|
|
|
Once the center of power for the large Austro-Hungarian Empire, Austria was reduced to a small republic after its defeat in World War I. Following annexation by Nazi Germany in 1938 and subsequent occupation by the victorious Allies in 1945, Austria's status remained unclear for a decade. A State Treaty signed in 1955 ended the occupation, recognized Austria's independence, and forbade unification with Germany. A constitutional law that same year declared the country's "perpetual neutrality" as a condition for Soviet military withdrawal. The Soviet Union's collapse in 1991 and Austria's entry into the European Union in 1995 have altered the meaning of this neutrality. A prosperous, democratic country, Austria entered the EU Economic and Monetary Union in 1999.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
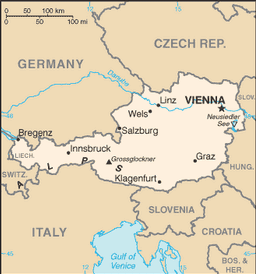
Central Europe, north of Italy and Slovenia
|
|
|
|
|
47 20 N, 13 20 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 83,871 sq km
country comparison to the world: 114
land:
82,445 sq km
water:
1,426 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Maine
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,562 km
border countries:
Czech Republic 362 km, Germany 784 km, Hungary 366 km, Italy 430 km, Liechtenstein 35 km, Slovakia 91 km, Slovenia 330 km, Switzerland 164 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
temperate; continental, cloudy; cold winters with frequent rain and some snow in lowlands and snow in mountains; moderate summers with occasional showers
|
|
|
|
|
in the west and south mostly mountains (Alps); along the eastern and northern margins mostly flat or gently sloping
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Neusiedler See 115 m
highest point:
Grossglockner 3,798 m
|
|
|
|
|
oil, coal, lignite, timber, iron ore, copper, zinc, antimony, magnesite, tungsten, graphite, salt, hydropower
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 16.59%
permanent crops:
0.85%
other:
82.56% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
1,170 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
84 cu km (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3.67 cu km/yr (35%/64%/1%)
per capita:
448 cu m/yr (1999)
|
|
|
|
|
landslides; avalanches; earthquakes
|
|
|
|
|
some forest degradation caused by air and soil pollution; soil pollution results from the use of agricultural chemicals; air pollution results from emissions by coal- and oil-fired power stations and industrial plants and from trucks transiting Austria between northern and southern Europe
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
landlocked; strategic location at the crossroads of central Europe with many easily traversable Alpine passes and valleys; major river is the Danube; population is concentrated on eastern lowlands because of steep slopes, poor soils, and low temperatures elsewhere
|
|
|
|
|
| People and Society ::Austria |
|
|
|
noun: Austrian(s)
adjective:
Austrian
|
|
|
|
|
Austrians 91.1%, former Yugoslavs 4% (includes Croatians, Slovenes, Serbs, and Bosniaks), Turks 1.6%, German 0.9%, other or unspecified 2.4% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
German (official nationwide) 88.6%, Turkish 2.3%, Serbian 2.2%, Croatian (official in Burgenland) 1.6%, other (includes Slovene, official in Carinthia, and Hungarian, official in Burgenland) 5.3% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 73.6%, Protestant 4.7%, Muslim 4.2%, other 3.5%, unspecified 2%, none 12% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
8,219,743 (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 13.9% (male 583,162/ female 555,976)
15-64 years:
67.6% (male 2,789,570/ female 2,768,420)
65 years and over:
18.5% (male 640,806/ female 881,809) (2012 est.)
