Legend:
 Definition Definition
 Field Listing Field Listing
 Rank Order Rank Order
|
Background:
|


Following a five-year struggle, Communist Khmer Rouge forces captured Phnom Penh in April 1975 and ordered the evacuation of all cities and towns; over 1.5 million displaced people died from execution, enforced hardships, or starvation. A 1978 Vietnamese invasion drove the Khmer Rouge into the countryside and touched off almost 13 years of civil war. The 1991 Paris Peace Accords mandated democratic elections and a ceasefire, which was not fully respected by the Khmer Rouge. UN-sponsored elections in 1993 helped restore some semblance of normalcy and the final elements of the Khmer Rouge surrendered in early 1999. Factional fighting in 1997 ended the first coalition government, but a second round of national elections in 1998 led to the formation of another coalition government and renewed political stability. The July 2003 elections were relatively peaceful, but negotiations among contending political parties have yet to yield a new coalition government.
|
|
Location:
|


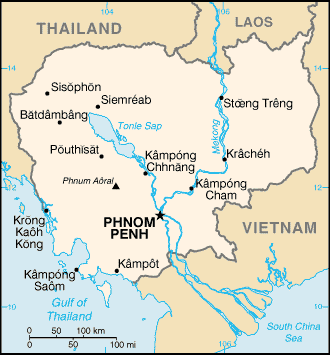
Southeastern Asia, bordering the Gulf of Thailand, between Thailand, Vietnam, and Laos
|
|
Geographic coordinates:
|


13 00 N, 105 00 E
|
|
Map references:
|


Southeast Asia
|
|
Area:
|



total: 181,040 sq km
land: 176,520 sq km
water: 4,520 sq km
|
|
Area - comparative:
|


slightly smaller than Oklahoma
|
|
Land boundaries:
|


total: 2,572 km
border countries: Laos 541 km, Thailand 803 km, Vietnam 1,228 km
|
|
Coastline:
|


443 km
|
|
Maritime claims - as described in UNCLOS 1982 (see Notes and Definitions):
|


territorial sea: 12 NM
continental shelf: 200 NM
contiguous zone: 24 NM
exclusive economic zone: 200 NM
|
|
Climate:
|


tropical; rainy, monsoon season (May to November); dry season (December to April); little seasonal temperature variation
|
|
Terrain:
|


mostly low, flat plains; mountains in southwest and north
|
|
Elevation extremes:
|


lowest point: Gulf of Thailand 0 m
highest point: Phnum Aoral 1,810 m
|
|
Natural resources:
|


oil and gas, timber, gemstones, some iron ore, manganese, phosphates, hydropower potential
|
|
Land use:
|


arable land: 20.96%
permanent crops: 0.61%
other: 78.43% (1998 est.)
|
|
Irrigated land:
|


2,700 sq km (1998 est.)
|
|
Natural hazards:
|


monsoonal rains (June to November); flooding; occasional droughts
|
|
Environment - current issues:
|


illegal logging activities throughout the country and strip mining for gems in the western region along the border with Thailand have resulted in habitat loss and declining biodiversity (in particular, destruction of mangrove swamps threatens natural fisheries); soil erosion; in rural areas, most of the population does not have access to potable water; declining fish stocks because of illegal fishing and overfishing
|
|
Environment - international agreements:
|


party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea
|
|
Geography - note:
|


a land of paddies and forests dominated by the Mekong River and Tonle Sap
|
|
Population:
|



13,363,421
note: estimates for this country take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2004 est.)
|
|
Age structure:
|


0-14 years: 38.3% (male 2,583,606; female 2,534,460)
15-64 years: 58.6% (male 3,742,178; female 4,095,303)
65 years and over: 3.1% (male 149,466; female 258,408) (2004 est.)
|
|
Median age:
|


total: 19.5 years
male: 18.8 years
female: 20.4 years (2004 est.)
|
|
Population growth rate:
|


