

| The World Factbook 2002 | ||


|
Taiwan |

|
|
| Introduction | Taiwan |
|
Background:
|
In 1895, military defeat forced China to cede Taiwan to Japan, however it reverted to Chinese control after World War II. Following the Communist victory on the mainland in 1949, 2 million Nationalists fled to Taiwan and established a government using the 1947 constitution drawn up for all of China. Over the next five decades, the ruling authorities gradually democratized and incorporated the native population within its governing structure. This culminated in 2000, when Taiwan underwent its first peaceful transfer of power from the Nationalist to the Democratic Progressive Party. Throughout this period, the island has prospered to become one of East Asia's economic "Tigers." The dominant political issues continue to be the relationship between Taiwan and China - specifically the question of eventual unification - as well as domestic political and economic reform. |
| Geography | Taiwan |
|
Location:
|
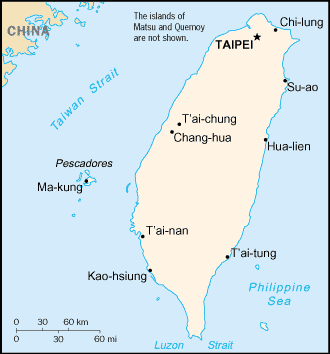
Eastern Asia, islands bordering the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, South China Sea, and Taiwan Strait, north of the Philippines, off the southeastern coast of China |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
23 30 N, 121 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Southeast Asia |
|
Area:
|
total: 35,980 sq km
note: includes the Pescadores, Matsu, and Quemoy water: 3,720 sq km land: 32,260 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly smaller than Maryland and Delaware combined |
|
Land boundaries:
|
0 km |
|
Coastline:
|
1,566.3 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
exclusive economic zone: 200 NM
territorial sea: 12 NM |
|
Climate:
|
tropical; marine; rainy season during southwest monsoon (June to August); cloudiness is persistent and extensive all year |
|
Terrain:
|
eastern two-thirds mostly rugged mountains; flat to gently rolling plains in west |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: South China Sea 0 m
highest point: Yu Shan 3,997 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
small deposits of coal, natural gas, limestone, marble, and asbestos |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 24%
permanent crops: 1% other: 75% |
|
Irrigated land:
|
NA sq km |
|
Natural hazards:
|
earthquakes and typhoons |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
air pollution; water pollution from industrial emissions, raw sewage; contamination of drinking water supplies; trade in endangered species; low-level radioactive waste disposal |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: none of the selected agreements because of Taiwan's international status
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements because of Taiwan's international status |
|
Geography - note:
|
strategic location adjacent to both the Taiwan Strait and the Luzon Strait |
| People | Taiwan |
|
Population:
|
22,548,009 (July 2002 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 21% (male 2,464,290; female 2,268,627)
15-64 years: 70% (male 8,010,014; female 7,774,296) 65 years and over: 9% (male 1,053,975; female 976,807) (2002 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
0.78% (2002 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
14.21 births/1,000 population (2002 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
6.08 deaths/1,000 population (2002 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
-0.3 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2002 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.08 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.09 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.03 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 1.08 male(s)/female total population: 1.05 male(s)/female (2002 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
6.8 deaths/1,000 live births (2002 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 76.74 years
female: 79.71 years (2002 est.) male: 73.99 years |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
1.76 children born/woman (2002 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
NA |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
NA |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Chinese (singular and plural)
adjective: Chinese |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Taiwanese (including Hakka) 84%, mainland Chinese 14%, aborigine 2% |
|
Religions:
|
mixture of Buddhist, Confucian, and Taoist 93%, Christian 4.5%, other 2.5% |
|
Languages:
|
Mandarin Chinese (official), Taiwanese (Min), Hakka dialects |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 86% (1980 est.) male: 93% (1980 est.) female: 79% (1980 est.) note: literacy for the total population has reportedly increased to 94% (1998 est.) |