population pyramid: 
|
|
|
|
|
total: 43.4 years
male:
42.3 years
female:
44.5 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.026% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 186
|
|
|
|
|
8.69 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214
|
|
|
|
|
10.23 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
|
|
|
|
|
1.79 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 68% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
0.6% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
VIENNA (capital) 1.693 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.73 male(s)/female
total population:
0.95 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 179
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4.26 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 195
male:
5.16 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
3.33 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 79.91 years
country comparison to the world: 33
male:
77 years
female:
82.97 years (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.41 children born/woman (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200
|
|
|
|
|
11% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|
|
4.749 physicians/1,000 population (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
7.71 beds/1,000 population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
|
|
|
|
|
0.3% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
15,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 100 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
|
|
|
|
|
11% (2008)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|
|
5.4% of GDP (2007)
country comparison to the world: 47
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
98%
male:
NA
female:
NA
|
|
|
|
|
total: 15 years
male:
15 years
female:
15 years (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10%
country comparison to the world: 103
male:
10.5%
female:
9.4% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Austria
conventional short form:
Austria
local long form:
Republik Oesterreich
local short form:
Oesterreich
|
|
|
|
|
federal republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Vienna
geographic coordinates:
48 12 N, 16 22 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
9 states (Bundeslaender, singular - Bundesland); Burgenland, Karnten (Carinthia), Niederoesterreich (Lower Austria), Oberoesterreich (Upper Austria), Salzburg, Steiermark (Styria), Tirol (Tyrol), Vorarlberg, Wien (Vienna)
|
|
|
|
|
12 November 1918 (republic proclaimed); notable earlier dates: 976 (Margravate of Austria established); 17 September 1156 (Duchy of Austria founded); 11 August 1804 (Austrian Empire proclaimed)
|
|
|
|
|
National Day, 26 October (1955); note - commemorates the passage of the law on permanent neutrality
|
|
|
|
|
1 October 1920; revised 1929; reinstated 1 May 1945; revised many times; note - during the period 1 May 1934-1 May 1945 there was a fascist (corporative) constitution in place
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts by the Constitutional Court
|
|
|
|
|
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
16 years of age; universal; note - reduced from 18 years of age in 2007
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Heinz FISCHER (SPOe) (since 8 July 2004)
head of government:
Chancellor Werner FAYMANN (SPOe) (since 2 December 2008); Vice Chancellor Michael SPINDELEGGER (OeVP) (since 21 April 2011)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers chosen by the president on the advice of the chancellor
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected for a six-year term (eligible for a second term) by direct popular vote and formally sworn into office before the Federal Assembly or Bundesversammlung; presidential election last held on 25 April 2010 (next to be held on 25 April 2016); chancellor formally chosen by the president but determined by the coalition parties forming a parliamentary majority; vice chancellor chosen by the president on the advice of the chancellor
election results:
Heinz FISCHER reelected president; percent of vote - Heinz FISCHER 79.33%, Barbara ROSENKRANZ 15.24%, Rudolf GEHRING 5.43%
note:
government coalition - SPOe and OeVP
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral Federal Assembly or Bundesversammlung consists of Federal Council or Bundesrat (62 seats; delegates appointed by state parliaments with each state receiving 3 to 12 seats in proportion to its population; members serve five- or six-year terms) and the National Council or Nationalrat (183 seats; members elected by popular vote for a five-year term under a system of proportional representation with partially-open party lists)
elections:
National Council - last held on 28 September 2008 (next to be held by September 2013)
election results:
National Council - percent of vote by party - SPOe 29.3%, OeVP 26%, FPOe 17.5%, BZOe 10.7%, Greens 10.4%, other 6.1%; seats by party - SPOe 57, OeVP 51, FPOe 34, BZOe 21, Greens 20; note - seats by party since 2010 - SPOe 57, OeVP 51, FPOe 39, BZOe 16, Greens 20
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Judicial Court or Oberster Gerichtshof; Administrative Court or Verwaltungsgerichtshof; Constitutional Court or Verfassungsgerichtshof
