


| The World Factbook | ||


|
Belarus |

|
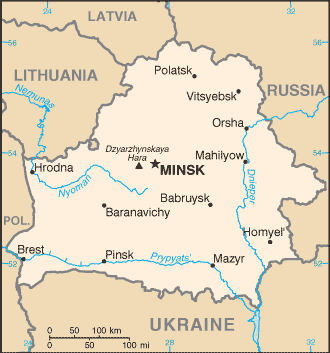
|
| Introduction | Belarus |
|
Background:
|
After seven decades as a constituent republic of the USSR, Belarus attained its independence in 1991. It has retained closer political and economic ties to Russia than any of the other former Soviet republics. Belarus and Russia signed a treaty on a two-state union on 8 December 1999 envisioning greater political and economic integration. Although Belarus agreed to a framework to carry out the accord, serious implementation has yet to take place. Since his election in July 1994 as the country's first president, Alexandr LUKASHENKO has steadily consolidated his power through authoritarian means. Government restrictions on freedom of speech and the press, peaceful assembly, and religion continue. |
| Geography | Belarus |
|
Location:
|
Eastern Europe, east of Poland |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
53 00 N, 28 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Europe |
|
Area:
|
total: 207,600 sq km
land: 207,600 sq km water: 0 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly smaller than Kansas |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 2,900 km
border countries: Latvia 141 km, Lithuania 502 km, Poland 407 km, Russia 959 km, Ukraine 891 km |
|
Coastline:
|
0 km (landlocked) |
|
Maritime claims:
|
none (landlocked) |
|
Climate:
|
cold winters, cool and moist summers; transitional between continental and maritime |
|
Terrain:
|
generally flat and contains much marshland |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Nyoman River 90 m
highest point: Dzyarzhynskaya Hara 346 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
forests, peat deposits, small quantities of oil and natural gas, granite, dolomitic limestone, marl, chalk, sand, gravel, clay |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 26.77%
permanent crops: 0.6% other: 72.63% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
1,310 sq km (2003) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
NA |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
soil pollution from pesticide use; southern part of the country contaminated with fallout from 1986 nuclear reactor accident at Chornobyl' in northern Ukraine |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
|
Geography - note:
|
landlocked; glacial scouring accounts for the flatness of Belarusian terrain and for its 11,000 lakes |
| People | Belarus |
|
Population:
|
10,293,011 (July 2006 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 15.7% (male 825,823/female 791,741)
15-64 years: 69.7% (male 3,490,442/female 3,682,950) 65 years and over: 14.6% (male 498,976/female 1,003,079) (2006 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 37.2 years
male: 34.5 years female: 39.9 years (2006 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
-0.06% (2006 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
11.16 births/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
14.02 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
2.3 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.5 male(s)/female total population: 0.88 male(s)/female (2006 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 13 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 13.92 deaths/1,000 live births female: 12.03 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 69.08 years
male: 63.47 years female: 74.98 years (2006 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
1.43 children born/woman (2006 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
0.3% (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
15,000 (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
1,000 (2001 est.) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Belarusian(s)
adjective: Belarusian |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Belarusian 81.2%, Russian 11.4%, Polish 3.9%, Ukrainian 2.4%, other 1.1% (1999 census) |
|
Religions:
|
Eastern Orthodox 80%, other (including Roman Catholic, Protestant, Jewish, and Muslim) 20% (1997 est.) |
|
Languages:
|
Belarusian, Russian, other |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99.6% male: 99.8% female: 99.5% (2003 est.) |
| Government | Belarus |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Republic of Belarus
conventional short form: Belarus local long form: Respublika Byelarus' local short form: Byelarus' former: Belorussian (Byelorussian) Soviet Socialist Republic |
|
Government type:
|
republic in name, although in fact a dictatorship |
|
Capital:
|
name: Minsk
geographic coordinates: 53 54 N, 27 34 E time difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time) daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
6 provinces (voblastsi, singular - voblasts') and 1 municipality* (horad); Brest, Homyel', Horad Minsk*, Hrodna, Mahilyow, Minsk, Vitsyebsk
note: administrative divisions have the same names as their administrative centers |
|
Independence:
|
