


| The World Factbook | ||


|
Cyprus |

|
|
| Introduction | Cyprus |
|
Background:
|
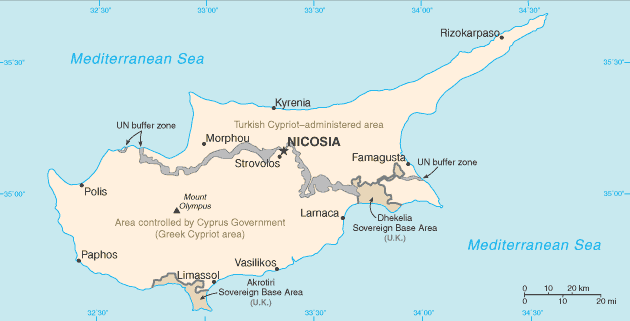
Independence from the UK was approved in 1960, with constitutional guarantees by the Greek Cypriot majority to the Turkish Cypriot minority. In 1974, a Greek-sponsored attempt to seize the government was met by military intervention from Turkey, which soon controlled almost 40% of the island. In 1983, the Turkish-held area declared itself the "Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus," but it is recognized only by Turkey. UN-led direct talks between the two sides to reach a comprehensive settlement to the division of the island began in January 2002 and will reach a culmination when a referendum of all Cypriots is held on 21 April 2004, just 10 days before the Greek part of Cyprus is scheduled to join the EU. |
| Geography | Cyprus |
|
Location:
|
Middle East, island in the Mediterranean Sea, south of Turkey |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
35 00 N, 33 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Middle East |
|
Area:
|
total: 9,250 sq km (of which 3,355 sq km are in the Turkish Cypriot area)
water: 10 sq km land: 9,240 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
about 0.6 times the size of Connecticut |
|
Land boundaries:
|
0 km |
|
Coastline:
|
648 km |
|
Maritime claims - as described in UNCLOS 1982 (see Notes and Definitions):
|
territorial sea: 12 NM
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation |
|
Climate:
|
temperate; Mediterranean with hot, dry summers and cool winters |
|
Terrain:
|
central plain with mountains to north and south; scattered but significant plains along southern coast |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Mediterranean Sea 0 m
highest point: Olympus 1,951 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
copper, pyrites, asbestos, gypsum, timber, salt, marble, clay earth pigment |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 14.4%
permanent crops: 4.5% other: 81.1% (2001 est.) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
382 sq km (2001 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
moderate earthquake activity; droughts |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
water resource problems (no natural reservoir catchments, seasonal disparity in rainfall, sea water intrusion to island's largest aquifer, increased salination in the north); water pollution from sewage and industrial wastes; coastal degradation; loss of wildlife habitats from urbanization |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution
signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants |
|
Geography - note:
|
the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea (after Sicily and Sardinia) |
| People | Cyprus |
|
Population:
|
775,927 (July 2004 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 21.4% (male 84,850; female 81,235)
15-64 years: 67.4% (male 264,441; female 258,150) 65 years and over: 11.2% (male 38,058; female 49,193) (2004 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 34.4 years
male: 33.4 years female: 35.5 years (2004 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
0.55% (2004 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
12.66 births/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
7.63 deaths/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
0.43 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/female total population: 1 male(s)/female (2004 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 7.36 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 5.44 deaths/1,000 live births (2004 est.) male: 9.19 deaths/1,000 live births |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 77.46 years
male: 75.11 years female: 79.92 years (2004 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
1.85 children born/woman (2004 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
0.1% (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
less than 1,000 (1999 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
NA |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Cypriot(s)
adjective: Cypriot |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Greek 77%, Turkish 18%, other 5% (2001) |
|
Religions:
|
Greek Orthodox 78%, Muslim 18%, Maronite, Armenian Apostolic, and other 4% |
|
Languages:
|
Greek, Turkish, English |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 97.6% male: 98.9% female: 96.3% (2003 est.) |
| Government | Cyprus |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Republic of Cyprus
conventional short form: Cyprus note: the Turkish Cypriot area refers to itself as the "Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus" (TRNC) |
|
Government type:
|
republic