|
|
|
|
|
Alliance for the Future of Austria or BZOe [Josef BUCHER]; Austrian People's Party or OeVP [Michael SPINDELEGGER]; Freedom Party of Austria or FPOe [Heinz Christian STRACHE]; Social Democratic Party of Austria or SPOe [Werner FAYMANN]; The Greens [Eva GLAWISCHNIG]; Communist Party of Austria of KPOe [Mirko MESSNER]; "Team Stronach for Austria" [Frank STRONACHI]
|
|
|
|
|
Austrian Trade Union Federation or OeGB (nominally independent but primarily Social Democratic); Federal Economic Chamber; Labor Chamber or AK (Social Democratic-leaning think tank); OeVP-oriented Association of Austrian Industrialists or IV; Roman Catholic Church, including its chief lay organization, Catholic Action
other:
three composite leagues of the Austrian People's Party or OeVP representing business, labor, farmers, and other nongovernment organizations in the areas of environment and human rights
|
|
|
|
|
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CD, CE, CEI, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-9, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PFP, Schengen Convention, SELEC (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIFIL, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Hans Peter MANZ
chancery:
3524 International Court NW, Washington, DC 20008-3035
telephone:
[1] (202) 895-6700
FAX:
[1] (202) 895-6750
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, Los Angeles, New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador William C. EACHO III
embassy:
Boltzmanngasse 16, A-1090, Vienna
mailing address:
use embassy street address
telephone:
[43] (1) 31339-0
FAX:
[43] (1) 3100682
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), white, and red; the flag design is certainly one of the oldest - if not the oldest - national banners in the world; according to tradition, in 1191, following a fierce battle in the Third Crusade, Duke Leopold V of Austria's white tunic became completely blood-spattered; upon removal of his wide belt or sash, a white band was revealed; the red-white-red color combination was subsequently adopted as his banner
|
|
|
|
|
black eagle
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Bundeshymne" (Federal Hymn)
lyrics/music:
Paula von PRERADOVIC/Wolfgang Amadeus MOZART or Johann HOLZER (disputed)
note:
adopted 1947; the anthem is also known as "Land der Berge, Land am Strome" (Land of the Mountains, Land on the River); Austria adopted a new national anthem after World War II to replace the former imperial anthem composed by Franz Josef HAYDN, which had been appropriated by Germany in 1922 and was now associated with the Nazi regime
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Austria, with its well-developed market economy, skilled labor force, and high standard of living, is closely tied to other EU economies, especially Germany's. Its economy features a large service sector, a sound industrial sector, and a small, but highly developed agricultural sector. Following several years of solid foreign demand for Austrian exports and record employment growth, the international financial crisis of 2008 and subsequent global economic downturn led to a sharp but brief recession. Austrian GDP contracted 3.8% in 2009 but saw positive growth of about 2% in 2010 and 2.7% in 2011. Growth fell below 1% in 2012. Unemployment did not rise as steeply in Austria as elsewhere in Europe, partly because the government subsidized reduced working hour schemes to allow companies to retain employees. Stabilization measures, stimulus spending, and an income tax reform pushed the budget deficit to 4.5% in 2010 and 2.6% in 2011, from only about 0.9% in 2008. The international financial crisis of 2008 caused difficulties for Austria's largest banks whose extensive operations in central, eastern, and southeastern Europe faced large losses. The government provided bank support - including in some instances, nationalization - to support aggregate demand and stabilize the banking system. Austria's fiscal position compares favorably with other euro-zone countries, but it faces considerable external risks, such as Austrian banks' continued high exposure to central and eastern Europe as well as political and economic uncertainties caused by the European sovereign debt crisis. In 2011 the government attempted to pass a constitutional amendment limiting public debt to 60% of GDP by 2020, but it was unable to obtain sufficient support in parliament and instead passed the measure as a simple law. In March 2012, the Austrian parliament approved an austerity budget that will bring public finances into balance by 2016. In 2012, the budget deficit rose to 2.9% of GDP.
|
|
|
|
|
$357.8 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
$355.6 billion (2011 est.)
$346.3 billion (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$391.5 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.6% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 175
2.7% (2011 est.)
2.1% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$42,500 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
$42,200 (2011 est.)
