


| The World Factbook | ||


|
Suriname |

|
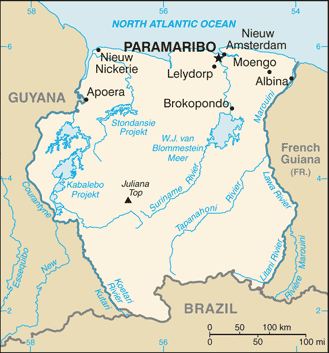
|
| Introduction | Suriname |
|
Background:
|
First explored by the Spaniards in the 16th century and then settled by the English in the mid-17th century, Suriname became a Dutch colony in 1667. With the abolition of slavery in 1863, workers were brought in from India and Java. Independence from the Netherlands was granted in 1975. Five years later the civilian government was replaced by a military regime that soon declared a socialist republic. It continued to exert control through a succession of nominally civilian administrations until 1987, when international pressure finally forced a democratic election. In 1990, the military overthrew the civilian leadership, but a democratically elected government - a four-party New Front coalition - returned to power in 1991 and has ruled since; the coalition expanded to eight parties in 2005. |
| Geography | Suriname |
|
Location:
|
Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between French Guiana and Guyana |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
4 00 N, 56 00 W |
|
Map references:
|
South America |
|
Area:
|
total: 163,270 sq km
land: 161,470 sq km water: 1,800 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly larger than Georgia |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 1,703 km
border countries: Brazil 593 km, French Guiana 510 km, Guyana 600 km |
|
Coastline:
|
386 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm |
|
Climate:
|
tropical; moderated by trade winds |
|
Terrain:
|
mostly rolling hills; narrow coastal plain with swamps |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: unnamed location in the coastal plain -2 m
highest point: Juliana Top 1,230 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
timber, hydropower, fish, kaolin, shrimp, bauxite, gold, and small amounts of nickel, copper, platinum, iron ore |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 0.36%
permanent crops: 0.06% other: 99.58% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
510 sq km (2003) |
|
Total renewable water resources:
|
122 cu km (2003) |
|
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
|
total: 0.67 cu km/yr (4%/3%/93%)
per capita: 1,489 cu m/yr (2000) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
NA |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
deforestation as timber is cut for export; pollution of inland waterways by small-scale mining activities |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
|
Geography - note:
|
smallest independent country on South American continent; mostly tropical rain forest; great diversity of flora and fauna that, for the most part, is increasingly threatened by new development; relatively small population, mostly along the coast |
| People | Suriname |
|
Population:
|
481,267 (July 2009 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 27.1% (male 66,603/female 64,035)
15-64 years: 66.6% (male 159,525/female 160,871) 65 years and over: 6.3% (male 13,004/female 17,229) (2009 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 27.9 years
male: 27.5 years female: 28.3 years (2009 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
1.103% (2009 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
16.8 births/1,000 population (2009 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
5.51 deaths/1,000 population (2008 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
-0.26 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2009 est.) |
|
Urbanization:
|
urban population: 75% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization: 1% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 0.99 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.76 male(s)/female total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2009 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 18.81 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 22.21 deaths/1,000 live births female: 15.18 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 73.73 years
male: 71 years female: 76.65 years (2009 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
1.99 children born/woman (2009 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
2.4% (2007 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
6,800 (2007 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
fewer than 500 (2003 est.) |
|
