
(territory of the US)

 |
Midway Islands (territory of the US) |
 |
| Introduction Geography People Government Economy Transportation Military Transnational Issues | ||
 |
||
| Midway Islands | Introduction | Top of Page |
| Background: | The US took formal possession of the islands in 1867. The laying of the trans-Pacific cable, which passed through the islands, brought the first residents in 1903. Between 1935 and 1947, Midway was used as a refueling stop for trans-Pacific flights. The US naval victory over a Japanese fleet off Midway in 1942 was one of the turning points of World War II. The islands continued to serve as a naval station until closed in 1993. Today the islands are a wildlife refuge open to the public. |
| Midway Islands | Geography | Top of Page |
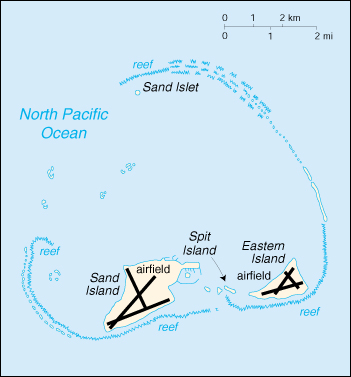
| Location: | Oceania, atoll in the North Pacific Ocean, about one-third of the way from Honolulu to Tokyo |
| Geographic coordinates: | 28 13 N, 177 22 W |
| Map references: | Oceania |
| Area: |
total:
6.2 sq km
land: 6.2 sq km water: 0 sq km note: includes Eastern Island, Sand Island, and Spit Island |
| Area - comparative: | about nine times the size of The Mall in Washington, DC |
| Land boundaries: | 0 km |
| Coastline: | 15 km |
| Maritime claims: |
exclusive economic zone:
200 NM
territorial sea: 12 NM |
| Climate: | subtropical, but moderated by prevailing easterly winds |
| Terrain: | low, nearly level |
| Elevation extremes: |
lowest point:
Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: unnamed location 13 m |
| Natural resources: | wildlife, terrestrial and aquatic |
| Land use: |
arable land:
0%
permanent crops: 0% permanent pastures: 0% forests and woodland: 0% other: 100% |
| Irrigated land: | 0 sq km (1998) |
| Natural hazards: | NA |
| Environment - current issues: | NA |
| Geography - note: | a coral atoll managed as a national wildlife refuge and open to the public for wildlife-related recreation in the form of wildlife observation and photography, sport fishing, snorkeling, and scuba diving |
| Midway Islands | People | Top of Page |
| Population: | no indigenous inhabitants; approximately 150 people make up the staff of US Fish and Wildlife Service and their services cooperator living at the atoll (July 2001 est.) |
| Midway Islands | Government | Top of Page |
| Country name: |
conventional long form:
none
conventional short form: Midway Islands |
| Dependency status: | unincorporated territory of the US; formerly administered from Washington, DC, by the US Navy, under Naval Facilities Engineering Command, Pacific Division; this facility has been operationally closed since 10 September 1993; on 31 October 1996, through a presidential executive order, the jurisdiction and control of the atoll was transferred to the Fish and Wildlife Service of the US Department of the Interior as part of the National Wildlife Refuge system |
| Legal system: | the laws of the US, where applicable, apply |
| Flag description: | the flag of the US is used |
| Midway Islands | Economy | Top of Page |
| Economy - overview: | The economy is based on providing support services for the national wildlife refuge activities located on the islands. All food and manufactured goods must be imported. |
| Midway Islands | Transportation | Top of Page |
| Highways: |
total:
NA km
paved: NA km unpaved: NA km |
| Waterways: | none |
| Pipelines: | 7.8 km |
| Ports and harbors: | Sand Island |
| Airports: | 3 (2000 est.) |
| Airports - with paved runways: |
total:
2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2 (2000 est.) |
| Airports - with unpaved runways: |
total:
1
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2000 est.) |
| Midway Islands | Military | Top of Page |
| Military - note: | defense is the responsibility of the US |
| Midway Islands | Transnational Issues | Top of Page |
| Disputes - international: | none |