note: a disaggregation of the two ethnic communities inhabiting the island began following the outbreak of communal strife in 1963; this separation was further solidified after the Turkish intervention in July 1974 after a Greek junta-based coup attempt gave the Turkish Cypriots de facto control in the north; Greek Cypriots control the only internationally recognized government; on 15 November 1983 Turkish Cypriot "President" Rauf DENKTASH declared independence and the formation of a "Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus" (TRNC), recognized only by Turkey; both sides publicly support a settlement based on a federation (Greek Cypriot position) or confederation (Turkish Cypriot position) |
|
Capital:
|
Nicosia |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
6 districts; Famagusta, Kyrenia, Larnaca, Limassol, Nicosia, Paphos; note - Turkish Cypriot area's administrative divisions include Kyrenia, all but a small part of Famagusta, and small parts of Lefkosia (Nicosia) and Larnaca |
|
Independence:
|
16 August 1960 (from UK); note - Turkish Cypriot area proclaimed self-rule on 13 February 1975 |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 1 October (1960); note - Turkish Cypriot area celebrates 15 November (1983) as Independence Day |
|
Constitution:
|
16 August 1960; negotiations to create the basis for a new or revised constitution to govern the island and to better relations between Greek and Turkish Cypriots have been held intermittently; in 1975 Turkish Cypriots created their own constitution and governing bodies within the "Turkish Federated State of Cyprus," which was renamed the "Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus" in 1983; a new constitution for the Turkish Cypriot area passed by referendum on 5 May 1985 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on common law, with civil law modifications |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Tassos PAPADOPOULOS (since 1 March 2003); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government; post of vice president is currently vacant; under the 1960 constitution, the post is reserved for a Turkish Cypriot
head of government: President Tassos PAPADOPOULOS (since 1 March 2003); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government; post of vice president is currently vacant; under the 1960 constitution, the post is reserved for a Turkish Cypriot cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed jointly by the president and vice president elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term; election last held 16 February 2003 (next to be held NA February 2008) note: Rauf R. DENKTASH has been "president" of the Turkish Cypriot area since 13 February 1975 ("president" elected by popular vote for a five-year term); elections last held 15 April 2000 (next to be held NA April 2005); results - Rauf R. DENKTASH reelected president after the other contender withdrew; Mehmet Ali TALAT has been "prime minister" of the Turkish Cypriot area since mid-January 2004; there is a Council of Ministers (cabinet) in the Turkish Cypriot area election results: Tassos PAPADOPOULOS elected president; percent of vote - Tassos PAPADOPOULOS 51.5%, Glafkos KLIRIDIS 38.8%, Alekos MARKIDIS 6.6% |
|
Legislative branch:
|
unicameral - Greek Cypriot area: House of Representatives or Vouli Antiprosopon (80 seats; 56 assigned to the Greek Cypriots, 24 to Turkish Cypriots; note - only those assigned to Greek Cypriots are filled; members are elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms); Turkish Cypriot area: Assembly of the Republic or Cumhuriyet Meclisi (50 seats; members are elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
election results: Greek Cypriot area: House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - AKEL 34.71%, DISY 34%, DIKO 14.84%, KISOS 6.51%, others 9.94%; seats by party - AKEL (Communist) 20, DISY 19, DIKO 9, KISOS 4, others 4; Turkish Cypriot area: Assembly of the Republic - percent of vote by party - CTP 35.8%, UBP 32.3%, Peace and Democratic Movement 13.4%, DP 12.3%; seats by party - CTP 19, UBP 18, Peace and Democratic Movement 6, DP 7 elections: Greek Cypriot area: last held 27 May 2001 (next to be held NA May 2006); Turkish Cypriot area: last held 14 December 2003 (next to be held NA December 2008) |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court (judges are appointed jointly by the president and vice president)
note: there is also a Supreme Court in the Turkish Cypriot area |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Greek Cypriot area: Democratic Party or DIKO [Tassos PAPADOPOULOS]; Democratic Rally or DISY [Nikos ANASTASIADHIS]; Fighting Democratic Movement or ADIK [Dinos MIKHAILIDIS]; Green Party of Cyprus [George PERDIKIS]; New Horizons [Nikolaus KOUTSOU]; Restorative Party of the Working People or AKEL (Communist Party) [Dimitrios CHRISTOFIAS]; Social Democrats Movement or KISOS (formerly United Democratic Union of Cyprus or EDEK) [Yiannakis OMIROU]; United Democrats Movement or EDE [George VASSILIOU]; Turkish Cypriot area: Democratic Party or DP [Serder DENKTASH]; National Birth Party or UDP [Enver EMIN]; National Unity Party or UBP [Dervis EROGLU]; Our Party or BP [Okyay SADIKOGLU]; Patriotic Unity Movement or YBH [Alpay DURDURAN]; Peace and Democratic Movement [Mustafa AKINCI]; Republican Turkish Party or CTP [Mehmet ALI TALAT] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