Major infectious diseases:
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever vectorborne disease: dengue fever, Mayaro virus, and malaria water contact disease: leptospirosis (2009) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Surinamer(s)
adjective: Surinamese |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Hindustani (also known locally as "East Indians"; their ancestors emigrated from northern India in the latter part of the 19th century) 37%, Creole (mixed white and black) 31%, Javanese 15%, "Maroons" (their African ancestors were brought to the country in the 17th and 18th centuries as slaves and escaped to the interior) 10%, Amerindian 2%, Chinese 2%, white 1%, other 2% |
|
Religions:
|
Hindu 27.4%, Protestant 25.2% (predominantly Moravian), Roman Catholic 22.8%, Muslim 19.6%, indigenous beliefs 5% |
|
Languages:
|
Dutch (official), English (widely spoken), Sranang Tongo (Surinamese, sometimes called Taki-Taki, is native language of Creoles and much of the younger population and is lingua franca among others), Caribbean Hindustani (a dialect of Hindi), Javanese |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 89.6% male: 92% female: 87.2% (2004 census) |
|
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
|
total: 12 years
male: 11 years female: 13 years (2002) |
|
Education expenditures:
|
NA |
| Government | Suriname |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Republic of Suriname
conventional short form: Suriname local long form: Republiek Suriname local short form: Suriname former: Netherlands Guiana, Dutch Guiana |
|
Government type:
|
constitutional democracy |
|
Capital:
|
name: Paramaribo
geographic coordinates: 5 50 N, 55 10 W time difference: UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time) |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
10 districts (distrikten, singular - distrikt); Brokopondo, Commewijne, Coronie, Marowijne, Nickerie, Para, Paramaribo, Saramacca, Sipaliwini, Wanica |
|
Independence:
|
25 November 1975 (from the Netherlands) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 25 November (1975) |
|
Constitution:
|
ratified 30 September 1987; effective 30 October 1987 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on Dutch legal system incorporating French penal theory; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Runaldo Ronald VENETIAAN (since 12 August 2000); Vice President Ramdien SARDJOE (since 3 August 2005); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Runaldo Ronald VENETIAAN (since 12 August 2000); Vice President Ram SARDJOE (since 3 August 2005) cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers appointed by the president elections: president and vice president elected by the National Assembly or, if no presidential or vice presidential candidate receives a two-thirds constitutional majority in the National Assembly after two votes, by a simple majority in the larger United People's Assembly (893 representatives from the national, local, and regional councils), for five-year terms (no term limits); election last held on 25 May 2005 (next to be held in 2010) election results: Runaldo Ronald VENETIAAN reelected president; percent of vote - Runaldo Ronald VENETIAAN 62.9%, Rabin PARMESSAR 35.4%, other 1.7%; note - after two votes in the parliament failed to secure a two-thirds majority for a candidate, the vote then went to a special session of the United People's Assembly on 3 August 2005 |
|
Legislative branch:
|
unicameral National Assembly or Nationale Assemblee (51 seats; members are elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections: last held on 25 May 2005 (next to be held in 2010) election results: percent of vote by party - NF 39.7%, NDP 22.2%, VVV 13.8%, A-Com 7.2%, A-1 5.9%, other 11.2%; seats by party - NF 23, NDP 15, VVV 5, A-Com 5, A-1 3 |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Cantonal Courts and a Court of Justice as an appellate court (justices are nominated for life); member of the Caribbean Court of Justice (CCJ) |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Alternative-1 or A-1 (a coalition of Amazone Party of Suriname or APS [Kenneth VAN GENDEREN], Democrats of the 21st Century or D-21 [Soewarto MOESTADJA], Nieuw Suriname or NS [Radjen Nanan PANDAY], Political Wing of the FAL or PVF [Jiwan SITAL], Trefpunt 2000 or T-2000 [Arti JESSURUN]); General Interior Development Party or