


| The World Factbook | ||


|
United Arab Emirates |

|
|
| Introduction | United Arab Emirates |
|
Background:
|
The Trucial States of the Persian Gulf coast granted the UK control of their defense and foreign affairs in 19th century treaties. In 1971, six of these states - Abu Zaby, 'Ajman, Al Fujayrah, Ash Shariqah, Dubayy, and Umm al Qaywayn - merged to form the United Arab Emirates (UAE). They were joined in 1972 by Ra's al Khaymah. The UAE's per capita GDP is on par with those of leading West European nations. Its generosity with oil revenues and its moderate foreign policy stance have allowed the UAE to play a vital role in the affairs of the region. |
| Geography | United Arab Emirates |
|
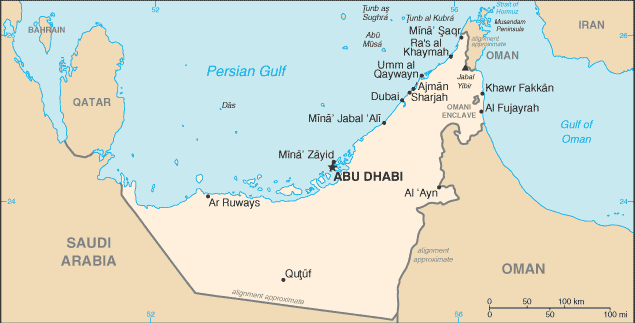
Location:
|
Middle East, bordering the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf, between Oman and Saudi Arabia |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
24 00 N, 54 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Middle East |
|
Area:
|
total: 82,880 sq km
land: 82,880 sq km water: 0 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly smaller than Maine |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 867 km
border countries: Oman 410 km, Saudi Arabia 457 km |
|
Coastline:
|
1,318 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm exclusive economic zone: 200 nm continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin |
|
Climate:
|
desert; cooler in eastern mountains |
|
Terrain:
|
flat, barren coastal plain merging into rolling sand dunes of vast desert wasteland; mountains in east |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Persian Gulf 0 m
highest point: Jabal Yibir 1,527 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
petroleum, natural gas |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 0.77%
permanent crops: 2.27% other: 96.96% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
760 sq km (2003) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
frequent sand and dust storms |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
lack of natural freshwater resources compensated by desalination plants; desertification; beach pollution from oil spills |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea |
|
Geography - note:
|
strategic location along southern approaches to Strait of Hormuz, a vital transit point for world crude oil |
| People | United Arab Emirates |
|
Population:
|
2,602,713 (July 2006 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 24.9% (male 331,012/female 317,643)
15-64 years: 71.2% (male 1,125,286/female 726,689) 65 years and over: 3.9% (male 74,700/female 27,383) (2006 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 28.1 years
male: 34.8 years female: 23.3 years (2006 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
1.52% (2006 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
18.96 births/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
4.4 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
0.66 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.55 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 2.73 male(s)/female total population: 1.43 male(s)/female (2006 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 14.09 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 16.57 deaths/1,000 live births female: 11.48 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 75.44 years
male: 72.92 years female: 78.08 years (2006 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
2.88 children born/woman (2006 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
0.18% (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
NA |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
NA |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Emirati(s)
adjective: Emirati |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Emirati 19%, other Arab and Iranian 23%, South Asian 50%, other expatriates (includes Westerners and East Asians) 8% (1982)
note: less than 20% are UAE citizens (1982) |
|
Religions:
|
Muslim 96% (Shi'a 16%), Christian, Hindu, and other 4% |
|
Languages:
|
Arabic (official), Persian, English, Hindi, Urdu |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 77.9% male: 76.1% female: 81.7% (2003 est.) |
| Government | United Arab Emirates |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: United Arab Emirates
conventional short form: none local long form: Al Imarat al Arabiyah al Muttahidah local short form: none former: Trucial Oman, Trucial States abbreviation: UAE |
|
Government type:
|
federation with specified powers delegated to the UAE federal government and other powers reserved to member emirates |
|
Capital:
|
Abu Dhabi |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
7 emirates (imarat, singular - imarah); Abu Zaby (Abu Dhabi), 'Ajman, Al Fujayrah, Ash Shariqah (Sharjah), Dubayy (Dubai), Ra's al Khaymah, Umm al Qaywayn (Quwayn) |
|
Independence:
|
2 December 1971 (from UK) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 2 December (1971) |
|
Constitution:
|
2 December 1971; made permanent in 1996 |
|
Legal system:
|
federal court system introduced in 1971; applies to all emirates except Dubayy (Dubai) and Ra's al Khaymah, which are not fully integrated into the federal judicial system; all emirates have secular courts to adjudicate criminal, civil, and commercial matters and Islamic courts to review family and religious disputes |
|
Suffrage:
|
none |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President KHALIFA bin Zayid al-Nuhayyan (since 3 November 2004), ruler of Abu Zaby (Abu Dhabi) (since 4 November 2004); Vice President and Prime Minister MUHAMMAD bin Rashid al-Maktum (since 5 January 2006)
