


| The World Factbook | ||


|
Afghanistan |

|
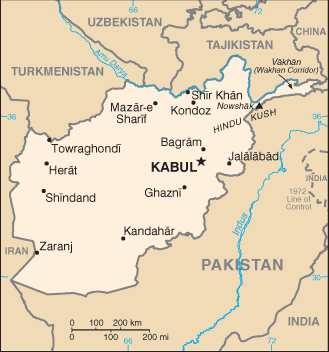
|
| Introduction | Afghanistan |
|
Background:
|
Ahmad Shah DURRANI unified the Pashtun tribes and founded Afghanistan in 1747. The country served as a buffer between the British and Russian empires until it won independence from notional British control in 1919. A brief experiment in democracy ended in a 1973 coup and a 1978 Communist counter-coup. The Soviet Union invaded in 1979 to support the tottering Afghan Communist regime, touching off a long and destructive war. The USSR withdrew in 1989 under relentless pressure by internationally supported anti-Communist mujahedin rebels. Subsequently, a series of civil wars saw Kabul finally fall in 1996 to the Taliban, a hardline Pakistani-sponsored movement that emerged in 1994 to end the country's civil war and anarchy. Following the 11 September 2001 terrorist attacks in New York City, a US, Allied, and anti-Taliban Northern Alliance military action toppled the Taliban for sheltering Osama BIN LADIN. The UN-sponsored Bonn Conference in 2001 established a process for political reconstruction that included the adoption of a new constitution and a presidential election in 2004, and National Assembly elections in 2005. On 7 December 2004, Hamid KARZAI became the first democratically elected president of Afghanistan. The National Assembly was inaugurated on 19 December 2005. |
| Geography | Afghanistan |
|
Location:
|
Southern Asia, north and west of Pakistan, east of Iran |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
33 00 N, 65 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Asia |
|
Area:
|
total: 647,500 sq km
land: 647,500 sq km water: 0 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly smaller than Texas |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 5,529 km
border countries: China 76 km, Iran 936 km, Pakistan 2,430 km, Tajikistan 1,206 km, Turkmenistan 744 km, Uzbekistan 137 km |
|
Coastline:
|
0 km (landlocked) |
|
Maritime claims:
|
none (landlocked) |
|
Climate:
|
arid to semiarid; cold winters and hot summers |
|
Terrain:
|
mostly rugged mountains; plains in north and southwest |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Amu Darya 258 m
highest point: Nowshak 7,485 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
natural gas, petroleum, coal, copper, chromite, talc, barites, sulfur, lead, zinc, iron ore, salt, precious and semiprecious stones |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 12.13%
permanent crops: 0.21% other: 87.66% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
27,200 sq km (2003) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
damaging earthquakes occur in Hindu Kush mountains; flooding; droughts |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
limited natural fresh water resources; inadequate supplies of potable water; soil degradation; overgrazing; deforestation (much of the remaining forests are being cut down for fuel and building materials); desertification; air and water pollution |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified: Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation |
|
Geography - note:
|
landlocked; the Hindu Kush mountains that run northeast to southwest divide the northern provinces from the rest of the country; the highest peaks are in the northern Vakhan (Wakhan Corridor) |
| People | Afghanistan |
|
Population:
|
31,056,997 (July 2006 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 44.6% (male 7,095,117/female 6,763,759)
15-64 years: 53% (male 8,436,716/female 8,008,463) 65 years and over: 2.4% (male 366,642/female 386,300) (2006 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 17.6 years
male: 17.6 years female: 17.6 years (2006 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
2.67% (2006 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
46.6 births/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
20.34 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
0.42 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.95 male(s)/female total population: 1.05 male(s)/female (2006 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 160.23 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 164.77 deaths/1,000 live births female: 155.45 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 43.34 years