Confederation of Cypriot Workers or SEK (pro-West); Confederation of Revolutionary Labor Unions or Dev-Is; Federation of Turkish Cypriot Labor Unions or Turk-Sen; Pan-Cyprian Labor Federation or PEO (Communist controlled) |
|
International organization participation:
|
Australia Group, C, CE, EBRD, EU (new member), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICFTU, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITU, NAM, NSG, OAS (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UPU, WCL, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTrO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Euripides L. EVRIVIADES
chancery: 2211 R Street NW, Washington, DC 20008 FAX: [1] (202) 483-6710 note: representative of the Turkish Cypriot area in the US is Ahmet ERDENGIZ; office at 1667 K Street NW, Washington, DC; telephone [1] (202) 887-6198 consulate(s): New York consulate(s) general: New York telephone: [1] (202) 462-5772 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Michael KLOSSON
embassy: corner of Metochiou and Ploutarchou Streets, Engomi, 2407 Nicosia mailing address: P. O. Box 24536, 1385 Nikosia telephone: [357] (22) 776400 FAX: [357] (22) 780944 |
|
Flag description:
|
white with a copper-colored silhouette of the island (the name Cyprus is derived from the Greek word for copper) above two green crossed olive branches in the center of the flag; the branches symbolize the hope for peace and reconciliation between the Greek and Turkish communities
note: the Turkish Cypriot flag has a horizontal red stripe at the top and bottom between which is a red crescent and red star on a white field |
| Economy | Cyprus |
|
Economy - overview:
|
The Greek Cypriot economy is prosperous but highly susceptible to external shocks. Erratic growth rates over the past decade reflect the economy's vulnerability to swings in tourist arrivals, caused by political instability in the region and fluctuations in economic conditions in Western Europe. Economic policy is focused on meeting the criteria for admission to the EU. EU-driven tax reforms in 2003 have introduced fiscal imbalances, which, coupled with a sluggish tourism sector, have resulted in growing fiscal deficits. As in the Turkish sector, water shortages are a perennial problem; a few desalination plants are now on-line. After 10 years of drought, the country received substantial rainfall from 2001-03, alleviating immediate concerns. The Turkish Cypriot economy has roughly one-third of the per capita GDP of the south. Because it is recognized only by Turkey, it has had much difficulty arranging foreign financing and investment. It remains heavily dependent on agriculture and government service, which together employ about half of the work force. To compensate for the economy's weakness, Turkey provides grants and loans to support economic development. Ankara provided $200 million in 2002 and pledged $450 million for the 2003-05 period. Future events throughout the island will be highly influenced by the outcome of negotiations on the UN-sponsored agreement to unite the Greek and Turkish areas. |
|
GDP:
|
Greek Cypriot area: purchasing power parity - $8.9 billion (2003 est.); Turkish Cypriot area: purchasing power parity - $1.217 billion (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
Greek Cypriot area: 1.6% (2003 est.); Turkish Cypriot area: 2.6% (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
Greek Cypriot area: purchasing power parity - $16,000 (2003 est.); Turkish Cypriot area: purchasing power parity - $5,600 (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
Greek Cypriot area: agriculture 4.9%; industry 19.9%; services 75.6%
Turkish Cypriot area: agriculture 10.6%; industry 20.5%; services 68.9% (2003) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
NA% |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%: NA% |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
Greek Cypriot area: 4% (2003 est.); Turkish Cypriot area: 12.6% (2003 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
Greek Cypriot area: 306,000; Turkish Cypriot area: 95,025 (2000) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
Greek Cypriot area: services 75.6%, industry 19.4%, agriculture 4.9% (2003); Turkish Cypriot area: services 68.9%, industry 20.5%, agriculture 10.6% (2003) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
Greek Cypriot area: 3.4%; Turkish Cypriot area: 5.6% (2003 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: Greek Cypriot area - $4.4 billion, Turkish Cypriot area - $231.3 million (2002 est.)
