
(territory of the US)

 |
Wake Island (territory of the US) |
 |
| Introduction Geography People Government Economy Communications Transportation Military Transnational Issues | ||
 |
||
| Wake Island | Introduction | Top of Page |
| Background: | The US annexed Wake Island in 1899 for a cable station. An important air and naval base was constructed in 1940-41. In December 1941 the island was captured by the Japanese and held until the end of World War II. In subsequent years, Wake was developed as a stopover and refueling site for military and commercial aircraft transiting the Pacific. Since 1974, the island's airstrip has been used by the US military and some commercial cargo planes, as well as for emergency landings. There are over 700 landings a year on the island. |
| Wake Island | Geography | Top of Page |
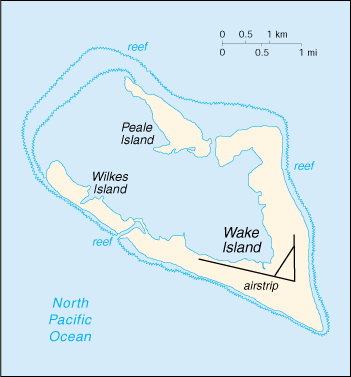
| Location: | Oceania, atoll in the North Pacific Ocean, about two-thirds of the way from Hawaii to the Northern Mariana Islands |
| Geographic coordinates: | 19 17 N, 166 36 E |
| Map references: | Oceania |
| Area: |
total:
6.5 sq km
land: 6.5 sq km water: 0 sq km |
| Area - comparative: | about 11 times the size of The Mall in Washington, DC |
| Land boundaries: | 0 km |
| Coastline: | 19.3 km |
| Maritime claims: |
exclusive economic zone:
200 NM
territorial sea: 12 NM |
| Climate: | tropical |
| Terrain: | atoll of three coral islands built up on an underwater volcano; central lagoon is former crater, islands are part of the rim |
| Elevation extremes: |
lowest point:
Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: unnamed location 6 m |
| Natural resources: | none |
| Land use: |
arable land:
0%
permanent crops: 0% permanent pastures: 0% forests and woodland: 0% other: 100% |
| Irrigated land: | 0 sq km (1998) |
| Natural hazards: | occasional typhoons |
| Environment - current issues: | NA |
| Geography - note: | strategic location in the North Pacific Ocean; emergency landing location for transpacific flights |
| Wake Island | People | Top of Page |
| Population: |
no indigenous inhabitants
note: US military personnel have left the island, but civilian personnel remain; as of December 2000, one US Army civilian and 123 civilian contractor personnel were present (January 2001 est.) |
| HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: | NA |
| Wake Island | Government | Top of Page |
| Country name: |
conventional long form:
none
conventional short form: Wake Island |
| Dependency status: | unincorporated territory of the US; administered from Washington, DC, by the Department of the Interior; activities on the island are managed by the US Army under a US Air Force permit |
| Legal system: | the laws of the US, where applicable, apply |
| Flag description: | the flag of the US is used |
| Wake Island | Economy | Top of Page |
| Economy - overview: | Economic activity is limited to providing services to contractors located on the island. All food and manufactured goods must be imported. |
| Electricity - production: | NA kWh |
| Wake Island | Communications | Top of Page |
| Telephone system: |
general assessment:
satellite communications; 1 DSN circuit off the Overseas Telephone System (OTS)
domestic: NA international: NA |
| Radio broadcast stations: |
AM 0, FM NA, shortwave NA
note: Armed Forces Radio/Television Service (AFRTS) radio service provided by satellite (1998) |
| Television broadcast stations: | 0 (1997) |
| Wake Island | Transportation | Top of Page |
| Waterways: | none |
| Ports and harbors: | none; two offshore anchorages for large ships |
| Airports: | 1 (2000 est.) |
| Airports - with paved runways: |
total:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2000 est.) |
| Transportation - note: | formerly an important commercial aviation base, now used by US military, some commercial cargo planes, and for emergency landings |
| Wake Island | Military | Top of Page |
| Military - note: | defense is the responsibility of the US |
| Wake Island | Transnational Issues | Top of Page |
| Disputes - international: | claimed by Marshall Islands |