

 |
Burma |  |
| Introduction Geography People Government Economy Communications Transportation Military Transnational Issues | ||
 |
||
| Burma | Introduction | Top of Page |
| Background: | Despite multiparty elections in 1990 that resulted in the main opposition party winning a decisive victory, the military junta ruling the country refused to hand over power. Key opposition leader and Nobel Peace Prize recipient AUNG San Suu Kyi, under house arrest from 1989 to 1995, was again placed under house detention in September 2000; her supporters are routinely harassed or jailed. |
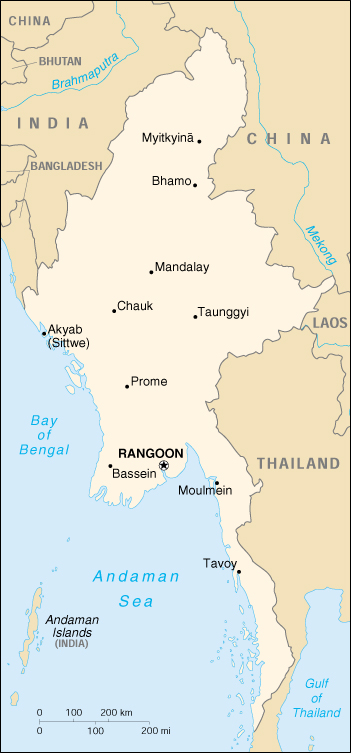
| Burma | Geography | Top of Page |
| Location: | Southeastern Asia, bordering the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal, between Bangladesh and Thailand |
| Geographic coordinates: | 22 00 N, 98 00 E |
| Map references: | Southeast Asia |
| Area: |
total:
678,500 sq km
land: 657,740 sq km water: 20,760 sq km |
| Area - comparative: | slightly smaller than Texas |
| Land boundaries: |
total:
5,876 km
border countries: Bangladesh 193 km, China 2,185 km, India 1,463 km, Laos 235 km, Thailand 1,800 km |
| Coastline: | 1,930 km |
| Maritime claims: |
contiguous zone:
24 NM
continental shelf: 200 NM or to the edge of the continental margin exclusive economic zone: 200 NM territorial sea: 12 NM |
| Climate: | tropical monsoon; cloudy, rainy, hot, humid summers (southwest monsoon, June to September); less cloudy, scant rainfall, mild temperatures, lower humidity during winter (northeast monsoon, December to April) |
| Terrain: | central lowlands ringed by steep, rugged highlands |
| Elevation extremes: |
lowest point:
Andaman Sea 0 m
highest point: Hkakabo Razi 5,881 m |
| Natural resources: | petroleum, timber, tin, antimony, zinc, copper, tungsten, lead, coal, some marble, limestone, precious stones, natural gas, hydropower |
| Land use: |
arable land:
15%
permanent crops: 1% permanent pastures: 1% forests and woodland: 49% other: 34% (1993 est.) |
| Irrigated land: | 10,680 sq km (1993 est.) |
| Natural hazards: | destructive earthquakes and cyclones; flooding and landslides common during rainy season (June to September); periodic droughts |
| Environment - current issues: | deforestation; industrial pollution of air, soil, and water; inadequate sanitation and water treatment contribute to disease |
| Environment - international agreements: |
party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Geography - note: | strategic location near major Indian Ocean shipping lanes |
| Burma | People | Top of Page |
| Population: |
41,994,678
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2001 est.) |
| Age structure: |
0-14 years:
29.14% (male 6,245,798; female 5,992,074)
15-64 years: 66.08% (male 13,779,571; female 13,970,707) 65 years and over: 4.78% (male 895,554; female 1,110,974) (2001 est.) |
| Population growth rate: | 0.6% (2001 est.) |
| Birth rate: | 20.13 births/1,000 population (2001 est.) |
| Death rate: | 12.3 deaths/1,000 population (2001 est.) |
| Net migration rate: | -1.84 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2001 est.) |
| Sex ratio: |
at birth:
1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 0.99 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.81 male(s)/female total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2001 est.) |
| Infant mortality rate: | 73.71 deaths/1,000 live births (2001 est.) |
| Life expectancy at birth: |
total population:
55.16 years
male: 53.73 years female: 56.68 years (2001 est.) |
| Total fertility rate: | 2.3 children born/woman (2001 est.) |
| HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: | 1.99% (1999 est.) |
| HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: | 530,000 (1999 est.) |