ABOP [Ronnie BRUNSWIJK]; National Democratic Party or NDP [Desire BOUTERSE]; New Front for Democracy and Development or NF (a coalition that includes A-Combination or A-Com, Democratic Alternative 1991 or DA-91, an independent, business-oriented party [Winston JESSURUN], National Party Suriname or NPS [Ronald VENETIAAN], United Reform Party or VHP [Ramdien SARDJOE], Pertjaja Luhur or PL [Salam Paul SOMOHARDJO], Surinamese Labor Party or SPA [Siegfried GILDS]); Party for Democracy and Development in Unity or DOE [Marten SCHALKWIJK]; People's Alliance for Progress or VVV (a coalition of Democratic National Platform 2000 or DNP-2000 [Jules WIJDENBOSCH], Grassroots Party for Renewal and Democracy or BVD [Tjan GOBARDHAN], Party for National Unity and Solidarity of the Highest Order or KTPI [Willy SOEMITA], Party for Progression, Justice, and Perseverance or PPRS [Renee KAIMAN], Pendawalima or PL [Raymond SAPOEN]); Progressive Laborers and Farmers Union or PALU [Jim HOK]; Progressive Political Party or PPP [Surinder MUNGRA]; Seeka [Paul ABENA]; Union of Progressive Surinamers or UPS [Sheoradj PANDAY] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
Association of Indigenous Village Chiefs [Ricardo PANE]; Association of Saramaccan Authorities or Maroon [Head Captain WASE]; Women's Parliament Forum or PVF [Iris GILLIAD] |
|
International organization participation:
|
ACP, Caricom, FAO, G-77, IADB, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDB, IFAD, IFRCS, IHO (suspended), ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO (subscriber), ITU, ITUC, LAES, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OIC, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCL, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Jacques Ruben Constantijn KROSS
chancery: Suite 460, 4301 Connecticut Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008 telephone: [1] (202) 244-7488 FAX: [1] (202) 244-5878 consulate(s) general: Miami |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Lisa Bobbie SCHREIBER HUGHES
embassy: Dr. Sophie Redmondstraat 129, Paramaribo mailing address: US Department of State, PO Box 1821, Paramaribo telephone: [597] 472-900 FAX: [597] 410-025 |
|
Flag description:
|
five horizontal bands of green (top, double width), white, red (quadruple width), white, and green (double width); there is a large, yellow, five-pointed star centered in the red band |
| Economy | Suriname |
|
Economy - overview:
|
The economy is dominated by the mining industry, with exports of alumina, gold, and oil accounting for about 85% of exports and 25% of government revenues, making the economy highly vulnerable to mineral price volatility. Prospects for local onshore oil production are good, and a drilling program is underway. Offshore oil drilling was given a boost in 2004 when the State Oil Company (Staatsolie) signed exploration agreements with several Western oil companies. Bidding on these new offshore blocks was completed in July 2006. The short-term economic outlook depends on the government's ability to control inflation and on the development of projects in the bauxite and gold mining sectors, though investment in these projects may slow with the tightening of global credit markets. Suriname has received aid for these projects from Netherlands, Belgium, and the European Development Fund. Suriname's economic prospects for the medium term will depend on continued commitment to responsible monetary and fiscal policies and to the introduction of structural reforms to liberalize markets and promote competition. In 2000, the government of Ronald VENETIAAN, returned to office and inherited an economy with inflation of over 100% and a growing fiscal deficit. He quickly implemented an austerity program, raised taxes, attempted to control spending, and tamed inflation. The VENETIAAN administration also has created a stabilization fund to insulate future revenue from commodity shocks. These economic policies are likely to remain in effect during VENETIAAN's third term. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$4.256 billion (2008 est.)
$4.015 billion (2007) $3.805 billion (2006) note: data are in 2008 US dollars |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$2.984 billion (2008 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
6% (2008 est.)
5.5% (2007 est.) 4.8% (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$8,900 (2008 est.)