head of government: Prime Minister and Vice President MUHAMMAD bin Rashid al-Maktum (since 5 January 2006); Deputy Prime Minister SULTAN bin Zayid al-Nuhayyan (since 20 November 1990); Deputy Prime Minister HAMDAN bin Zayid al-Nuhayyan (since 20 October 2003) cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president note: there is also a Federal Supreme Council (FSC) composed of the seven emirate rulers; the FSC is the highest constitutional authority in the UAE; establishes general policies and sanctions federal legislation; meets four times a year; Abu Zaby (Abu Dhabi) and Dubayy (Dubai) rulers have effective veto power elections: president and vice president elected by the FSC for five-year terms; election last held 3 November 2004 upon the death of the UAE's Founding Father and first President ZAYID bin Sultan Al Nuhayyan (next to be held 2009); prime minister and deputy prime minister appointed by the president election results: KHALIFA bin Zayid al-Nuhayyan elected president by a unanimous vote of the FSC; MUHAMMAD bin Rashid al-Maktum unanimously reaffirmed vice president |
|
Legislative branch:
|
unicameral Federal National Council (FNC) or Majlis al-Ittihad al-Watani (40 seats; members appointed by the rulers of the constituent states to serve two-year terms)
elections: President KHALIFA in December 2005 announced that indirect elections would be held in early 2006 for half of the seats in the FNC; the other half would be filled by appointment note: reviews legislation, but cannot change or veto |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Union Supreme Court (judges are appointed by the president) |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
none |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
NA |
|
International organization participation:
|
ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, FAO, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt (signatory), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAPEC, OIC, OPCW, OPEC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Asri Said Ahmad al-DHAHIRI
chancery: 3522 International Court NW, Suite 400, Washington, DC 20008 telephone: [1] (202) 243-2400 FAX: [1] (202) 243-2432 consulate(s): New York, Houston |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Michele J. SISON
embassy: Embassies District, Plot 38 Sector W59-02, Street No. 4, Abu Dhabi mailing address: P. O. Box 4009, Abu Dhabi telephone: [971] (2) 414-2200 FAX: [971] (2) 414-2469 consulate(s) general: Dubai |
|
Flag description:
|
three equal horizontal bands of green (top), white, and black with a wider vertical red band on the hoist side |
| Economy | United Arab Emirates |
|
Economy - overview:
|
The UAE has an open economy with a high per capita income and a sizable annual trade surplus. Its wealth is based on oil and gas output (about 30% of GDP), and the fortunes of the economy fluctuate with the prices of those commodities. Since the discovery of oil in the UAE more than 30 years ago, the UAE has undergone a profound transformation from an impoverished region of small desert principalities to a modern state with a high standard of living. At present levels of production, oil and gas reserves should last for more than 100 years. The government has increased spending on job creation and infrastructure expansion and is opening up its utilities to greater private sector involvement. Higher oil revenue, strong liquidity, and cheap credit in 2005 led to a surge in asset prices (shares and real estate) and consumer inflation. Any sharp correction to the UAE's equity markets could damage investor and consumer sentiment and affect bank asset quality. In April 2004, the UAE signed a Trade and Investment Framework Agreement (TIFA) with Washington and in November 2004 agreed to undertake negotiations toward a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the US. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$74.67 billion (2005 est.) |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$101.6 billion (2005 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
6.7% (2005 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$29,100 (2005 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 4%
industry: 58.5% services: 37.5% (2002 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
2.8 million
note: 73.9% of the population in the 15-64 age group is non-national (2005 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: 7%
industry: 15% services: 78% (2000 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
2.4% (2001) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
NA% |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%: NA% |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
4.5% (2005 est.) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
20.7% of GDP (2005 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $34.93 billion
expenditures: $29.41 billion; including capital expenditures of $3.4 billion (2005 est.) |
|
Public debt:
|
17.5% of GDP (2005 est.) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
dates, vegetables, watermelons; poultry, eggs, dairy products; fish |
|
Industries:
|
petroleum and petrochemicals; fishing, aluminum, cement, fertilizers, commercial ship repair, construction materials, some boat building, handicrafts, textiles |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
4% (2000) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
45.12 billion kWh (2004) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 100%
hydro: 0% nuclear: 0% other: 0% (2001) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
38.32 billion kWh (2002) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2004) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2004) |
|
Oil - production:
|
2.396 million bbl/day (2005 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
310,000 bbl/day (2004 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
2.5 million bbl/day (2004 est.) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
0 bbl/day (2004) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
97.8 billion bbl (2005 est.) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