1.8% (2004 est.)
|
|
Birth rate:
|



27.13 births/1,000 population (2004 est.)
|
|
Death rate:
|



9.1 deaths/1,000 population (2004 est.)
|
|
Net migration rate:
|


0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2004 est.)
|
|
Sex ratio:
|


at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.91 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.58 male(s)/female
total population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2004 est.)
|
|
Infant mortality rate:
|



total: 73.67 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 64.44 deaths/1,000 live births (2004 est.)
male: 82.51 deaths/1,000 live births
|
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|



total population: 58.41 years
male: 55.71 years
female: 61.23 years (2004 est.)
|
|
Total fertility rate:
|



3.51 children born/woman (2004 est.)
|
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|



2.7% (2001 est.)
|
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|



170,000 (2001 est.)
|
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|



12,000 (2001 est.)
|
|
Nationality:
|


noun: Cambodian(s)
adjective: Cambodian
|
|
Ethnic groups:
|


Khmer 90%, Vietnamese 5%, Chinese 1%, other 4%
|
|
Religions:
|


Theravada Buddhist 95%, other 5%
|
|
Languages:
|


Khmer (official) 95%, French, English
|
|
Literacy:
|


definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 69.9%
male: 80.5%
female: 60.3% (2003 est.)
|
|
Country name:
|


conventional long form: Kingdom of Cambodia
conventional short form: Cambodia
local short form: Kampuchea
local long form: Preahreacheanacha Kampuchea (phonetic pronunciation)
former: Kingdom of Cambodia, Khmer Republic, Democratic Kampuchea, People's Republic of Kampuchea, State of Cambodia
|
|
Government type:
|


multiparty democracy under a constitutional monarchy established in September 1993
|
|
Capital:
|


Phnom Penh
|
|
Administrative divisions:
|


20 provinces (khaitt, singular and plural) and 4 municipalities* (krong, singular and plural); Banteay Mean Chey, Batdambang, Kampong Cham, Kampong Chhnang, Kampong Spoe, Kampong Thum, Kampot, Kandal, Koh Kong, Keb*, Kracheh, Mondol Kiri, Otdar Mean Chey, Pailin*, Phnom Penh*, Pouthisat, Preah Sihanouk (formerly Kompong Som)*, Preah Vihear, Prey Veng, Rotanakir, Siem Reab, Stoeng Treng, Svay Rieng, Takao
|
|
Independence:
|


9 November 1953 (from France)
|
|
National holiday:
|


Independence Day, 9 November (1953)
|
|
Constitution:
|


promulgated 21 September 1993
|
|
Legal system:
|


primarily a civil law mixture of French-influenced codes from the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) period, royal decrees, and acts of the legislature, with influences of customary law and remnants of communist legal theory; increasing influence of common law in recent years
|
|
Suffrage:
|


18 years of age; universal
|
|
Executive branch:
|


chief of state: King NORODOM Sihanouk (reinstated 24 September 1993)
head of government: Prime Minister HUN Sen (since 30 November 1998) and Deputy Prime Ministers SAR Kheng (since 1993) and TOL Lah (since 1998)
cabinet: Council of Ministers in theory appointed by the monarch; in practice named by the prime minister
elections: none; the monarch is chosen by a Royal Throne Council; following legislative elections, a member of the majority party or majority coalition is named prime minister by the Chairman of the National Assembly and appointed by the king
|
|
Legislative branch:
|


bicameral consists of the National Assembly (123 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms) and the Senate (61 seats; two members appointed by the monarch, two elected by the National Assembly, and 57 elected by "functional constituencies"; members serve five-year terms)
elections: National Assembly - last held 27 July 2003 (next to be held in July 2008); Senate - last held 2 March 1999 (scheduled to be held in 2004 but delayed)
election results: National Assembly - percent of vote by party - CPP 47%, SRP 22%, FUNCINPEC 21%, other 10%; seats by party - CPP 73, FUNCINPEC 26, SRP 24; Senate - percent of vote by party - NA%; seats by party - CPP 31, FUNCINPEC 21, SRP 7, other 2 (July 2003)
|
|
Judicial branch:
|