expenditures: Greek Cypriot area - $539 million, including capital expenditures of $539 million, Turkish Cypriot area - $432.8 million, including capital expenditures of NA (2003 est.) |
|
Industries:
|
food, beverages, textiles, chemicals, metal products, tourism, wood products |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
Greek Cypriot area: -1.4% (2002); Turkish Cypriot area: -0.3% (2002) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
3.401 billion kWh; Turkish Cypriot area: NA kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 100%
other: 0% (2001) hydro: 0% nuclear: 0% |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
Greek Cypriot area: 3.163 billion kWh; Turkish Cypriot area: NA kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
0 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
49,000 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
NA |
|
Oil - imports:
|
NA |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
potatoes, citrus, vegetables, barley, grapes, olives, vegetables, poultry, pork, lamb, kids, dairy |
|
Exports:
|
Greek Cypriot area: $1.054 billion f.o.b. Turkish Cypriot area: $46 million f.o.b. (2003 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
Greek Cypriot area: citrus, potatoes, pharmaceuticals, cement, clothing and cigarettes; Turkish Cypriot area: citrus, potatoes, textiles |
|
Exports - partners:
|
UK 26.7%, Greece 6.6%, France 4.9%, Poland 4.3% (2002) |
|
Imports:
|
Greek Cypriot area: $4.637 billion f.o.b.; Turkish Cypriot area: $301 million f.o.b. (2003 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
Greek Cypriot area: consumer goods, petroleum and lubricants, intermediate goods, machinery, transport equipment; Turkish Cypriot area: food, minerals, chemicals, machinery |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Russia 17.1%, Greece 7.1%, Germany 6.6%, France 6.4%, UK 6.3%, Italy 6.3%, South Korea 5.4%, Japan 5.1% (2002) |
|
Debt - external:
|
Greek Cypriot area: $8 billion; Turkish Cypriot area: $NA (2002) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
Greek Cypriot area - $17 million (1998); Turkish Cypriot area - $700 million from Turkey in grants and loans (1990-97), which are usually forgiven (1998) |
|
Currency:
|
Greek Cypriot area: Cypriot pound (CYP); Turkish Cypriot area: Turkish lira (TRL) |
|
Currency code:
|
CYP; TRL |
|
Exchange rates:
|
Cypriot pounds per US dollar - 0.52 (2003), 0.61 (2002), 0.64 (2001), 0.62 (2000), 0.54 (1999), Turkish lira per US dollar 1.505 million (2003), 1.507 million (2002), 1,225,590 (2001), 625,218 (2000), 418,783 (1999) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year |
| Communications | Cyprus |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
Greek Cypriot area: 405,000 (1998); Turkish Cypriot area: 83,162 (1998) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
Greek Cypriot area: 68,000 (1998); Turkish Cypriot area: 70,000 (1999) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: excellent in both the Greek Cypriot and Turkish Cypriot areas
domestic: open-wire, fiber-optic cable, and microwave radio relay international: country code - 357; tropospheric scatter; 3 coaxial and 5 fiber-optic submarine cables; satellite earth stations - 3 Intelsat (1 Atlantic Ocean and 2 Indian Ocean), 2 Eutelsat, 2 Intersputnik, and 1 Arabsat |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
Greek Cypriot area: AM 7, FM 60, shortwave 1 (1998); Turkish Cypriot area: AM 3, FM 11, shortwave 1 (1998) |
|
Radios:
|
Greek Cypriot area: 310,000 (1997); Turkish Cypriot area: 56,450 (1994) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
Greek Cypriot area: 4 (plus 225 low-power repeaters) (September 1995);; Turkish Cypriot area: 4 (plus 5 repeaters) (September 1995) |