| Government | Taiwan |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Taiwan local short form: T'ai-wan local long form: none former: Formosa |
|
Government type:
|
multiparty democratic regime headed by popularly elected president and unicameral legislature |
|
Capital:
|
Taipei |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
the central administrative divisions include the provinces of Fu-chien (some 20 offshore islands of Fujian Province including Quemoy and Matsu) and Taiwan (the island of Taiwan and the Pescadores islands); Taiwan is further subdivided into 16 counties (hsien, singular and plural), 5 municipalities* (shih, singular and plural), and 2 special municipalities** (chuan-shih, singular and plural); Chang-hua, Chia-i, Chia-i*, Chi-lung*, Hsin-chu, Hsin-chu*, Hua-lien, I-lan, Kao-hsiung, Kao-hsiung**, Miao-li, Nan-t'ou, P'eng-hu, P'ing-tung, T'ai-chung, T'ai-chung*, T'ai-nan, T'ai-nan*, T'ai-pei, T'ai-pei**, T'ai-tung, T'ao-yuan, and Yun-lin; the provincial capital is at Chung-hsing-hsin-ts'un
note: Taiwan uses the Wade-Giles system for romanization |
|
National holiday:
|
Republic Day (Anniversary of the Chinese Revolution), 10 October (1911) |
|
Constitution:
|
1 January 1947, amended in 1992, 1994, 1997, and 1999 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on civil law system; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations |
|
Suffrage:
|
20 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Shui-bian CHEN (since 20 May 2000) and Vice President Annette Hsiu-lien LU (since 20 May 2000)
election results: Shui-bian CHEN elected president; percent of vote - Shui-bian CHEN (DPP) 39.3%, James SOONG (independent) 36.84%, LIEN Chan (KMT) 23.1%, HSU Hsin-liang (independent) 0.63%, LEE Ao (CNP) 0.13% elections: president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for four-year terms; election last held 18 March 2000 (next to be held NA March 2004); premier appointed by the president; vice premiers appointed by the president on the recommendation of the premier head of government: Premier (President of the Executive Yuan) Shyi-kun YU (since 1 February 2002) and Vice Premier (Vice President of the Executive Yuan) Hsin-yi LIN (since 1 February 2002) cabinet: Executive Yuan appointed by the president |
|
Legislative branch:
|
unicameral Legislative Yuan (225 seats - 168 elected by popular vote, 41 elected on the basis of the proportion of islandwide votes received by participating political parties, eight elected from overseas Chinese constituencies on the basis of the proportion of islandwide votes received by participating political parties, eight elected by popular vote among the aboriginal populations; members serve three-year terms) and unicameral National Assembly (300 seat nonstanding body; delegates nominated by parties and elected by proportional representation within three months of a Legislative Yuan call to amend the Constitution, impeach the president, or change national borders)
elections: Legislative Yuan - last held 8 December 2001 (next to be held NA December 2004); note - the National Assembly is a nonstanding body and is called into session election results: Legislative Yuan - percent of vote by party - DPP 39%, KMT 30%, PFP 20%, TSU 6%, independents and other parties 5%; seats by party - DPP 87, KMT 68, PFP 46, TSU 13, independents and other parties 11 |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Judicial Yuan (justices appointed by the president with consent of the National Assembly; note - beginning in 2003, justices will be appointed by the president with consent of the Legislative Yuan) |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Democratic Progressive Party or DPP [Frank Chang-ting HSIEH, chairman]; Kuomintang or KMT (Nationalist Party) [LIEN Chan, chairman]; People First Party or PFP [James Chu-yu SOONG, chairman]; Taiwan Solidarity Union or TSU [Chu-wen HUANG, chairman]; other minor parties |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
Taiwan independence movement, various business and environmental groups
note: debate on Taiwan independence has become acceptable within the mainstream of domestic politics on Taiwan; political liberalization and the increased representation of opposition parties in Taiwan's legislature have opened public debate on the island's national identity; a broad popular consensus has developed that Taiwan currently enjoys de facto independence and - whatever the ultimate outcome regarding reunification or independence - that Taiwan's people must have the deciding voice; advocates of Taiwan independence oppose the stand that the island will eventually unify with mainland China; goals of the Taiwan independence movement include establishing a sovereign nation on Taiwan and entering the UN; other organizations supporting Taiwan independence include the World United Formosans for Independence and the Organization for Taiwan Nation Building |
