


| The World Factbook | ||


|
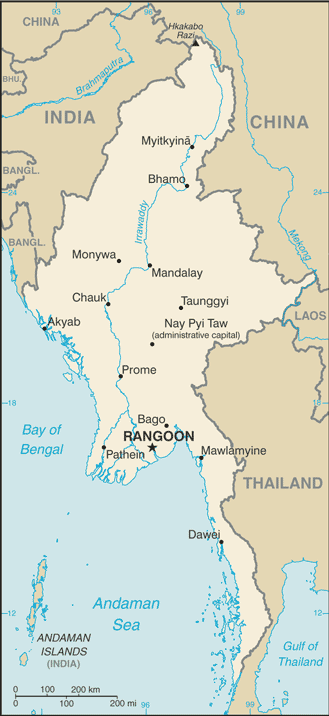
Burma |

|
|
| Introduction | Burma |
|
Background:
|
Britain conquered Burma over a period of 62 years (1824-1886) and incorporated it into its Indian Empire. Burma was administered as a province of India until 1937 when it became a separate, self-governing colony; independence from the Commonwealth was attained in 1948. Gen. NE WIN dominated the government from 1962 to 1988, first as military ruler, then as self-appointed president, and later as political kingpin. Despite multiparty legislative elections in 1990 that resulted in the main opposition party - the National League for Democracy (NLD) - winning a landslide victory, the ruling junta refused to hand over power. NLD leader and Nobel Peace Prize recipient AUNG SAN SUU KYI, who was under house arrest from 1989 to 1995 and 2000 to 2002, was imprisoned in May 2003 and subsequently transferred to house arrest, where she remains virtually incommunicado. In February 2006, the junta extended her detention for another year. Her supporters, as well as all those who promote democracy and improved human rights, are routinely harassed or jailed. |
| Geography | Burma |
|
Location:
|
Southeastern Asia, bordering the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal, between Bangladesh and Thailand |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
22 00 N, 98 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Southeast Asia |
|
Area:
|
total: 678,500 sq km
land: 657,740 sq km water: 20,760 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly smaller than Texas |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 5,876 km
border countries: Bangladesh 193 km, China 2,185 km, India 1,463 km, Laos 235 km, Thailand 1,800 km |
|
Coastline:
|
1,930 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm exclusive economic zone: 200 nm continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin |
|
Climate:
|
tropical monsoon; cloudy, rainy, hot, humid summers (southwest monsoon, June to September); less cloudy, scant rainfall, mild temperatures, lower humidity during winter (northeast monsoon, December to April) |
|
Terrain:
|
central lowlands ringed by steep, rugged highlands |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Andaman Sea 0 m
highest point: Hkakabo Razi 5,881 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
petroleum, timber, tin, antimony, zinc, copper, tungsten, lead, coal, some marble, limestone, precious stones, natural gas, hydropower |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 14.92%
permanent crops: 1.31% other: 83.77% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
18,700 sq km (2003) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
destructive earthquakes and cyclones; flooding and landslides common during rainy season (June to September); periodic droughts |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
deforestation; industrial pollution of air, soil, and water; inadequate sanitation and water treatment contribute to disease |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
|
Geography - note:
|
strategic location near major Indian Ocean shipping lanes |
| People | Burma |
|
Population:
|
47,382,633
note: estimates for this country take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2006 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 26.4% (male 6,335,236/female 6,181,216)
15-64 years: 68.5% (male 16,011,723/female 16,449,626) 65 years and over: 5.1% (male 1,035,853/female 1,368,979) (2006 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 27 years
male: 26.4 years female: 27.6 years (2006 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
0.81% (2006 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
17.91 births/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
9.83 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.02 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.76 male(s)/female total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2006 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 61.85 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 72.68 deaths/1,000 live births female: 50.38 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 60.97 years
male: 58.07 years female: 64.03 years (2006 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
1.98 children born/woman (2006 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
1.2% (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
330,000 (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
20,000 (2003 est.) |
|
Major infectious diseases:
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria are high risks in some locations note: highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified among birds in this country or surrounding region; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2007) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Burmese (singular and plural)
adjective: Burmese |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Burman 68%, Shan 9%, Karen 7%, Rakhine 4%, Chinese 3%, Indian 2%, Mon 2%, other 5% |
|
Religions:
|
Buddhist 89%, Christian 4% (Baptist 3%, Roman Catholic 1%), Muslim 4%, animist 1%, other 2% |