44.79 billion cu m (2003 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
37.88 billion cu m (2003 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
7.19 billion cu m (2003 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2003 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
6.006 trillion cu m (2005) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$25.66 billion (2005 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$103.1 billion f.o.b. (2005 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
crude oil 45%, natural gas, reexports, dried fish, dates |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Japan 24.9%, South Korea 9.9%, India 5.4%, Thailand 5% (2004) |
|
Imports:
|
$60.15 billion f.o.b. (2005 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
machinery and transport equipment, chemicals, food |
|
Imports - partners:
|
China 9.9%, India 9.8%, Japan 6.8%, Germany 6.5%, UK 6.2%, France 6.1%, US 6% (2004) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$23.53 billion (2005 est.) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$30.21 billion (2005 est.) |
|
Economic aid - donor:
|
since its founding in 1971, the Abu Dhabi Fund for Development has given about $5.2 billion in aid to 56 countries (2004) |
|
Currency (code):
|
Emirati dirham (AED) |
|
Currency code:
|
AED |
|
Exchange rates:
|
Emirati dirhams per US dollar - 3.6725 (2005), 3.6725 (2004), 3.6725 (2003), 3.6725 (2002), 3.6725 (2001)
note: officially pegged to the US dollar since February 2002 |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year |
| Communications | United Arab Emirates |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
1,187,700 (2004) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
3,683,100 (2004) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: modern fiber-optic integrated services; digital network with rapidly growing use of mobile cellular telephones; key centers are Abu Dhabi and Dubai
domestic: microwave radio relay, fiber optic and coaxial cable international: country code - 971; satellite earth stations - 3 Intelsat (1 Atlantic Ocean and 2 Indian Ocean) and 1 Arabsat; submarine cables to Qatar, Bahrain, India, and Pakistan; tropospheric scatter to Bahrain; microwave radio relay to Saudi Arabia |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 13, FM 8, shortwave 2 (2004) |
|
Radios:
|
820,000 (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
15 (2004) |
|
Televisions:
|
310,000 (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.ae |
|
Internet hosts:
|
118,495 (2005) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
1 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
1,384,800 (2005) |
| Transportation | United Arab Emirates |
|
Airports:
|
35 (2005) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 22
over 3,047 m: 9 2,438 to 3,047 m: 2 1,524 to 2,437 m: 4 914 to 1,523 m: 4 under 914 m: 3 (2005) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 13
over 3,047 m: 1 2,438 to 3,047 m: 2 1,524 to 2,437 m: 3 914 to 1,523 m: 3 under 914 m: 4 (2005) |
|
Heliports:
|
2 (2005) |
|
Pipelines:
|
condensate 469 km; gas 2,655 km; liquid petroleum gas 300 km; oil 2,936 km; oil/gas/water 5 km (2004) |
|
Roadways:
|
total: 1,088 km
paved: 1,088 km (including 253 km of expressways) (1999) |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 56 ships (1000 GRT or over) 621,292 GRT/833,840 DWT
by type: bulk carrier 4, cargo 11, chemical tanker 5, container 6, liquefied gas 1, passenger/cargo 3, petroleum tanker 19, roll on/roll off 6, specialized tanker 1 foreign-owned: 10 (Greece 2, Kuwait 8) registered in other countries: 234 (The Bahamas 14, Barbados 1, Belize 3, Cambodia 2, Cyprus 11, Dominica 3, Georgia 1, Hong Kong 1, India 7, Iran 1, Jamaica 3, Jordan 12, North Korea 7, Liberia 15, Libya 1, Malta 5, Marshall Islands 2, Mexico 1, Mongolia 3, Panama 89, Philippines 2, Qatar 1, Saint Kitts and Nevis 20, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 12, Saudi Arabia 1, Sierra Leone 1, Singapore 7, Sri Lanka 2, unknown 6) (2005) |
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Al Fujayrah, Khawr Fakkan, Mina' Jabal 'Ali, Mina' Rashid, Mina' Saqr, Mina' Zayid, Sharjan |
| Military | United Arab Emirates |
|
Military branches:
|
Army, Navy (includes Marines and Coast Guard), Air and Air Defense Force, paramilitary forces (includes Federal Police Force) |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
18 years of age (est.); no conscription (2001) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 18-49: 653,181
females age 18-49: 497,394 (includes non-nationals; 2005 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 18-49: 526,671
females age 18-49: 419,975 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching military service age annually:
|
males: 30,706
females age 18-49: 29,617 (2005 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$1.6 billion (FY00) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
3.1% (FY00) |
| Transnational Issues | United Arab Emirates |
|
Disputes - international:
|
the United Arab Emirate 2006 Yearbook published a map and text rescinding the 1974 boundary with Saudi Arabia, as stipulated in a treaty filed with the UN in 1993, on the grounds that the agreement was not formally ratified; boundary agreement was signed and ratified with Oman in 2003 for entire border, including Oman's Musandam Peninsula and Al Madhah enclaves, but contents of the agreement and maps showing the alignment have not been published; Iran and UAE dispute Tunb Islands and Abu Musa Island, which Iran occupies |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
the UAE is a drug transshipment point for traffickers given its proximity to Southwest Asian drug producing countries; the UAE's position as a major financial center makes it vulnerable to money laundering; anti-money-laundering controls improving, but informal banking remains unregulated |
|
This page was last updated on 16 May, 2006 |