| HIV/AIDS - deaths: | 48,000 (1999 est.) |
| Nationality: |
noun:
Burmese (singular and plural)
adjective: Burmese |
| Ethnic groups: | Burman 68%, Shan 9%, Karen 7%, Rakhine 4%, Chinese 3%, Mon 2%, Indian 2%, other 5% |
| Religions: | Buddhist 89%, Christian 4% (Baptist 3%, Roman Catholic 1%), Muslim 4%, animist 1%, other 2% |
| Languages: | Burmese, minority ethnic groups have their own languages |
| Literacy: |
definition:
age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 83.1% male: 88.7% female: 77.7% (1995 est.) note: these are official statistics; estimates of functional literacy are likely closer to 30% (1999 est.) |
| Burma | Government | Top of Page |
| Country name: |
conventional long form:
Union of Burma
conventional short form: Burma local long form: Pyidaungzu Myanma Naingngandaw (translated by the US Government as Union of Myanma and by the Burmese as Union of Myanmar) local short form: Myanma Naingngandaw former: Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma |
| Government type: | military regime |
| Capital: | Rangoon (regime refers to the capital as Yangon) |
| Administrative divisions: | 7 divisions* (yin-mya, singular - yin) and 7 states (pyine-mya, singular - pyine); Chin State, Ayeyarwady*, Bago*, Kachin State, Kayin State, Kayah State, Magway*, Mandalay*, Mon State, Rakhine State, Sagaing*, Shan State, Tanintharyi*, Yangon* |
| Independence: | 4 January 1948 (from UK) |
| National holiday: | Independence Day, 4 January (1948) |
| Constitution: | 3 January 1974 (suspended since 18 September 1988); national convention started on 9 January 1993 to draft a new constitution; progress has since been stalled |
| Legal system: | has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction |
| Suffrage: | 18 years of age; universal |
| Executive branch: |
chief of state:
Prime Minister and Chairman of the State Peace and Development Council Gen. THAN SHWE (since 23 April 1992); note - the prime minister is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government: Prime Minister and Chairman of the State Peace and Development Council Gen. THAN SHWE (since 23 April 1992); note - the prime minister is both the chief of state and head of government cabinet: State Peace and Development Council (SPDC); military junta, so named 15 November 1997, which initially assumed power 18 September 1988 under the name State Law and Order Restoration Council; the SPDC oversees the cabinet elections: none; the prime minister assumed power upon resignation of the former prime minister |
| Legislative branch: |
unicameral People's Assembly or Pyithu Hluttaw (485 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
elections: last held 27 May 1990, but Assembly never convened election results: percent of vote by party - NA%; seats by party - NLD 392, SNLD 23, NUP 10, other 60 |
| Judicial branch: | remnants of the British-era legal system are in place, but there is no guarantee of a fair public trial; the judiciary is not independent of the executive |
| Political parties and leaders: | National League for Democracy or NLD [AUNG SHWE, chairman, AUNG SAN SUU KYI, general secretary]; National Unity Party or NUP (proregime) [THA KYAW]; Shan Nationalities League for Democracy or SNLD [U KHUN TUN OO]; Union Solidarity and Development Association or USDA (proregime, a social and political organization) [THAN AUNG, general secretary]; and other smaller parties |
| Political pressure groups and leaders: | All Burma Student Democratic Front or ABSDF; Kachin Independence Army or KIA; Karen National Union or KNU; National Coalition Government of the Union of Burma or NCGUB [Dr. SEIN WIN] consists of individuals legitimately elected to the People's Assembly but not recognized by the military regime; the group fled to a border area and joined with insurgents in December 1990 to form a parallel government; several Shan factions; United Wa State Army or UWSA |