|
Televisions:
|
Greek Cypriot area: 248,000 (1997); Turkish Cypriot area: 52,300 (1994) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.cy |
|
Internet hosts:
|
2,692 (2002) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
6 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
210,000 (2002) |
| Transportation | Cyprus |
|
Railways:
|
0 km |
|
Highways:
|
total: 13,491 km
note: Greek Cypriot area: 11,141 km; Turkish Cypriot area: 2,350 km unpaved: Greek Cypriot area: 4,713 km; Turkish Cypriot area: 980 km (2000/1996) paved: Greek Cypriot area: 6,428 km; Turkish Cypriot area: 1,370 km |
|
Waterways:
|
none |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Famagusta, Kyrenia, Larnaca, Limassol, Paphos, Vasilikos |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 1,066 ships (1,000 GRT or over) 22,016,374 GRT/35,760,004 DWT
registered in other countries: 100 (2003 est.) by type: bulk 403, cargo 276, chemical tanker 28, combination bulk 21, combination ore/oil 2, container 145, liquefied gas 1, multi-functional large load carrier 2, passenger 8, passenger/cargo 1, petroleum tanker 109, refrigerated cargo 30, roll on/roll off 29, short-sea/passenger 5, specialized tanker 3, vehicle carrier 3 foreign-owned: Austria 11, Belgium 1, Bulgaria 1, Canada 6, China 13, Croatia 2, Cuba 8, Egypt 2, Estonia 2, Germany 210, Greece 499, Guam 1, Hong Kong 5, India 6, Iran 3, Ireland 1, Israel 3, Italy 2, Japan 20, South Korea 6, Latvia 11, Malta 1, Mexico 1, Monaco 3, Netherlands 18, Norway 7, Panama 1, Philippines 2, Poland 20, Portugal 2, Russia 51, Singapore 2, Slovenia 4, Spain 5, Sudan 2, Sweden 6, Switzerland 1, Ukraine 2, United Kingdom 16, United States 4, Vietnam 1 |
|
Airports:
|
17 (2003 est.) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 13
2,438 to 3,047 m: 7 1,524 to 2,437 m: 2 under 914 m: 1 (2003 est.) 914 to 1,523 m: 3 |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 2 under 914 m: 2 (2003 est.) |
|
Heliports:
|
10 (2003 est.) |
| Military | Cyprus |
|
Military branches:
|
Greek Cypriot area: Greek Cypriot National Guard (GCNG; including air and naval elements), Greek Cypriot Police
Turkish Cypriot area: Turkish Cypriot Security Force (GKK) |
|
Military manpower - military age:
|
18 years of age (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - availability:
|
males age 15-49: 202,966 (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - fit for military service:
|
males age 15-49: 139,255 (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - reaching military age annually:
|
males: 6,614 (2004 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$384 million (FY02) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
3.8% (FY02) |
| Transnational Issues | Cyprus |
|
Disputes - international:
|
hostilities in 1974 divided the island into two de facto autonomous areas, a Greek Cypriot area controlled by the internationally recognized Cypriot Government and a Turkish-Cypriot area, separated by a UN buffer zone; March 2003 reunification talks failed, but Turkish-Cypriots later opened their borders to temporary visits by Greek Cypriots; a UN-brokered peace plan attempts to break the stalemate over final status before the Greek Cypriot area enters the EU in May 2004 |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
minor transit point for heroin and hashish via air routes and container traffic to Europe, especially from Lebanon and Turkey; some cocaine transits as well; despite a strengthening of anti-money laundering legislation, remains highly vulnerable to money laundering; identification of benefiting owners and reporting of suspicious transactions by nonresident-controlled companies in offshore sector remains weak |
|
This page was last updated on 11 May, 2004 |