25 August 1991 (from Soviet Union) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 3 July (1944); note - 3 July 1944 was the date Minsk was liberated from German troops, 25 August 1991 was the date of independence from the Soviet Union |
|
Constitution:
|
15 March 1994; revised by national referendum of 24 November 1996 giving the presidency greatly expanded powers and became effective 27 November 1996; revised again 17 October 2004 removing presidential term limits |
|
Legal system:
|
based on civil law system |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Aleksandr LUKASHENKO (since 20 July 1994)
head of government: Prime Minister Sergei SIDORSKIY (since 19 December 2003); First Deputy Prime Minister Vladimir SEMASHKO (since December 2003) cabinet: Council of Ministers elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term; first election took place 23 June and 10 July 1994; according to the 1994 constitution, the next election should have been held in 1999, however, Aleksandr LUKASHENKO extended his term to 2001 via a November 1996 referendum; subsequent election held 9 September 2001; an October 2004 referendum ended presidential term limits and allowed the president to run in a third election, which was held on 19 March 2006; prime minister and deputy prime ministers appointed by the president election results: Aleksandr LUKASHENKO reelected president; percent of vote - Aleksandr LUKASHENKO 82.6%, Aleksandr MILINKEVICH 6%, Aleksandr KOZULIN 2.3%; note - election marred by electoral fraud |
|
Legislative branch:
|
bicameral National Assembly or Natsionalnoye Sobranie consists of the Council of the Republic or Soviet Respubliki (64 seats; 56 members elected by regional councils and 8 members appointed by the president, all for four-year terms) and the Chamber of Representatives or Palata Predstaviteley (110 seats; members elected by universal adult suffrage to serve four-year terms)
elections: last held 17 and 31 October 2004; international observers widely denounced the elections as flawed and undemocratic, based on massive government falsification; pro-LUKASHENKO candidates won every seat, after many opposition candidates were disqualified for technical reasons election results: Soviet Respubliki - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; Palata Predstaviteley - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court (judges are appointed by the president); Constitutional Court (half of the judges appointed by the president and half appointed by the Chamber of Representatives) |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
pro-government parties: Agrarian Party or AP [Mikhail SHIMANSKY]; Belarusian Communist Party or KPB; Belarusian Patriotic Movement (Belarusian Patriotic Party) or BPR [Nikolai ULAKHOVICH, chairman]; Liberal Democratic Party of Belarus [Sergei GAYDUKEVICH]; Party of Labor and Justice [Viktor SOKOLOV]; Social-Sports Party [Vladimir ALEXANDROVICH]
opposition parties: 10 Plus Coalition [Alyaksandr MILINKEVICH], includes: Belarusian Party of Communists or PKB [Syarhey KALYAKIN]; Belarusian Party of Labor (unregistered) [Aleksandr BUKHVOSTOV, Leonid LEMESHONAK]; Belarusian Popular Front or BPF [Vintsyuk VYACHORKA]; Belarusian Social-Democratic Gramada [Stanislav SHUSHKEVICH]; Green Party [Oleg GROMYKO]; Party of Freedom and Progress (unregistered) [Vladimir NOVOSYAD]; United Civic Party or UCP [Anatol LYABEDKA]; Women's Party "Nadezhda" [Valentina MATUSEVICH, chairperson] other opposition includes: Belarusian Social-Democratic Party Nardonaya Hromada or BSDP NH [Alyaksandr KOZULIN, chairman]; Christian Conservative BPF [Zyanon PAZNIAK]; Ecological Party of Greens [Mikhail KARTASH]; Party of Popular Accord [Sergei YERMAKK]; Republican Party [Vladimir BELAZOR] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
Assembly of Pro-Democratic NGOs [Sergey MATSKEVICH]; Belarusian Congress of Democratic Trade Unions [Alyaksandr YAROSHUK]; Belarusian Helsinki Committee [Tatiana PROTKO]; Belarusian Organization of Working Women [Irina ZHIKHAR]; Charter 97 [Andrey SANNIKOV]; Lenin Communist Union of Youth (youth wing of the Belarusian Party of Communists or PKB); National Strike Committee of Entrepreneurs [Aleksandr VASILYEV, Valery LEVONEVSKY]; Partnership NGO [Nikolay ASTREYKA]; Perspektiva kiosk watchdog NGO [Anatol SHUMCHENKO]; Vyasna [Ales BYALATSKY]; Women's Independent Democratic Movement [Ludmila PETINA]; Youth Front (Malady Front) [Dzmitryy DASHKEVICH, Syarhey BAKHUN]; Zubr youth group [Vladimir KOBETS] |
|
International organization participation:
|
BSEC (observer), CEI, CIS, EAEC, EAPC, EBRD, GCTU, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, NSG, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, PFP, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer) |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Mikhail KHVOSTOV
chancery: 1619 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20009 telephone: [1] (202) 986-1604 FAX: [1] (202) 986-1805 consulate(s) general: New York |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Karen B. STEWART
embassy: 46 Starovilenskaya Street, Minsk 220002 mailing address: PSC 78, Box B Minsk, APO 09723 telephone: [375] (17) 210-12-83, 217-7347, 217-7348 FAX: [375] (17) 234-7853 |