male: 43.16 years female: 43.53 years (2006 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
6.69 children born/woman (2006 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
0.01% (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
NA |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
NA |
|
Major infectious diseases:
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever vectorborne disease: malaria is a high risk countrywide below 2,000 meters from March through November animal contact disease: rabies note: highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified among birds in this country or surrounding region; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2007) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Afghan(s)
adjective: Afghan |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Pashtun 42%, Tajik 27%, Hazara 9%, Uzbek 9%, Aimak 4%, Turkmen 3%, Baloch 2%, other 4% |
|
Religions:
|
Sunni Muslim 80%, Shi'a Muslim 19%, other 1% |
|
Languages:
|
Afghan Persian or Dari (official) 50%, Pashtu (official) 35%, Turkic languages (primarily Uzbek and Turkmen) 11%, 30 minor languages (primarily Balochi and Pashai) 4%, much bilingualism |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 36% male: 51% female: 21% (1999 est.) |
|
People - note:
|
of the estimated 4 million refugees in October 2001, 2.3 million have returned |
| Government | Afghanistan |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Islamic Republic of Afghanistan
conventional short form: Afghanistan local long form: Jomhuri-ye Eslami-ye Afghanestan local short form: Afghanestan former: Republic of Afghanistan |
|
Government type:
|
Islamic republic |
|
Capital:
|
name: Kabul
geographic coordinates: 34 31 N, 69 12 E time difference: UTC+4.5 (9.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time) |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
34 provinces (velayat, singular - velayat); Badakhshan, Badghis, Baghlan, Balkh, Bamian, Daykondi, Farah, Faryab, Ghazni, Ghowr, Helmand, Herat, Jowzjan, Kabol, Kandahar, Kapisa, Khowst, Konar, Kondoz, Laghman, Lowgar, Nangarhar, Nimruz, Nurestan, Oruzgan, Paktia, Paktika, Panjshir, Parvan, Samangan, Sar-e Pol, Takhar, Vardak, Zabol |
|
Independence:
|
19 August 1919 (from UK control over Afghan foreign affairs) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 19 August (1919) |
|
Constitution:
|
new constitution drafted 14 December 2003-4 January 2004; signed 16 January 2004 |
|
Legal system:
|
according to the new constitution, no law should be "contrary to Islam"; the state is obliged to create a prosperous and progressive society based on social justice, protection of human dignity, protection of human rights, realization of democracy, and to ensure national unity and equality among all ethnic groups and tribes; the state shall abide by the UN charter, international treaties, international conventions that Afghanistan signed, and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan Hamid KARZAI (since 7 December 2004); Vice Presidents Ahmad Zia MASOOD and Abdul Karim KHALILI (since 7 December 2004); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government; former King ZAHIR Shah holds the honorific, "Father of the Country," and presides symbolically over certain occasions but lacks any governing authority; the honorific is not hereditary
head of government: President of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan Hamid KARZAI (since 7 December 2004); Vice Presidents Ahmad Zia MASOOD and Abdul Karim KHALILI (since 7 December 2004) cabinet: 25 ministers; note - under the new constitution, ministers are appointed by the president and approved by the National Assembly elections: the president and two vice presidents are elected by direct vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); if no candidate receives 50% or more of the vote in the first round of voting, the two candidates with the most votes will participate in a second round; a president can only be elected for two terms; election last held 9 October 2004 (next to be held in 2009) election results: Hamid KARZAI elected president; percent of vote - Hamid KARZAI 55.4%, Yunus QANUNI 16.3%, Ustad Mohammad MOHAQQEQ 11.6%, Abdul Rashid DOSTAM 10.0%, Abdul Latif PEDRAM 1.4%, Masooda JALAL 1.2% |
|
Legislative branch:
|
