation has been hampered by rugged terrain and the high cost of developing infrastructure. Agriculture provides a subsistence livelihood for 75% of the population. Mineral deposits, including copper, gold, and oil, account for nearly two-thirds of export earnings. The government of Prime Minister SOMARE has expended much of its energy remaining in power. He was the first prime minister ever to serve a full five-year term. The government also brought stability to the national budget, largely through expenditure control; however, it relaxed spending constraints in 2006 and 2007 as elections approached. Numerous challenges still face the government including regaining investor confidence, restoring integrity to state institutions, promoting economic efficiency by privatizing moribund state institutions, and balancing relations with Australia, its former colonial ruler. Other socio-cultural challenges could upend the economy including a worsening HIV/AIDS epidemic, currently the highest rate in all of East Asia and the Pacific, and chronic law and order and land tenure issues. Australia supplied more than $300 million in aid in FY07/08, which accounts for nearly 20% of the national budget. A consortium led by a major American oil company hopes to begin the commercialization of the country's estimated 637 billion cubic meters of natural gas reserves through the construction of a liquefied natural gas (LNG) production facility by 2010. The project has the potential to double the GDP of Papua New Guinea. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$13.29 billion (2008 est.)
$12.5 billion (2007) $11.79 billion (2006) note: data are in 2008 US dollars |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$6.363 billion (2008 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
6.3% (2008 est.)
6% (2007 est.) 2.6% (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$2,200 (2008 est.)
$2,200 (2007 est.) $2,100 (2006 est.) note: data are in 2008 US dollars |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 32.8%
industry: 36.5% services: 30.6% (2008 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
3.639 million (2008 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: 75%
industry: NA% services: NA% (2005 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
1.9% up to 80% in urban areas (2004) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
37% (2002 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 1.7%
highest 10%: 40.5% (1996) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
50.9 (1996) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
19.9% of GDP (2008 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $3.098 billion
expenditures: $2.949 billion (2008 est.) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year |
|
Public debt:
|
34% of GDP (2008 est.) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
8.8% (2008 est.) |
|
Central bank discount rate:
|
7.38% (31 December 2007) |
|
Commercial bank prime lending rate:
|
9.78% (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of money:
|
$1.685 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of quasi money:
|
$1.482 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of domestic credit:
|
$1.486 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Market value of publicly traded shares:
|
$4.863 billion (2005) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
coffee, cocoa, copra, palm kernels, tea, sugar, rubber, sweet potatoes, fruit, vegetables, vanilla; shell fish, poultry, pork |
|
Industries:
|
copra crushing, palm oil processing, plywood production, wood chip production; mining of gold, silver, and copper; crude oil production, petroleum refining; construction, tourism |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
6.3% (2008 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
2.875 billion kWh (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
2.674 billion kWh (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 54.1%
hydro: 45.9% nuclear: 0% other: 0% (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
42,100 bbl/day (2008 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
29,050 bbl/day (2006 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
39,310 bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
24,150 bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
88 million bbl (1 January 2008 est.) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
140 million cu m (2006 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
140 million cu m (2006 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
226.5 billion cu m (1 January 2008 est.) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$438 million (2008 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$5.658 billion f.o.b. (2008 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
oil, gold, copper ore, logs, palm oil, coffee, cocoa, crayfish, prawns |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Australia 27.3%, Japan 9.5%, China 5.7% (2007) |
|
Imports:
|
$3.013 billion f.o.b. (2008 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods, food, fuels, chemicals |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Australia 51.3%, Singapore 11.6%, China 7.9%, Japan 5.7% (2007) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$2.548 billion (31 December 2008 est.) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$1.582 billion (31 December 2008 est.) |
|
Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:
|
$NA |
|
Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:
|
$NA |
|
Currency (code):
|
kina (PGK) |
|
Currency code:
|
PGK |
|
Exchange rates:
|
kina (PGK) per US dollar - 2.6956 (2008 est.), 3.03 (2007), 3.0643 (2006), 3.08 (2005), 3.2225 (2004) |
| Communications | Papua New Guinea |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
60,000 (2007) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
300,000 (2007) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: services are minimal; facilities provide radiotelephone and telegraph, coastal radio, aeronautical radio, and international radio communication services
domestic: access to telephone services is now widely available; combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity is 6 per 100 persons international: country code - 675; submarine cables to Australia and Guam; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Pacific Ocean); international radio communication service (2007) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 8, FM 19, shortwave 28 (1998) |
|
Radios:
|
410,000 (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
3 (all in the Port Moresby area; stations at Mt. Hagen, Goroka, Lae, and Rabaul are planned) (2004) |
|
Televisions:
|
59,841 (1999) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.pg |
|
Internet hosts:
|
3,422 (2008) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
3 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
110,000 (2006) |
| Transportation | Papua New Guinea |
|
Airports:
|
557 (2008) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 21
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2 1,524 to 2,437 m: 14 914 to 1,523 m: 4 under 914 m: 1 (2008) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 536
1,524 to 2,437 m: 8 914 to 1,523 m: 62 under 914 m: 466 (2008) |
|
Heliports:
|
2 (2007) |
|
Pipelines:
|
oil 195 km (2008) |
|
Roadways:
|
total: 19,600 km
paved: 686 km unpaved: 18,914 km (2000) |
|
Waterways:
|
11,000 km (2006) |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 21
by type: bulk carrier 2, cargo 17, petroleum tanker 2 foreign-owned: 6 (UAE 6) (2008) |
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Kimbe, Lae, Madang, Rabaul, Wewak |
| Military | Papua New Guinea |
|
Military branches:
|
Papua New Guinea Defense Force (PNGDF; includes Maritime Operations Element, Air Operations Element) (2009) |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
16 years of age for voluntary military service (with parental consent); no conscription (2008) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 1,481,417
females age 16-49: 1,385,040 (2008 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 1,110,175
females age 16-49: 1,127,758 (2009 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:
|
male: 64,636
female: 62,803 (2009 est.) |
|
Military expenditures:
|
1.4% of GDP (2005 est.) |
| Transnational Issues | Papua New Guinea |
|
Disputes - international:
|
relies on assistance from Australia to keep out illegal cross-border activities from primarily Indonesia, including goods smuggling, illegal narcotics trafficking, and squatters and secessionists |
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
refugees (country of origin): 10,177 (Indonesia) (2007) |
|
Trafficking in persons:
|
current situation: Papua New Guinea is a country of destination for women and children from Malaysia, the Philippines, Thailand, and China trafficked for the purpose of commercial sexual exploitation; internal trafficking of women and children for the purposes of sexual exploitation and involuntary domestic servitude occurs as well
tier rating: Tier 3 - Papua New Guinea does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; the current legal framework does not contain elements of crimes that characterize trafficking; the government lacks victim protection services or a systematic procedure to identify victims of trafficking; the government did not prosecute anyone in 2007 for trafficking; Papua New Guinea has not ratified the 2000 UN TIP Protocol (2008) |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
major consumer of cannabis |
|
This page was last updated on 14 May, 2009 |