| International organization participation: | ARF, AsDB, ASEAN, CCC, CP, ESCAP, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Intelsat (nonsignatory user), Interpol, IOC, ITU, NAM, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTrO |
| Diplomatic representation in the US: |
chief of mission:
Ambassador-designate U LINN MYAING
chancery: 2300 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008 telephone: [1] (202) 332-9044 FAX: [1] (202) 332-9046 consulate(s) general: New York |
| Diplomatic representation from the US: |
chief of mission:
Permanent Charge d'Affaires Priscilla A. CLAPP
embassy: 581 Merchant Street, Rangoon (GPO 521) mailing address: Box B, APO AP 96546 telephone: [95] (1) 282055, 282182 FAX: [95] (1) 280409 |
| Flag description: | red with a blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing, all in white, 14 five-pointed stars encircling a cogwheel containing a stalk of rice; the 14 stars represent the 14 administrative divisions |
| Burma | Economy | Top of Page |
| Economy - overview: | Burma has a mixed economy with private activity dominant in agriculture, light industry, and transport, and with substantial state-controlled activity, mainly in energy, heavy industry, and the rice trade. Government policy in the 1990s has aimed at revitalizing the economy after three decades of tight central planning. Private activity markedly increased in the early to mid-1990s, but began to decline in the past several years due to frustrations with the unfriendly business environment and political pressure from western nations. Published estimates of Burma's foreign trade are greatly understated because of the volume of black-market, illicit, and border trade. A major ongoing problem is the failure to achieve monetary and fiscal stability. Burma remains a poor Asian country and living standards for the majority have not improved over the past decade. Short-term growth will continue to be restrained because of poor government planning and minimal foreign investment. |
| GDP: | purchasing power parity - $63.7 billion (2000 est.) |
| GDP - real growth rate: | 4.9% (2000 est.) |
| GDP - per capita: | purchasing power parity - $1,500 (2000 est.) |
| GDP - composition by sector: |
agriculture:
42%
industry: 17% services: 41% (2000 est.) |
| Population below poverty line: | 23% (1997 est.) |
| Household income or consumption by percentage share: |
lowest 10%:
2.8%
highest 10%: 32.4% (1998) |
| Inflation rate (consumer prices): | 18% (1999) |
| Labor force: | 19.7 million (FY98/99 est.) |
| Labor force - by occupation: | agriculture 65%, industry 10%, services 25% (1999 est.) |
| Unemployment rate: | 7.1% (official FY97/98 est.) |
| Budget: |
revenues:
$7.9 billion
expenditures: $12.2 billion, including capital expenditures of $5.7 billion (FY96/97) |
| Industries: | agricultural processing; textiles and footwear; wood and wood products; copper, tin, tungsten, iron; construction materials; pharmaceuticals; fertilizer |
| Industrial production growth rate: | NA% |
| Electricity - production: | 4.813 billion kWh (1999) |
| Electricity - production by source: |
fossil fuel:
68.56%
hydro: 31.44% nuclear: 0% other: 0% (1999) |
| Electricity - consumption: | 4.476 billion kWh (1999) |
| Electricity - exports: | 0 kWh (1999) |
| Electricity - imports: | 0 kWh (1999) |
| Agriculture - products: | paddy rice, corn, oilseed, sugarcane, pulses; hardwood |
| Exports: | $1.3 billion (f.o.b., 1999) |
| Exports - commodities: | apparel 36%, foodstuffs 22%, wood products 21%, precious stones 5% (1999) |
| Exports - partners: |
India 13%, Singapore 11%, China 11%, US 8% (1999 est.)