$8,500 (2007 est.) $8,200 (2006 est.) note: data are in 2008 US dollars |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 10.8%
industry: 24.4% services: 64.8% (2005 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
156,700 (2004) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: 8%
industry: 14% services: 78% (2004) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
9.5% (2004) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
70% (2002 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%: NA% |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $392.6 million
expenditures: $425.9 million (2004) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
6.4% (2007 est.) |
|
Commercial bank prime lending rate:
|
13.77% (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of money:
|
$416.6 million (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of quasi money:
|
$824.4 million (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of domestic credit:
|
$651 million (31 December 2007) |
|
Market value of publicly traded shares:
|
$NA |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
paddy rice, bananas, palm kernels, coconuts, plantains, peanuts; beef, chickens; shrimp; forest products |
|
Industries:
|
bauxite and gold mining, alumina production; oil, lumbering, food processing, fishing |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
6.5% (1994 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
1.595 billion kWh (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
1.457 billion kWh (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 25.2%
hydro: 74.8% nuclear: 0% other: 0% (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
13,000 bbl/day (2007 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
12,370 bbl/day (2006 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
2,899 bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
6,369 bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
88 million bbl (1 January 2008 est.) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
0 cu m (1 January 2006 est.) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$24 million (2007 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$1.391 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
alumina, gold, crude oil, lumber, shrimp and fish, rice, bananas |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Canada 26.8%, Norway 20.2%, Belgium 9.2%, US 8.9%, UAE 7.9%, France 7.2% (2007) |
|
Imports:
|
$1.297 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
capital equipment, petroleum, foodstuffs, cotton, consumer goods |
|
Imports - partners:
|
US 27%, Netherlands 17.3%, Trinidad and Tobago 14.3%, China 5.9%, Japan 5.1% (2007) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$263.3 million (2006) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$504.3 million (2005 est.) |
|
Currency (code):
|
Surinam dollar (SRD) |
|
Currency code:
|
SRG |
|
Exchange rates:
|
Surinamese dollars (SRD) per US dollar - 2.745 (2007), 2.745 (2006), 2.7317 (2005), 2.7336 (2004), 2.6013 (2003)
note: in January 2004, the government replaced the guilder with the Surinamese dollar, tied to a US dollar-dominated currency basket |
| Communications | Suriname |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
81,500 (2006) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
320,000 (2006) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: international facilities are good
domestic: combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity about 90 telephones per 100 persons; microwave radio relay network international: country code - 597; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 4, FM 13, shortwave 1 (1998) |
|
Radios:
|
300,000 (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
3 (plus 7 repeaters) (2000) |
|
Televisions:
|
63,000 (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.sr |
|
Internet hosts:
|
33 (2008) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
2 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
44,000 (2007) |
| Transportation | Suriname |
|
Airports:
|
50 (2008) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 5
over 3,047 m: 1 under 914 m: 4 (2008) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 45
914 to 1,523 m: 5 under 914 m: 40 (2008) |
|
Pipelines:
|
oil 50 km (2008) |
|
Roadways:
|
total: 4,304 km
paved: 1,130 km unpaved: 3,174 km (2003) |
|
Waterways:
|
1,200 km (most navigable by ships with drafts up to 7 m) (2008) |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 1
by type: cargo 1 (2008) |
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Paramaribo, Wageningen |
| Military | Suriname |
|
Military branches:
|
National Army (Nationaal Leger, NL; includes Naval Wing, Air Wing) (2007) |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
18 years of age (est.); recruitment is voluntary, with personnel drawn almost exclusively from the Creole community (2007) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 130,534
females age 16-49: 130,243 (2008 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 107,367
females age 16-49: 111,000 (2009 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:
|
male: 4,251
female: 4,265 (2009 est.) |
|
Military expenditures:
|
0.6% of GDP (2006 est.) |
| Transnational Issues | Suriname |
|
Disputes - international:
|
area claimed by French Guiana between Riviere Litani and Riviere Marouini (both headwaters of the Lawa); Suriname claims a triangle of land between the New and Kutari/Koetari rivers in a historic dispute over the headwaters of the Courantyne; Guyana seeks United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) arbitration to resolve the long-standing dispute with Suriname over the axis of the territorial sea boundary in potentially oil-rich waters |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
growing transshipment point for South American drugs destined for Europe via the Netherlands and Brazil; transshipment point for arms-for-drugs dealing |
|
This page was last updated on 14 May, 2009 |