

| The World Factbook | ||


|
Gaza Strip | |
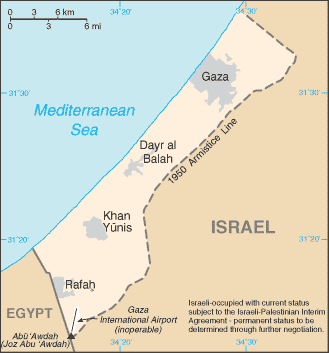
|
| Introduction | Gaza Strip |
|
Background:
|
The Israel-PLO Declaration of Principles on Interim Self-Government Arrangements (the DOP), signed in Washington on 13 September 1993, provided for a transitional period not exceeding five years of Palestinian interim self-government in the Gaza Strip and the West Bank. Under the DOP, Israel agreed to transfer certain powers and responsibilities to the Palestinian Authority (PA) as part of the interim self-governing arrangements in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. A transfer of powers and responsibilities for the Gaza Strip and Jericho took place pursuant to the Israel-PLO 4 May 1994 Cairo Agreement on the Gaza Strip and the Jericho Area and in additional areas of the West Bank pursuant to the Israel-PLO 28 September 1995 Interim Agreement, the Israel-PLO 15 January 1997 Protocol Concerning Redeployment in Hebron, the Israel-PLO 23 October 1998 Wye River Memorandum, and the 4 September 1999 Sharm el-Sheikh Agreement. The DOP provides that Israel will retain responsibility during the transitional period for external and internal security and for public order of settlements and Israeli citizens. Direct negotiations to determine the permanent status of Gaza and West Bank began in September 1999 after a three-year hiatus, but were derailed by a second intifadah that broke out in September 2000. In April 2003 the Quartet (US, EU, UN, and Russia) presented a roadmap to a final settlement of the conflict by 2005 based on reciprocal steps by the two parties leading to two states, Israel and a democratic Palestine. The proposed date for a permanent status agreement has been postponed indefinitely due to violence and accusations that both sides have not followed through on their commitments. Longtime Palestinian leader Yasir ARAFAT died in November 2004 and Mahmud ABBAS was elected PA president in January 2005, bringing hope of a turning point in the conflict. In February 2005 Israel and the PA agreed to the Sharm el-Sheikh Commitments, focused on security issues, in an effort to move the peace process forward. Progress has been slow because of different interpretations of the verbal agreement by the two sides. In September 2005, Israel withdrew all its settlers and soldiers and dismantled its military facilities in the Gaza Strip and four northern West Bank settlements. Nonetheless, Israel controls maritime, airspace, and most access to the Gaza Strip. An agreement signed by the PA and Israel in November 2005 authorized the reopening of the Rafah border crossing between the Gaza Strip and Egypt under joint PA and Egyptian control, with monitoring provided by the EU. |
| Geography | Gaza Strip |
|
Location:
|
Middle East, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Egypt and Israel |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
31 25 N, 34 20 E |
|
Map references:
|
Middle East |
|
Area:
|
total: 360 sq km
land: 360 sq km water: 0 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly more than twice the size of Washington, DC |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 62 km
border countries: Egypt 11 km, Israel 51 km |
|
Coastline:
|
40 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
Israeli-occupied with current status subject to the Israeli-Palestinian Interim Agreement - permanent status to be determined through further negotiation |
|
Climate:
|
temperate, mild winters, dry and warm to hot summers |
|
Terrain:
|
flat to rolling, sand- and dune-covered coastal plain |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Mediterranean Sea 0 m
highest point: Abu 'Awdah (Joz Abu 'Auda) 105 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
arable land, natural gas |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 29%
permanent crops: 21% other: 50% (2002) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
150 sq km; note - includes West Bank (2003) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
droughts |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
desertification; salination of fresh water; sewage treatment; water-borne disease; soil degradation; depletion and contamination of underground water resources |
|
Geography - note:
|
strategic strip of land along Mideast-North African trade routes has experienced an incredibly turbulent history; the town of Gaza itself has been besieged countless times in its history |
| People | Gaza Strip |
|
Population:
|
1,428,757 (July 2006 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 48.1% (male 351,642/female 335,060)
15-64 years: 49.4% (male 360,147/female 345,318) 65 years and over: 2.6% (male 15,231/female 21,359) (2006 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 15.8 years
male: 15.7 years female: 16 years (2006 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
3.71% (2006 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
39.45 births/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
3.8 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
1.48 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.04 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.71 male(s)/female total population: 1.04 male(s)/female (2006 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 22.4 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 23.48 deaths/1,000 live births female: 21.27 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 71.97 years
male: 70.67 years female: 73.34 years (2006 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
5.78 children born/woman (2006 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
NA |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
NA |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
NA |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: NA
adjective: NA |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Palestinian Arab and other 99.4%, Jewish 0.6% |
|
Religions:
|
Muslim (predominantly Sunni) 98.7%, Christian 0.7%, Jewish 0.6% |
|
Languages:
|
Arabic, Hebrew (spoken by many Palestinians), English (widely understood) |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 91.9% male: 96.3% female: 87.4% (2003 est.) |
| Government | Gaza Strip |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Gaza Strip local long form: none local short form: Qita Ghazzah |
| Economy | Gaza Strip |
|
Economy - overview:
|