|
International organization participation:
|
APEC, AsDB, BCIE, ICC, ICFTU, IFRCS, IOC, WCL, WTrO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
none; unofficial commercial and cultural relations with the people of the US are maintained through an unofficial instrumentality, the Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in the US with headquarters in Taipei and field offices in Washington and 12 other US cities |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
none; unofficial commercial and cultural relations with the people on Taiwan are maintained through an unofficial instrumentality - the American Institute in Taiwan (AIT) - which has offices in the US and Taiwan; US office located at 1700 N. Moore St., Suite 1700, Arlington, VA 22209-1996, telephone: [1] (703) 525-8474, FAX: [1] (703) 841-1385); Taiwan offices located at #7 Lane 134, Hsin Yi Road, Section 3, Taipei, Taiwan, telephone: [886] (2) 2709-2000, FAX: [886] (2) 2702-7675; #2 Chung Cheng 3rd Road, 5th Floor, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, telephone: [886] (7) 224-0154 through 0157, FAX: [886] (7) 223-8237; and the American Trade Center, Room 3208 International Trade Building, Taipei World Trade Center, 333 Keelung Road Section 1, Taipei, Taiwan 10548, telephone: [886] (2) 2720-1550, FAX: [886] (2) 2757-7162 |
|
Flag description:
|
red with a dark blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing a white sun with 12 triangular rays |
| Economy | Taiwan |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Taiwan has a dynamic capitalist economy with gradually decreasing guidance of investment and foreign trade by government authorities. In keeping with this trend, some large government-owned banks and industrial firms are being privatized. Real growth in GDP has averaged about 8% during the past three decades. Exports have provided the primary impetus for industrialization. The trade surplus is substantial, and foreign reserves are the world's third largest. Agriculture contributes 2% to GDP, down from 35% in 1952. Traditional labor-intensive industries are steadily being moved offshore and replaced with more capital- and technology-intensive industries. Taiwan has become a major investor in China, Thailand, Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Vietnam; 50,000 Taiwanese businesses are established in China. Because of its conservative financial approach and its entrepreneurial strengths, Taiwan suffered little compared with many of its neighbors from the Asian financial crisis in 1998-99. The global economic downturn, however, combined with poor policy coordination by the new administration and increasing bad debts in the banking system, pushed Taiwan into recession in 2001, the first whole year of negative growth since 1947. Unemployment also reached a level not seen since the 1970s oil crisis. |
|
GDP:
|
purchasing power parity - $386 billion (2001 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
-2.2% (2001 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
purchasing power parity - $17,200 (2001 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 2%
industry: 32% services: 66% (2000 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
1% (2000 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%: NA% |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
32.6 (2000) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
0.5% (2001 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
9.8 million (2001 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
services 56%, industry 36%, agriculture 8% (2001 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
4.5% (2001 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $36 billion
expenditures: $36.1 billion, including capital expenditures of $NA (2002 est.) |
|
Industries:
|
electronics, petroleum refining, chemicals, textiles, iron and steel, machinery, cement, food processing |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
-5% (2001 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
149.78 billion kWh (2000) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 69.48%
hydro: 5.82% other: 0% (2000) nuclear: 24.7% |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
139.295 billion kWh (2000) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2000) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2000) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