|
Languages:
|
Burmese, minority ethnic groups have their own languages |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 85.3% male: 89.2% female: 81.4% (2002) |
| Government | Burma |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Union of Burma
conventional short form: Burma local long form: Pyidaungzu Myanma Naingngandaw (translated by the US Government as Union of Myanma and by the Burmese as Union of Myanmar) local short form: Myanma Naingngandaw former: Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma note: since 1989 the military authorities in Burma have promoted the name Myanmar as a conventional name for their state; this decision was not approved by any sitting legislature in Burma, and the US Government did not adopt the name, which is a derivative of the Burmese short-form name Myanma Naingngandaw |
|
Government type:
|
military junta |
|
Capital:
|
name: Rangoon (Yangon)
geographic coordinates: 16 47 N, 96 10 E time difference: UTC+6.5 (11.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time) note: Nay Pyi Taw is administrative capital |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
7 divisions (taing-myar, singular - taing) and 7 states (pyi ne-myar, singular - pyi ne)
divisions: Ayeyarwady, Bago, Magway, Mandalay, Sagaing, Tanintharyi, Yangon states: Chin State, Kachin State, Kayah State, Kayin State, Mon State, Rakhine State, Shan State |
|
Independence:
|
4 January 1948 (from UK) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 4 January (1948); Union Day, 12 February (1947) |
|
Constitution:
|
3 January 1974; suspended since 18 September 1988; national convention convened in 1993 to draft a new constitution but collapsed in 1996; reconvened in 2004 but does not include participation of democratic opposition |
|
Legal system:
|
based on British common law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: Chairman of the State Peace and Development Council (SPDC) Sr. Gen. THAN SHWE (since 23 April 1992)
head of government: Prime Minister, Gen SOE WIN (since 19 October 2004) cabinet: Cabinet is overseen by SPDC; military junta assumed power 18 September 1988 under name State Law and Order Restoration Council (SLORC) elections: none |
|
Legislative branch:
|
unicameral People's Assembly or Pyithu Hluttaw (485 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
elections: last held 27 May 1990, but Assembly never allowed by junta to convene election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NLD 392 (opposition), SNLD 23 (opposition), NUP 10 (pro-government), other 60 |
|
Judicial branch:
|
remnants of the British-era legal system are in place, but there is no guarantee of a fair public trial; the judiciary is not independent of the executive |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
National League for Democracy or NLD [AUNG SHWE, chairman, AUNG SAN SUU KYI, general secretary]; National Unity Party or NUP (pro-regime) [TUN YE]; Shan Nationalities League for Democracy or SNLD [HKUN HTUN OO]; and other smaller parties |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
Ethnic Nationalities Council or ENC (based in Thailand); Federation of Trade Unions-Burma or FTUB (exile trade union and labor advocates); National Coalition Government of the Union of Burma or NCGUB (self-proclaimed government in exile) ["Prime Minister" Dr. SEIN WIN] consists of individuals, some legitimately elected to the People's Assembly in 1990 (the group fled to a border area and joined insurgents in December 1990 to form parallel government in exile); Kachin Independence Organization or KIO; Karen National Union or KNU; Karenni National People's Party or KNPP; National Council-Union of Burma or NCUB (exile coalition of opposition groups); several Shan factions; United Wa State Army or UWSA; Union Solidarity and Development Association or USDA (pro-regime, a social and political mass-member organization) [HTAY OO, general secretary]; 88 Generation Students (pro-democracy movement) [MIN KO] |
|
International organization participation:
|
APT, ARF, AsDB, ASEAN, BIMSTEC, CP, EAS, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, ISO (correspondent), ITU, NAM, OPCW (signatory), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires MYINT LWIN
chancery: 2300 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008 telephone: [1] (202) 332-3344 FAX: [1] (202) 332-4351 consulate(s) general: New York |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Shari VILLAROSA
embassy: 581 Merchant Street, Rangoon (GPO 521) mailing address: Box B, APO AP 96546 telephone: [95] (1) 379-880, 379-881 FAX: [95] (1) 256-018 |
|
Flag description:
|
red with a blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing 14, white, five-pointed stars encircling a cogwheel containing a stalk of rice; the 14 stars represent the seven administrative divisions and seven states |