|
Flag description:
|
red horizontal band (top) and green horizontal band one-half the width of the red band; a white vertical stripe on the hoist side bears Belarusian national ornamentation in red |
| Economy | Belarus |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Belarus's economy in 2006 posted more than 8% growth. The government has succeeded in lowering inflation over the past several years. Trade with Russia - by far its largest single trade partner - decreased in 2006, largely as a result of a change in the way the Value Added Tax (VAT) on trade was collected. Trade with European countries increased. Belarus has seen little structural reform since 1995, when President LUKASHENKO launched the country on the path of "market socialism." In keeping with this policy, LUKASHENKO reimposed administrative controls over prices and currency exchange rates and expanded the state's right to intervene in the management of private enterprises. Since 2005, the government has re-nationalized a number of private companies. In addition, businesses have been subject to pressure by central and local governments, e.g., arbitrary changes in regulations, numerous rigorous inspections, retroactive application of new business regulations, and arrests of "disruptive" businessmen and factory owners. A wide range of redistributive policies has helped those at the bottom of the ladder; the Gini coefficient is among the lowest in the world. Because of these restrictive economic policies, Belarus has had trouble attracting foreign investment, which remains low. Growth has been strong in recent years, despite the roadblocks in a tough, centrally directed economy with a high, but decreasing, rate of inflation. Belarus receives heavily discounted oil and natural gas from Russia and much of Belarus' growth can be attributed to the re-export of Russian oil at market prices. This growth will be threatened in 2007, however, when Russia raises energy prices closer to world market prices for Belarus. Russia is planning to increase Belarusian gas prices from $47 per thousand cubic meters (tcm) to $100 per tcm for 2007, gradually increasing to world prices by 2011. Russia has also introduced an export duty on oil shipped to Belarus, which will increase gradually through 2009, and a requirement that Belarusian duties on re-exported Russian oil be shared with Russia - 70% will go to Russia in 2007, 80% in 2008, and 85% in 2009. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$80.74 billion (2006 est.) |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$28.56 billion (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
8.3% (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$7,800 (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 9.3%
industry: 31.6% services: 59.1% (2005 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
4.3 million (31 December 2005) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: 14%
industry: 34.7% services: 51.3% (2003 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
1.6% officially registered unemployed; large number of underemployed workers (2005) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
27.1% (2003 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 5.1%
highest 10%: 20% (1998) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
30.4 (2000) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
9.5% (2006 est.) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
25.9% of GDP (2006 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $6.578 billion
expenditures: $7.164 billion; including capital expenditures of $180 million (2006 est.) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
grain, potatoes, vegetables, sugar beets, flax; beef, milk |
|
Industries:
|
metal-cutting machine tools, tractors, trucks, earthmovers, motorcycles, televisions, chemical fibers, fertilizer, textiles, radios, refrigerators |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
15.6% (2005 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
29.33 billion kWh (2004) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 99.5%
hydro: 0.1% nuclear: 0% other: 0.4% (2001) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
31.05 billion kWh (2004) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
4.723 billion kWh (2004) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
8.5 billion kWh (2004) |
|
Oil - production:
|
34,260 bbl/day (2004 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
165,000 bbl/day (2004 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
14,500 bbl/day (2003 est.) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
360,000 bbl/day (2004 est.) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
180 million cu m (2004 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
20.5 billion cu m (2005 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2004 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