Supreme Council of the Magistracy (provided for in the constitution and formed in December 1997); Supreme Court (and lower courts) exercises judicial authority
|
|
Political parties and leaders:
|


Cambodian Pracheachon Party (Cambodian People's Party) or CPP [CHEA Sim]; National United Front for an Independent, Neutral, Peaceful, and Cooperative Cambodia or FUNCINPEC [Prince NORODOM Ranariddh]; Sam Rangsi Party or SRP [SAM Rangsi]
|
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|


NA
|
|
International organization participation:
|


ACCT, ARF, AsDB, ASEAN, CP, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO (subscriber), ITU, NAM, OPCW (signatory), PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTrO (observer)
|
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|


chief of mission: Ambassador ROLAND Eng
FAX: [1] (202) 726-8381
telephone: [1] (202) 726-7742
chancery: 4530 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20011
|
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|


chief of mission: Ambassador Charles Aaron RAY
embassy: 27 EO Street 240, Phnom Penh
mailing address: Box P, APO AP 96546
telephone: [855] (23) 216-436/438
FAX: [855] (23) 216-437/811
|
|
Flag description:
|


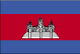
three horizontal bands of blue (top), red (double width), and blue with a white three-towered temple representing Angkor Wat outlined in black in the center of the red band; only flag in the world to incorporate a building in its design
|
|
Economy - overview:
|


Cambodia's economy slowed dramatically in 1997-1998 due to the regional economic crisis, civil violence, and political infighting. Foreign investment and tourism fell off. In 1999, the first full year of peace in 30 years, progress was made on economic reforms. Growth resumed and has remained about 5.0% during 2000-2003. Tourism was Cambodia's fastest growing industry, with arrivals up 34% in 2000 and up another 40% in 2001 before the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks in the US. Cambodia expects 1 million foreign tourists in 2004. Economic growth has been largely driven by expansion in the clothing sector and tourism. Clothing exports were fostered by the U.S.-Cambodian Bilateral Textile Agreement signed in 1999. Even given Cambodia's recent growth, the long-term development of the economy after decades of war remains a daunting challenge. The population lacks education and productive skills, particularly in the poverty-ridden countryside, which suffers from an almost total lack of basic infrastructure. Fear of renewed political instability and a dysfunctional legal system coupled with government corruption discourage foreign investment. The Cambodian government continues to work with bilateral and multilateral donors to address the country's many pressing needs. The major economic challenge for Cambodia over the next decade will be fashioning an economic environment in which the private sector can create enough jobs to handle Cambodia's demographic imbalance. About 60% of the population is 20 years or younger; most of these citizens will seek to enter the workforce over the course of the next 10 years.
|
|
GDP:
|



purchasing power parity - $22.76 billion (2003 est.)
|
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|



5.5% (2003 est.)
|
|
GDP - per capita:
|



purchasing power parity - $1,700 (2003 est.)
|
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|


agriculture: 30%
industry: 40%
services: 30% (2003 est.)
|
|
Population below poverty line:
|


36% (1997 est.)
|
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|


lowest 10%: 2.9%
highest 10%: 33.8% (1997)
|
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|


40.4 (1997)
|
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|



3% (2003 est.)
|
|
Labor force:
|



7 million (2003 est.)
|
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|


agriculture 75% (2003 est.)
|
|
Unemployment rate:
|



2.5% (2000 est.)
|
|
Budget:
|


revenues: $438 million
expenditures: $630, including capital expenditures of $291 million of which 75% was financed by external assistance (2002 est.)
|
|
Industries:
|


tourism, garments, rice milling, fishing, wood and wood products, rubber, cement, gem mining, textiles
|
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|



22% (2002 est.)
|
|
Electricity - production:
|



119 million kWh (2001)
|
|
Electricity - production by source:
|


fossil fuel: 65%
hydro: 35%
other: 0% (2001)
nuclear: 0%
|
|
Electricity - consumption:
|