High population density, limited land access, and strict internal and external controls have kept economic conditions in the Gaza Strip - the smaller of the two areas under the Palestinian Authority (PA)- even more degraded than in the West Bank. The beginning of the second intifadah in September 2000 sparked an economic downturn, largely the result of Israeli closure policies; these policies, which were imposed in response to security interests in Israel, disrupted labor and commodity relationships with the Gaza Strip. In 2001, and even more severely in 2003, Israeli military measures in PA areas resulted in the destruction of much capital plant, the disruption of administrative structure, and widespread business closures. Including the West Bank, the UN estimates that more than 100,000 Palestinians out of the 125,000 who used to work in Israel or in joint industrial zones have lost their jobs. Half the labor force is unemployed. Israeli withdrawal from the Gaza Strip in September 2005 offers some medium-term opportunities for economic growth, especially given the removal of restrictions on internal movement. In addition, recent agreements and continuing negotiations on the administration of Gaza's border crossings increase the prospects for trade. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$768 million (2003 est.) |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
NA |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
4.5% (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$600 (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 9%
industry: 28% services: 63% (includes West Bank) (2002 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
278,000 (April-June 2005) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: 11.9%
industry: 18% services: 70.1% (2005) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
31% (includes West Bank) (January-September 2005 avg.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
81% (2004 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%: NA% |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
3% (includes West Bank) (2004) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $964 million
expenditures: $1.34 billion; including capital expenditures of $NA; note - these budget data include West Bank (2004) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
olives, citrus, vegetables; beef, dairy products |
|
Industries:
|
generally small family businesses that produce textiles, soap, olive-wood carvings, and mother-of-pearl souvenirs; the Israelis have established some small-scale modern industries in an industrial center, but operations ceased prior to Israel's evacuation of Gaza Strip settlements |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
NA% |
|
Electricity - production:
|
NA kWh; note - electricity supplied by the Gaza Strip power plant and by an Israeli utility |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
NA kWh |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
NA kWh; note - some electricity supplied by an Israeli utility (2005) |
|
Exports:
|
$270 million f.o.b.; note - includes West Bank (2003) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
citrus, flowers, textiles |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Israel, Egypt, West Bank (2004) |
|
Imports:
|
$1.952 billion c.i.f.; note - includes West Bank (2003) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
food, consumer goods, construction materials |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Israel, Egypt, West Bank (2004) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$0; note - includes West Bank (2002) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$2 billion; note - includes West Bank (2004 est.) |
|
Currency (code):
|
new Israeli shekel (ILS) |
|
Currency code:
|
ILS |
|
Exchange rates:
|
new Israeli shekels per US dollar - 4.4877 (2005), 4.482 (2004), 4.5541 (2003), 4.7378 (2002), 4.2057 (2001) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year |
| Communications | Gaza Strip |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
357,300 (total for Gaza Strip and West Bank) (2004) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
974,300 (cellular subscribers in both Gaza Strip and West Bank) (2004) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: NA
domestic: Israeli company BEZEK and the Palestinian company PALTEL are responsible for fixed line services in the Gaza Strip; the Palestinian JAWAL company provides cellular services international: country code - 970 |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 0, FM 8, shortwave 0 (2005) |
|
Radios:
|
NA; note - most Palestinian households have radios (1999) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
1 (2005) |
|
Televisions:
|
NA; note - most Palestinian households have televisions (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.ps |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
3 (1999) |
|
Internet users:
|
160,000 (includes West Bank) (2004) |
| Transportation | Gaza Strip |
|
Airports:
|
2 (2001)
note: includes Gaza International Airport (GIA), inaugurated on 24 November 1998 as part of agreements stipulated in the September 1995 Oslo II Accord and the 23 October 1998 Wye River Memorandum; GIA has been largely closed since October 2000 by Israeli orders and its runway was destroyed by the Israeli Defense Forces in December 2001 (2005) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 1
over 3,047 m: 1 (2005) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 1
under 914 m: 1 (2005) |
|
Heliports:
|
1 (2005) |
|
Roadways:
|
note: see entry for West Bank |
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Gaza |
| Military | Gaza Strip |
|
Military branches:
|
in accordance with the peace agreement, the Palestinian Authority is not permitted conventional military forces; there are, however, public security forces (2002) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 18-49: 260,855 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 18-49: 221,530 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching military service age annually:
|
males age 18-49: 15,196 (2005 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
NA |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
NA |
| Transnational Issues | Gaza Strip |
|
Disputes - international:
|
West Bank and Gaza Strip are Israeli-occupied with current status subject to the Israeli-Palestinian Interim Agreement - permanent status to be determined through further negotiation; Israel removed settlers and military personnel from the Gaza Strip in August 2005 |
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
refugees (country of origin): 986,034 (Palestinian Refugees (UNRWA)) (2005) |
|
This page was last updated on 16 May, 2006 |