the bicameral National Assembly consists of the Wolesi Jirga or House of People (no more than 249 seats), directly elected for five-year terms, and the Meshrano Jirga or House of Elders (102 seats, one-third elected from provincial councils for four-year terms, one-third elected from local district councils for three-year terms
note: on rare occasions the government may convene a Loya Jirga (Grand Council) on issues of independence, national sovereignty, and territorial integrity; it can amend the provisions of the constitution and prosecute the president; it is made up of members of the National Assembly and chairpersons of the provincial and district councils elections: last held 18 September 2005 (next to be held for the Wolesi Jirga by September 2009; next to be held for the provincial councils to the Meshrano Jirga by September 2008) election results: the single non-transferable vote (SNTV) system used in the election did not make use of political party slates; most candidates ran as independents |
|
Judicial branch:
|
the constitution establishes a nine-member Stera Mahkama or Supreme Court (its nine justices are appointed for 10-year terms by the president with approval of the Wolesi Jirga) and subordinate High Courts and Appeals Courts; there is also a minister of justice; a separate Afghan Independent Human Rights Commission established by the Bonn Agreement is charged with investigating human rights abuses and war crimes |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
note - includes only political parties approved by the Ministry of Justice; De Afghan Watan Islami Gond [Mohammad Osman SALEKZADA]; De Afghanistan De Mili Mubarizeeno Islami Gond [Amanat NINGARHAREE]; De Afghanistan De Mili Wahdat Wolesi Tahreek [Abdul Hakim NOORZAI]; De Afghanistan De Solay Ghorzang Gond [Shahnawaz TANAI]; De Afghanistan De Solay Mili Islami Gond [Shah Mohammood Popal ZAI]; Hezb-e Esteqlal-e-Mili Afghanistan [Taj Mohammad WARDAK]; Hezb-e Hambastagee Mili Aqwam-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad Zarif NASERI]; Hezb-e Harakat-e-Islami-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad Ali JAWID]; Hezb-e Jamihat-e-Islami [Ustad RABBANI]; Hezb-e Paiwand Mihahani Afghanistan [Sayed Kamal SADAT]; Hezb-e-Aarman-e-Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Ilhaj Saraj-u-din ZAFAREE]; Hezb-e-Aazaadi Khwahan Maihan [Abdul Hadi DABEER]; Hezb-e-Aazadee Khwahan Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Feda Mohammad EHSAS]; Hezb-e-Adalat-e-Islami Afghanistan [Mohammad Kabir MARZBAN]; Hezb-e-Afghan Melat [Anwarul Haq AHADI]; Hezb-e-Afghanistan-e-Naween [Mohammad Yunis QANUNI]; Hezb-e-Afghanistan-e-Wahid [Mohammad Wasil RAHIMEE]; Hezb-e-Azadee-e-Afghanistan [Ilaj Abdul MALEK]; Hezb-e-Democracy Afghanistan [Tawos ARAB]; Hezb-e-Domcrat-e-Afghanistan [Abdul Kabir RANJBAR]; Hezb-e-Eatedal-e-Mili Islami-e-Afghanistan [Qara Bik Eized YAAR]; Hezb-e-Eqtedar-e-Mili [Sayed Mustafa KAZEMI]; Hezb-e-Falah-e-Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Ustad Mohammad ZAREEF]; Hezb-e-Hambastagee Mili Jawanan-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad Jamil KARZAI]; Hezb-e-Hambastagee-e-Afghanistan [Abdul Khaleq NEMAT]; Hezb-e-Harakat-e-Islami Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Ilhaj Said Hussain ANWARY]; Hezb-e-Harakat-e-Mili Wahdat-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad Nadir AATASH]; Hezb-e-Ifazat Az Uqooq-e-Bashar Wa Inkishaf-e-Afghanistan [Baryalai NASRATI]; Hezb-e-Islami-e-Afghanistan-e-Jawan [Sayed Jawad HUSSINEE]; Hezb-e-Isteqlal-e-Afghanistan [Dr. Ghulam Farooq NEJRABEE]; Hezb-e-Jamahat-ul-Dawat ilal Quran-wa-Sunat-e-Afghanistan [Mawlawee Samiullah NAJEEBEE]; Hezb-e-Jamhoree Khwahane-Afghanistan [Sebghatullah SANJAR]; Hezb-e-Junbish Democracy Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Sharif NAZARI]; Hezb-e-Junbish Mili Islami-e-Afghanistan [Sayed NOORULLAH]; Hezb-e-Kangra-e-Mili-e-Afghanistan [Abdul Latif PEDRAM]; Hezb-e-Kar Wa Tawsiha-e-Afghanistan [Zulfiqar OMID]; Hezb-e-Lebral-e-Aazadee Khwa-e-Afghanistan [Ajmal SUHAIL]; Hezb-e-Majmeh Mili Faleen-Sulh-e-Afghanistan [Shamsul Haq Noor SHAMS]; Hezb-e-Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Ahmad Shah ASAR]; Hezb-e-Mardom-e-Mosalman-e-Afghanistan [Besmellah JOYAN]; Hezb-e-Mili Afghanistan [Abdul Rashid ARYAN]; Hezb-e-Mili Heward [GHULAM MOHAMMAD]; Hezb-e-Mili Islami-e-Afghanistan [Rohullah LOUDIN]; Hezb-e-Mili Wahdat-e-Aqwam-e-Islami-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad Shah KHOGYANI]; Hezb-e-Mutahed Mili [Noorul Haq ULOOMI]; Hezb-e-Nahzat-e-Aazadee Wa Democracy-e-Afghanistan [Abdul Raqib Jawid KOHISTANEE]; Hezb-e-Nahzat-e-Hambastagee Mili-e-Afghanistan [Pir Sayed Eshaq GAILANEE]; Hezb-e-Nakhbagan-e-Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Abdul Hamid JAWAD]; Hezb-e-Paiwand Mili Afghanistan [Sayed Mansoor NADREEI]; Hezb-e-Rastakhaiz-e-Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Sayed Zahir Qayed Omul BELADI]; Hezb-e-Refah-e-Afghanistan [Meer Asef ZAEEFI]; Hezb-e-Refah-e-Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Mia Gul WASIQ]; Hezb-e-Refah-e-Mili Afghanistan [Mohammad Hassan JAHFAREE]; Hezb-e-Resalat-e-Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Noor Aqa ROEENE]; Hezb-e-Sahadat-e-Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad Zubair PAIROZ]; Hezb-e-Sahadat-e-Mili Islami-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad Osman SALEKZADA]; Hezb-e-Subat-e-Mili Islami-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad Same KHAROTI]; Hezb-e-Sulh Wa Wahdat-e-Mili-e-Afghanistan [Gulabuddin Shir ZAEE]; Hezb-e-Sulh-e-Mili Islami Aqwam-e-Afghanistan [Abdul Qaher SHARIATEE]; Hezb-e-Tafahum Wa Democracy-e-Afghanistan [Ahamad SHAHEEN]; Hezb-e-Tahreek Wahdat-e-Mili-e-Afghanistan [Sultan Mohammad GHAZI]; Hezb-e-Tahreek Wahdat-ul-Musimeen Afghanistan [Wazir Mohammad WAHDAT]; Hezb-e-Tanzim Jabha Mili Nejat-e-Afghanistan [Seghatullah MOJADDEDI]; Hezb-e-Taraqee Democrat Afghanistan [Wali ARYA]; Hezb-e-Taraqee Mili Afghanistan [Dr. Aref BAKTASH]; Hezb-e-Umat-e-Islam-e-Afghanistan [Toran Noor Aqa Ahmad ZAI]; Hezb-e-Wahdat-e-Islami Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Ustad Mohammad MOHAQQEQ]; Hezb-e-Wahdat-e-Islami-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad Karim KHALILI]; Hezb-e-Wahdat-e-Islami-e-Melat-e-Afghanistan [Qurban Ali URFANI]; Hezb-e-Wahdat-e-Mili Afghanistan [Abdul Rashid JALILI]; Hezb-e-Wahdat-e-Mili Islami-e-Afghanistan [Mohammad AKBAREE]; Mahaz-e-Mili Islami Afghanistan [Pir Sayed Ahmad GAILANEE]; Mili Dreez Gong [Habibullah JANBDAD]; Nahzat-e-Hakemyat-e-Mardom-e-Afghanistan [Hayatullah SUBHANEE]; Nahzat-e-Mili Afghanistan [Ahmad Wali MASOOUD]; Tanzim Daawat-e-Islami-e-Afghanistan [Abdul Rasoul SAYYAF]; (20 August 2005) |
|
International organization participation:
|
AsDB, CP, ECO, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO (correspondent), ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, OSCE (partner), SACEP, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer) |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Said Tayeb JAWAD
chancery: 2341 Wyoming Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008 telephone: [1] (202) 483-6410 FAX: [1] (202) 483-6488 consulate(s) general: Los Angeles, New York |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Ronald E. NEUMANN
embassy: The Great Masood Road, Kabul mailing address: U.S. Embassy Kabul, APO, AE 09806 telephone: [00 93] (20) 230-0436 FAX: [00 93] (20) 230-1364 |
|
Flag description:
|
three equal vertical bands of black (hoist), red, and green, with a gold emblem centered on the red band; the emblem features a temple-like structure encircled by a wreath on the left and right and by a bold Islamic inscription above |
| Economy | Afghanistan |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Afghanistan's economy is recovering from decades of conflict. The economy has improved significantly since the fall of the Taliban regime in 2001 largely because of the infusion of international assistance, the recovery of the agricultural sector, and service sector growth. Real GDP growth probably exceeded 8% in 2006. Despite the progress of the past few years, Afghanistan is extremely poor, landlocked, and highly dependent on foreign aid, agriculture, and trade with neighboring countries. Much of the population continues to suffer from shortages of housing, clean water, electricity, medical care, and jobs. Criminality, insecurity, and the Afghan Government's inability to extend rule of law to all parts of the country pose challenges to future economic growth. It will probably take the remainder of the decade and continuing donor aid and attention to significantly raise Afghanistan's living standards from its current status, among the lowest in the world. While the international community remains committed to Afghanistan's development, pledging over $24 billion at three donors' conferences since 2002, Kabul will need to overcome a number of challenges. Expanding poppy cultivation and a growing opium trade generate roughly $3 billion in illicit economic activity and looms as one of Kabul's most serious policy concerns. Other long-term challenges include: budget sustainability, job creation, corruption, government capacity, and rebuilding war torn infrastructure. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$21.5 billion (2004 est.) |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$8.8 billion (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
8.4% (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$800 (2004 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 38%
industry: 24% services: 38% note: data exclude opium production (2005 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
15 million (2004 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: 80%
industry: 10% services: 10% (2004 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
40% (2005 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
53% (2003) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%: NA% |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
16.3% (2005 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $269 million
expenditures: $561 million; including capital expenditures of $41.7 million note: Afghanistan has also received $273 million from the Reconstruction Trust Fund and $63 million from the Law and Order Trust Fund (FY04-05 budget est.) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
opium, wheat, fruits, nuts; wool, mutton, sheepskins, lambskins |
|
Industries:
|
small-scale production of textiles, soap, furniture, shoes, fertilizer, cement; handwoven carpets; natural gas, coal, copper |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
NA% |
|
Electricity - production:
|
734.3 million kWh (2004) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 36.3%
hydro: 63.7% nuclear: 0% other: 0% (2001) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
782.9 million kWh (2004) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2004) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
100 million kWh (2004) |
|
Oil - production:
|
0 bbl/day (2004) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
4,500 bbl/day (2004 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
NA bbl/day |
|
Oil - imports:
|
NA bbl/day |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
0 bbl (1 January 2002) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
20 million cu m (2004 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
20 million cu m (2004 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2004 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2004 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
99.96 billion cu m (1 January 2005 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$471 million; note - not including illicit exports or reexports (2005 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
opium, fruits and nuts, handwoven carpets, wool, cotton, hides and pelts, precious and semi-precious gems |
|
Exports - partners:
|
US 25.8%, India 21.2%, Pakistan 20.3%, Finland 4.1% (2005) |
|
Imports:
|
$3.87 billion (2005 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
capital goods, food, textiles, petroleum products |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Pakistan 39%, US 9.6%, Germany 5.6%, India 5.3%, Turkey 4.2%, Turkmenistan 4.1% (2005) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$8 billion in bilateral debt, mostly to Russia; Afghanistan has $500 million in debt to Multilateral Development Banks (2004) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
international pledges made by more than 60 countries and international financial institutions at the Berlin Donors Conference for Afghan reconstruction in March 2004 reached $8.9 billion for 2004-09 |
|
Currency (code):
|
afghani (AFA) |
|
Currency code:
|
AFA |
|
Exchange rates:
|
afghanis per US dollar - 46 (2006), 47.7 (2005), 48 (2004), 49 (2003), 41 (2002)
note: in 2002, the afghani was revalued and the currency stabilized at about 40 to 50 afghanis to the US dollar; before 2002, the market rate varied widely from the official rate |
|
Fiscal year:
|
21 March - 20 March |