| Economy | Burma |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Burma, a resource-rich country, suffers from pervasive government controls, inefficient economic policies, and rural poverty. The junta took steps in the early 1990s to liberalize the economy after decades of failure under the "Burmese Way to Socialism," but those efforts stalled, and some of the liberalization measures were rescinded. Lacking monetary or fiscal stability, the economy suffers from serious macroeconomic imbalances - including rising inflation, fiscal deficits, multiple official exchange rates that overvalue the Burmese kyat, a distorted interest rate regime, unrelable statistics, and an inablility to reconcile national accounts to determine a realistic GDP figure. Most overseas development assistance ceased after the junta began to suppress the democracy movement in 1988 and subsequently refused to honor the results of the 1990 legislative elections. In response to the government of Burma's attack in May 2003 on AUNG SAN SUU KYI and her convoy, the US imposed new economic sanctions in August 2003 against Burma - including a ban on imports of Burmese products and a ban on provision of financial services by US persons. Further, a poor investment climate hampers attracting outside investment slowing the inflow of foreign exchange. The most productive sectors will continue to be in extractive industries, especially oil and gas, mining, and timber with the latter especially causing environmental degradation. Other areas, such as manufacturing and services, are struggling with inadequate infrastructure, unpredictable import/export policies, deteriorating health and education systems, and endemic corruption. A major banking crisis in 2003 shuttered the country's 20 private banks and disrupted the economy. As of 2006, the largest private banks operate under tight restrictions limiting the private sector's access to formal credit. Official statistics are inaccurate. Published statistics on foreign trade are greatly understated because of the size of the black market and unofficial border trade - often estimated to be as large as the official economy. Though the Burmese government has good economic relations with its neighbors, better investment and business climates and an improved political situation are needed to promote serious foreign investment, exports, and tourism. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$83.84 billion (2006 est.) |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$9.6 billion (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
2.6% (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$1,800 (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 50%
industry: 15% services: 35% (2006 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
28.49 million (2006 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: 70%
industry: 7% services: 23% (2001 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
10.2% (2006 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
25% (2000 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 2.8%
highest 10%: 32.4% (1998) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
21.4% (2006 est.) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
11.8% of GDP (2006 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $2.18 billion
expenditures: $2.36 billion; including capital expenditures of NA (2006 est.) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
rice, pulses, beans, sesame, groundnuts, sugarcane; hardwood; fish and fish products |
|
Industries:
|
agricultural processing; wood and wood products; copper, tin, tungsten, iron; cement, construction materials; pharmaceuticals; fertilizer; natural gas; garments, jade and gems |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
NA% |
|
Electricity - production:
|
6.02 billion kWh (FY05/06) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 44.5%
hydro: 43.4% nuclear: 0% other: 12.1% (2002) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
5.325 billion kWh (FY05/06) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2006) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2006) |
|
Oil - production:
|
9,500 bbl/day (2006 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
20,460 bbl/day (2006 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
5,000 bbl/day (2006 est.) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
14,230 bbl/day (2006 est.) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
less than 100 million bbl (2005) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
10.2 billion cu m (2004 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
2.7 billion cu m (2004 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
7.5 billion cu m (2004 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2004 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
283.2 billion cu m (1 January 2005 est.) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$1.247 billion (2006 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$3.56 billion f.o.b.
note: official export figures are grossly underestimated due to the value of timber, gems, narcotics, rice, and other products smuggled to Thailand, China, and Bangladesh (2006 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
gas, wood products, pulses, beans, fish, rice, clothing, jade and gems |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Thailand 43.8%, India 12.1%, China 6.7%, Japan 5% (2005) |
|
Imports:
|
$1.98 billion f.o.b.