note: official trade statistics do not include trade in illicit goods - such as narcotics, teak, and gems - or the largely unrecorded border trade with China and Thailand |
| Imports: | $2.5 billion (f.o.b., 1999) |
| Imports - commodities: | machinery, transport equipment, construction materials, food products |
| Imports - partners: | Singapore 28%, Thailand 12%, China 10%, Japan 10%, South Korea 9% (1999 est.) |
| Debt - external: | $6 billion (FY99/00 est.) |
| Economic aid - recipient: | $99 million (FY98/99) |
| Currency: | kyat (MMK) |
| Currency code: | MMK |
| Exchange rates: | kyats per US dollar - official rate - 6.5972 (January 2001), 6.5167 (2000), 6.2858 (1999), 6.3432 (1998), 6.2418 (1997), 5.9176 (1996); kyats per US dollar - black market exchange rate - 435 (yearend 2000) |
| Fiscal year: | 1 April - 31 March |
| Burma | Communications | Top of Page |
| Telephones - main lines in use: | 250,000 (2000) |
| Telephones - mobile cellular: | 8,492 (1997) |
| Telephone system: |
general assessment:
meets minimum requirements for local and intercity service for business and government; international service is good
domestic: NA international: satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) |
| Radio broadcast stations: | AM 2, FM 3, shortwave 3 (1998) |
| Radios: | 4.2 million (1997) |
| Television broadcast stations: | 2 (1998) |
| Televisions: | 320,000 (2000) |
| Internet country code: | .mm |
| Internet Service Providers (ISPs): |
1
note: as of September 2000, Internet connections were legal only for the government, tourist offices, and a few large businesses (2000) |
| Internet users: | 500 (2000) |
| Burma | Transportation | Top of Page |
| Railways: |
total:
3,991 km
narrow gauge: 3,991 km 1.000-m gauge |
| Highways: |
total:
28,200 km
paved: 3,440 km unpaved: 24,760 km (1996) |
| Waterways: |
12,800 km
note: 3,200 km navigable by large commercial vessels |
| Pipelines: | crude oil 1,343 km; natural gas 330 km |
| Ports and harbors: | Bassein, Bhamo, Chauk, Mandalay, Moulmein, Myitkyina, Rangoon, Akyab (Sittwe), Tavoy |
| Merchant marine: |
total:
37 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 411,181 GRT/632,769 DWT
ships by type: bulk 11, cargo 20, container 1, passenger/cargo 3, petroleum tanker 2 note: includes some foreign-owned ships registered here as a flag of convenience: Japan 2 (2000 est.) |
| Airports: | 80 (2000 est.) |
| Airports - with paved runways: |
total:
9
over 3,047 m: 3 2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 1,524 to 2,437 m: 4 914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2000 est.) |
| Airports - with unpaved runways: |
total:
71
over 3,047 m: 2 1,524 to 2,437 m: 15 914 to 1,523 m: 22 under 914 m: 32 (2000 est.) |
| Heliports: | 1 (2000 est.) |
| Burma | Military | Top of Page |
| Military branches: | Army, Navy, Air Force |
| Military manpower - military age: | 18 years of age |
| Military manpower - availability: |
males age 15-49:
12,050,964
females age 15-49: 12,070,017 note: both sexes liable for military service (2001 est.) |
| Military manpower - fit for military service: |
males age 15-49:
6,425,514
females age 15-49: 6,419,677 (2001 est.) |
| Military manpower - reaching military age annually: |
males:
470,667
females: 479,691 (2001 est.) |
| Military expenditures - dollar figure: | $39 million (FY97/98) |
| Military expenditures - percent of GDP: | 2.1% (FY97/98) |
| Burma | Transnational Issues | Top of Page |
| Disputes - international: | sporadic border hostilities with Thailand over border alignment and ethnic Shan rebels operating in cross-border region |
| Illicit drugs: | world's second largest producer of illicit opium, after Afghanistan (potential production in 1999 - 1,090 metric tons, down 38% due to drought; cultivation in 1999 - 89,500 hectares, a 31% decline from 1998); surrender of drug warlord KHUN SA's Mong Tai Army in January 1996 was hailed by Rangoon as a major counternarcotics success, but lack of government will and ability to take on major narcotrafficking groups and lack of serious commitment against money laundering continues to hinder the overall antidrug effort; becoming a major source of methamphetamine for regional consumption |