| Communications | Afghanistan |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
280,000 (2005) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
1.4 million (2005) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: very limited telephone and telegraph service; many Afghans utilize growing cellular phone coverage in major cities
domestic: telephone service is improving with the licensing of several wireless telephone service providers in 2005 and 2006; approximately 4 in 100 Afghans own a wireless telephone; telephone main lines remain limited. international: country code - 93; five VSAT's installed in Kabul, Herat, Mazar-e-Sharif, Kandahar, and Jalalabad provide international and domestic voice and data connectivity |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 21, FM 5, shortwave 1 (broadcasts in Pashtu, Afghan Persian (Dari), Urdu, and English) (2006) |
|
Radios:
|
167,000 (1999) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
at least 7 (1 government-run central television station in Kabul and regional stations in 6 of the 34 provinces) (2006) |
|
Televisions:
|
100,000 (1999) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.af |
|
Internet hosts:
|
22 (2006) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
1 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
30,000 (2005) |
|
Communications - note:
|
in March 2003, 'af' was established as Afghanistan's domain name; Internet access is growing through Internet cafes as well as public "telekiosks" in Kabul (2005) |
| Transportation | Afghanistan |
|
Airports:
|
46 (2006) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 11
over 3,047 m: 3 2,438 to 3,047 m: 3 1,524 to 2,437 m: 3 914 to 1,523 m: 1 under 914 m: 1 (2006) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 35
over 3,047 m: 1 2,438 to 3,047 m: 5 1,524 to 2,437 m: 16 914 to 1,523 m: 4 under 914 m: 9 (2006) |
|
Heliports:
|
9 (2006) |
|
Pipelines:
|
gas 466 km (2006) |
|
Roadways:
|
total: 34,782 km
paved: 8,229 km unpaved: 26,553 km (2004) |
|
Waterways:
|
1,200 km (chiefly Amu Darya, which handles vessels up to 500 DWT) (2005) |
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Kheyrabad, Shir Khan |
| Military | Afghanistan |
|
Military branches:
|
Afghan National Army (includes Afghan Air Force) (2006) |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
22 years of age; inductees are contracted into service for a 4-year term (2005) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 22-49: 4,952,812
females age 22-49: 4,663,963 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 22-49: 2,662,946
females age 22-49: 2,508,574 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching military service age annually:
|
males age 18-49: 275,362
females age 22-49: 259,935 (2005 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$122.4 million (2005 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
1.9% (2006 est.) |
| Transnational Issues | Afghanistan |
|
Disputes - international:
|
Pakistan, with UN and other international assistance, repatriated 2.3 million Afghan refugees with less than a million still remaining, many at their own choosing; Pakistan has proposed and Afghanistan protests construction of a fence and laying of mines along portions of their border; Coalition and Pakistani forces continue to monitor remote tribal areas to control the border with Afghanistan and stem terrorist and other illegal activities |
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
IDPs: 136,565 (mostly Pashtuns and Kuchis displaced in south and west due to drought and instability) (2006) |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
world's largest producer of opium; cultivation dropped 48% to 107,400 hectares in 2005; better weather and lack of widespread disease returned opium yields to normal levels, meaning potential opium production declined by only 10% to 4,475 metric tons; if the entire poppy crop were processed, it is estimated that 526 metric tons of heroin could be processed; many narcotics-processing labs throughout the country; drug trade is a source of instability and some antigovernment groups profit from the trade; significant domestic use of opiates; 80-90% of the heroin consumed in Europe comes from Afghan opium; vulnerable to narcotics money laundering through informal financial networks; source of hashish |
|
This page was last updated on 8 March, 2007 |