note: import figures are grossly underestimated due to the value of consumer goods, diesel fuel, and other products smuggled in from Thailand, China, Malaysia, and India (2006 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
fabric, petroleum products, fertilizer, plastics, machinery, transport equipment; cement, construction materials, crude oil; food products, edible oil |
|
Imports - partners:
|
China 28.8%, Thailand 21.8%, Singapore 18.4%, Malaysia 7.6% (2005) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$1.01 billion (2006 est.) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$7.162 billion (2006 est.) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$127 million (2001 est.) |
|
Currency (code):
|
kyat (MMK) |
|
Currency code:
|
MMK |
|
Exchange rates:
|
kyats per US dollar - 1,280 (2006), 5.761 (2005), 5.7459 (2004), 6.0764 (2003), 6.5734 (2002)
note: unofficial exchange rates ranged in 2004 from 815 kyat/US dollar to nearly 970 kyat/US dollar, and by yearend 2005, the unofficial exchange rate was 1,075 kyat/US dollar; data shown for 2002-05 are official exchange rates |
|
Fiscal year:
|
1 April - 31 March |
| Communications | Burma |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
476,200 (2005) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
183,400 (2005) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: barely meets minimum requirements for local and intercity service for business and government; international service is fair
domestic: NA international: country code - 95; satellite earth station - 2, Intelsat (Indian Ocean), and ShinSat |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 1, FM 1, shortwave NA (2004) |
|
Radios:
|
4.2 million (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
2 (2004) |
|
Televisions:
|
320,000 (2000) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.mm |
|
Internet hosts:
|
42 (2006) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
1
note: as of September 2000, Internet connections were legal only for the government, tourist offices, and a few large businesses (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
78,000 (2005) |
| Transportation | Burma |
|
Airports:
|
85 (2006) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 21
over 3,047 m: 8 2,438 to 3,047 m: 7 1,524 to 2,437 m: 4 914 to 1,523 m: 1 under 914 m: 1 (2006) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 64
over 3,047 m: 1 1,524 to 2,437 m: 13 914 to 1,523 m: 18 under 914 m: 32 (2006) |
|
Heliports:
|
1 (2006) |
|
Pipelines:
|
gas 2,224 km; oil 558 km (2006) |
|
Railways:
|
total: 3,955 km
narrow gauge: 3,955 km 1.000-m gauge (2005) |
|
Roadways:
|
total: 27,000 km
paved: 3,200 km unpaved: 23,800 km (2005) |
|
Waterways:
|
12,800 km (2005) |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 34 ships (1000 GRT or over) 402,699 GRT/620,642 DWT
by type: bulk carrier 8, cargo 20, passenger 2, passenger/cargo 3, specialized tanker 1 foreign-owned: 9 (Germany 5, Japan 4) (2006) |
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Moulmein, Rangoon, Sittwe |
| Military | Burma |
|
Military branches:
|
Myanmar Armed Forces (Tatmadaw): Army, Navy, Air Force (2005) |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
18 years of age for voluntary military service for both sexes (2004) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 18-49: 12,268,850
females age 18-49: 12,469,771 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 18-49: 7,946,701
females age 18-49: 8,543,705 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching military service age annually:
|
males age 18-49: 469,841
females: 455,689 (2005 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$39 million (FY97) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
2.1% (2005 est.) |
| Transnational Issues | Burma |
|
Disputes - international:
|
over half of Burma's population consists of diverse ethnic groups with substantial numbers of kin beyond its borders; despite continuing border committee talks, significant differences remain with Thailand over boundary alignment and the handling of ethnic rebels, refugees, and illegal cross-border activities; ethnic Karens flee into Thailand to escape fighting between Karen rebels and Burmese troops; in 2005 Thailand sheltered about 121,000 Burmese refugees; Karens also protest Thai support for a Burmese hydroelectric dam on the Salween River near the border; environmentalists in Burma and Thailand continue to voice concern over China's construction of hydroelectric dams upstream on the Nujiang/Salween River in Yunnan Province; India seeks cooperation from Burma to keep Indian Nagaland separatists from hiding in remote Burmese uplands |
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
IDPs: 540,000 (government offensives against ethnic insurgent groups near the eastern borders; most IDPs are ethnic Karen, Karenni, Shan, Tavoyan, and Mon) (2006) |
|
Trafficking in persons:
|
current situation: Burma is a source country for men, women, and children trafficked to East and Southeast Asia for sexual exploitation, domestic service, and forced commercial labor; a significant number of victims are economic migrants who wind up in forced or bonded labor and forced prostitution; to a lesser extent, Burma is a country of transit and destination for women trafficked from China for sexual exploitation; internal trafficking of persons occurs primarily for labor in industrial zones and agricultural estates; internal trafficking of women and girls for sexual exploitation occurs from villages to urban centers and other areas; the military junta's economic mismanagement, human rights abuses, and policy of using forced labor are driving factors behind Burma's large trafficking problem
tier rating: Tier 3 - Burma does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
remains world's second largest producer of illicit opium with an estimated production in 2005 of 380 metric tons, up 13% from 2004 and cultivation in 2005 was 40,000 hectares, a 10% increase from 2004; the decline in opium production in the United Wa State Army's areas of greatest control was more than offset by increases in south and east Shan state; lack of government will to take on major narcotrafficking groups and lack of serious commitment against money laundering continues to hinder the overall antidrug effort; major source of methamphetamine and heroin for regional consumption; currently under Financial Action Task Force countermeasures due to continued failure to address its inadequate money-laundering controls (2005) |
|
This page was last updated on 8 March, 2007 |