rice, corn, vegetables, fruit, tea; pigs, poultry, beef, milk; fish |
|
Exports:
|
$122 billion (f.o.b., 2001) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
machinery and electrical equipment 55%, metals, textiles, plastics, chemicals |
|
Exports - partners:
|
US 23.5%, Hong Kong 21.1%, Europe 16%, ASEAN 12.2%, Japan 11.2% (2000) |
|
Imports:
|
$109 billion (f.o.b., 2001) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
machinery and electrical equipment 50%, minerals, precision instruments |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Japan 27.5%, US 17.9%, Europe 13.6%, South Korea 6.4% (2000) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$40 billion (2000) |
|
Currency:
|
new Taiwan dollar (TWD) |
|
Currency code:
|
TWD |
|
Exchange rates:
|
new Taiwan dollars per US dollar - 34.494 (yearend 2001), 33.082 (yearend 2000), 31.395 (yearend 1999), 32.216 (1998), 32.052 (1997), 27.5 (1996) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
1 July - 30 June (up to FY98/99); 1 July 1999 - 31 December 2000 for FY00; calendar year (after FY00) |
| Communications | Taiwan |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
12.49 million (September 2000) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
16 million (September 2000) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: provides telecommunications service for every business and private need
domestic: thoroughly modern; completely digitalized international: satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Pacific Ocean and 1 Indian Ocean); submarine cables to Japan (Okinawa), Philippines, Guam, Singapore, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Australia, Middle East, and Western Europe (1999) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 218, FM 333, shortwave 50 (1999) |
|
Radios:
|
16 million (1994) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
29 (plus two repeaters) (1997) |
|
Televisions:
|
8.8 million (1998) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.tw |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
8 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
11.6 million (2001) |
| Transportation | Taiwan |
|
Railways:
|
total: 1,108 km
narrow gauge: 1,108 km 1.067-m gauge (519 km electrified) note: in addition to the above routes in common carrier service, there are several thousand kilometers of 1.067-m gauge routes that are dedicated to industrial use (2001) |
|
Highways:
|
total: 34,901 km
paved: 31,271 km (including 538 km of expressways) unpaved: 3,630 km (1998 est.) |
|
Waterways:
|
NA |
|
Pipelines:
|
petroleum products 3,400 km; natural gas 1,800 km (1999) |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Chi-lung (Keelung), Hua-lien, Kao-hsiung, Su-ao, T'ai-chung |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 152 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 4,262,451 GRT/6,596,950 DWT
note: includes some foreign-owned ships registered here as a flag of convenience: Hong Kong 3, Japan 1 (2002 est.) ships by type: bulk 40, cargo 28, combination bulk 3, container 53, petroleum tanker 17, refrigerated cargo 9, roll on/roll off 2 |
|
Airports:
|
39 (2001) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 36
over 3,047 m: 8 2,438 to 3,047 m: 9 914 to 1,523 m: 8 under 914 m: 3 (2001) 1,524 to 2,437 m: 8 |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 3
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 under 914 m: 2 (2001) |
|
Heliports:
|
3 (2001) |
| Military | Taiwan |
|
Military branches:
|
Army, Navy (including Marine Corps), Air Force, Coast Guard Administration, Armed Forces Reserve Command, Combined Service Forces Command |
|
Military manpower - military age:
|
19 years of age (2002 est.) |
|
Military manpower - availability:
|
males age 15-49: 6,575,625 (2002 est.) |
|
Military manpower - fit for military service:
|
males age 15-49: 5,018,882 (2002 est.) |
|
Military manpower - reaching military age annually:
|
males: 198,766 (2002 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$8,041,200,000 (FY01) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
2.8% (FY01) |
| Transnational Issues | Taiwan |
|
Disputes - international:
|
involved in complex dispute over the Spratly Islands with China, Malaysia, Philippines, Vietnam, and possibly Brunei; Paracel Islands occupied by China, but claimed by Taiwan and Vietnam; claims Japanese-administered Senkaku-shoto (Senkaku Islands/Diaoyu Tai), as does China |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
regional transit point for heroin and methamphetamine; major problem with domestic consumption of methamphetamine and heroin |
|
This page was last updated on 1 January 2002 |