110.6 million kWh (2001)
|
|
Electricity - exports:
|


0 kWh (2001)
|
|
Electricity - imports:
|


0 kWh (2001)
|
|
Oil - production:
|



0 bbl/day (2001 est.)
|
|
Oil - consumption:
|



3,600 bbl/day (2001 est.)
|
|
Oil - exports:
|



NA
|
|
Oil - imports:
|



NA
|
|
Agriculture - products:
|


rice, rubber, corn, vegetables, cashews, tapioca
|
|
Exports:
|



$1.616 billion f.o.b. (2003 est.)
|
|
Exports - commodities:
|


Clothing, timber, rubber, rice, fish, tobacco, footwear
|
|
Exports - partners:
|


US 59.8%, Germany 9.2%, UK 7%, Singapore 4.4% (2002)
|
|
Imports:
|



$2.124 billion f.o.b. (2003 est.)
|
|
Imports - commodities:
|


petroleum products, cigarettes, gold, construction materials, machinery, motor vehicles, pharmaceutical products
|
|
Imports - partners:
|


Thailand 22.9%, Singapore 15.7%, Hong Kong 15.1%, China 11.2%, Taiwan 8.5%, South Korea 5.1%, Vietnam 4.8% (2002)
|
|
Debt - external:
|



$2.4 billion (2002 est.)
|
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|


$548 million pledged in grants and concessional loans for 2001 by international donors (actual disbursement in 2002 was about $500 million)
|
|
Currency:
|


riel (KHR)
|
|
Currency code:
|


KHR
|
|
Exchange rates:
|


riels per US dollar - 3,973.33 (2003), 3,912.08 (2002), 3,916.33 (2001), 3,840.75 (2000), 3,807.83 (1999)
|
|
Fiscal year:
|


calendar year
|
|
Railways:
|



total: 602 km
narrow gauge: 602 km 1.000-m gauge (2003)
|
|
Highways:
|



total: 12,323 km
paved: 1,996 km
unpaved: 10,327 km (2000 est)
|
|
Waterways:
|


3,700 km
note: navigable all year to craft drawing 0.6 m or less; 282 km navigable to craft drawing as much as 1.8 m
|
|
Ports and harbors:
|


Kampong Som (Sihanoukville), Kampot, Krong Kaoh Kong, Phnom Penh, Sre Ambol, Keo Phoh Port (privately owned) (2003)
|
|
Merchant marine:
|


total: 467 ships (1,000 GRT or over) 1,913,910 GRT/2,713,967 DWT
registered in other countries: 19 (2003 est.)
by type: bulk 42, cargo 360, chemical tanker 6, combination bulk 3, container 13, liquefied gas 1, livestock carrier 4, multi-functional large load carrier 1, passenger/cargo 1, petroleum tanker 16, refrigerated cargo 13, roll on/roll off 5, short-sea/passenger 2
foreign-owned: Algeria 2, Angola 1, Aruba 1, Bahamas 1, Belize 10, British Virgin Islands 7, Bulgaria 1, Canada 4, China 35, Cyprus 14, Egypt 8, Finland 1, France 1, Georgia 1, Germany 1, Gibraltar 1, Greece 9, Honduras 8, Hong Kong 12, Indonesia 2, Iran 1, Italy 2, Japan 1, Jordan 1, North Korea 2, South Korea 31, Lebanon 2, Liberia 7, Malaysia 1, Malta 2, Marshall Islands 11, Netherlands 2, Nigeria 2, Norway 1, Panama 8, Romania 1, Russia 81, Saint Kitts and Nevis 2, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 5, Samoa 2, Singapore 7, Spain 1, Syria 19, Taiwan 1, Turkey 11
|
|
Airports:
|


20 (2003 est.)
|
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|


total: 5
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2003 est.)
|
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|


total: 15
under 914 m: 1 (2003 est.)
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2
914 to 1,523 m: 12
|
|
Heliports:
|


2 (2003 est.)
|
This page was last updated on 11 May, 2004
|