16.22 billion cu m (2004 est.) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$-511.8 million (2006 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$19.61 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
machinery and equipment, mineral products, chemicals, metals, textiles, foodstuffs |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Russia 35.8%, Netherlands 15.1%, UK 7%, Ukraine 5.7%, Poland 5.3%, Germany 4.4% (2005) |
|
Imports:
|
$21.12 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
mineral products, machinery and equipment, chemicals, foodstuffs, metals |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Russia 60.6%, Germany 6.7%, Ukraine 5.4% (2005) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$1.329 billion (2006 est.) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$5.498 billion (30 June 2006 est.) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$194.3 million (1995) |
|
Currency (code):
|
Belarusian ruble (BYB/BYR) |
|
Currency code:
|
BYB/BYR |
|
Exchange rates:
|
Belarusian rubles per US dollar - 2,144.6 (2006), 2,150 (2005), 2,160.26 (2004), 2,051.27 (2003), 1,790.92 (2002) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year |
| Communications | Belarus |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
3,284,300 (2005) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
4.098 million (2005) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: Belarus lags behind its neighbors in upgrading telecommunications infrastructure; state-owned Beltelcom, is the sole provider of fixed line local and long distance service; modernization of the network to digital switching progressing slowly
domestic: fixed line penetration is improving although rural areas continue to be underserved; four GSM wireless networks are experiencing rapid growth; strict government controls on telecommunications technologies international: country code - 375; Belarus is a member of the Trans-European Line (TEL), Trans-Asia-Europe (TAE) fiber-optic line, and has access to the Trans-Siberia Line (TSL); three fiber-optic segments provide connectivity to Latvia, Poland, Russia, and Ukraine; worldwide service is available to Belarus through this infrastructure; additional analog lines to Russia; Intelsat, Eutelsat, and Intersputnik earth stations |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 28, FM 37, shortwave 11 (1998) |
|
Radios:
|
3.02 million (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
47 (plus 27 repeaters) (1995) |
|
Televisions:
|
2.52 million (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.by |
|
Internet hosts:
|
33,641 (2006) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
23 (2002) |
|
Internet users:
|
3.394 million (2005) |
| Transportation | Belarus |
|
Airports:
|
86 (2006) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 41
over 3,047 m: 2 2,438 to 3,047 m: 22 1,524 to 2,437 m: 4 914 to 1,523 m: 1 under 914 m: 12 (2006) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 45
over 3,047 m: 1 2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 1,524 to 2,437 m: 2 914 to 1,523 m: 6 under 914 m: 35 (2006) |
|
Heliports:
|
1 (2006) |
|
Pipelines:
|
gas 5,223 km; oil 2,321 km; refined products 1,686 km (2006) |
|
Railways:
|
total: 5,512 km
broad gauge: 5,497 km 1.520-m gauge (874 km electrified) standard gauge: 15 km 1.435 m (2005) |
|
Roadways:
|
total: 93,310 km
paved: 81,180 km unpaved: 12,130 km (2004) |
|
Waterways:
|
2,500 km (use limited by location on perimeter of country and by shallowness) (2003) |
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Mazyr |
| Military | Belarus |
|
Military branches:
|
Belarus Armed Forces: Land Force, Air and Air Defense Force (2006) |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
18-27 years of age for compulsory military service; conscript service obligation - 18 months (2005) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 18-49: 2,520,644
females age 18-49: 2,564,696 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 18-49: 1,657,984
females age 18-49: 2,102,793 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching military service age annually:
|
males age 18-49: 85,202
females age 18-49: 82,037 (2005 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$420.5 million (2006) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
1.4% (2005 est.) |
| Transnational Issues | Belarus |
|
Disputes - international:
|
as of January 2007, ground demarcations of the boundaries with Latvia and Lithuania were complete and mapped with final ratification documentation in preparation; 1997 boundary delimitation treaty with Ukraine remains unratified over unresolved financial claims, preventing demarcation and diminishing border security |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
limited cultivation of opium poppy and cannabis, mostly for the domestic market; transshipment point for illicit drugs to and via Russia, and to the Baltics and Western Europe; a small and lightly regulated financial center; new anti-money-laundering legislation does not meet international standards; few investigations or prosecutions of money-laundering activities |
|
This page was last updated on 8 March, 2007 |