$41,300 (2010 est.)
note:
data are in 2012 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 1.5%
industry:
29.4%
services:
69.1% (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.655 million (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 5.5%
industry:
27.5%
services:
67% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
4.2% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 4%
highest 10%:
22% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
26 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 129
31 (1995)
|
|
|
|
|
22% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $187.3 billion
expenditures:
$198.6 billion (2012 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
47.8% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
-2.9% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
|
|
|
|
|
74.3% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
72.2% of GDP (2011 est.)
note:
this is general government gross debt, defined in the Maastricht Treaty as consolidated general government gross debt at nominal value, outstanding at the end of the year; it covers the following categories of government liabilities (as defined in ESA95): currency and deposits (AF.2), securities other than shares excluding financial derivatives (AF.3, excluding AF.34), and loans (AF.4); the general government sector comprises the sub-sectors of central government, state government, local government and social security funds; as a percentage of GDP, the GDP used as a denominator is the gross domestic product in current year prices
|
|
|
|
|
2.3% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
3.5% (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.4% (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
3.3% (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$194.8 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
$176.5 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
note:
see entry for the European Union for money supply for the entire euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 17 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own borders
|
|
|
|
|
$426.5 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
$400.8 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$549 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
$526.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$82.37 billion (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 41
$118 billion (31 December 2010)
$107.2 billion (31 December 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
grains, potatoes, wine, fruit; dairy products, cattle, pigs, poultry; lumber
|
|
|
|
|
7.5% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
$8.17 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
$7.75 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$164.1 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
$173.6 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, motor vehicles and parts, paper and paperboard, metal goods, chemicals, iron and steel, textiles, foodstuffs
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 32.3%, Italy 7.8%, Switzerland 4.4%, France 4.2% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$173.9 billion (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
$183.3 billion (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, motor vehicles, chemicals, metal goods, oil and oil products; foodstuffs
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 42.8%, Italy 6.8%, Switzerland 5.5%, Netherlands 4% (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
$25.16 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
$22.28 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$883.5 billion (30 June 2011)
country comparison to the world: 18
$755 billion (30 June 2010)
|
|
|
|
|
$290.2 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
$271.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$313.9 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
$300.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
euros (EUR) per US dollar -
0.7838 (2012 est.)
0.7185 (2011 est.)
755 (2010 est.)
0.7198 (2009 est.)
0.6827 (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
calendar year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
59.47 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|
|
63.8 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
|
|
|
|
|
16.75 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
24.98 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
|
21.11 million kW (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
19.6% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191
|
|
|
|
|
0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
|
|
|
|
|
38.7% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|
|
20.4% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
25,750 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
|
|
|
|
|
137,100 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
|
|
|
|
|
50 million bbl (1 January 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
|
|
|
|
|
188,500 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|
|
262,900 bbl/day (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
46,680 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
|
|
|
|
|
158,300 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
|
|
|
|
|
1.776 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|
|
9.015 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
|
|
|
|
|
4.96 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
|
|
|
|
|
14.28 billion cu m (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
|
|
|
|
|
16.14 billion cu m (1 January 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
|
|
|
|
|
69.46 million Mt (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.388 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
13.023 million (2011)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: highly developed and efficient
domestic:
fixed-line subscribership has been in decline since the mid-1990s with mobile-cellular subscribership eclipsing it by the late 1990s; the fiber-optic net is very extensive; all telephone applications and Internet services are available
international:
country code - 43; satellite earth stations - 15; in addition, there are about 600 VSATs (very small aperture terminals) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
Austria's public broadcaster, Osterreichischer Rundfunk (ORF), was the main broadcast source until commercial radio and TV service was introduced in the 1990s; cable and satellite TV are available, including German TV stations (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.at
|
|
|
|
|
3.512 million (2012)
country comparison to the world: 30
|
|
|
|
|
6.143 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 43
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
52 (2012)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
total: 24
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
5
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
4
under 914 m:
13 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 28
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
3
under 914 m:
24 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 3,028 km; oil 663 km; refined products 157 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 6,399 km
country comparison to the world: 29
standard gauge:
5,927 km 1.435-m gauge (3,853 km electrified)
narrow gauge:
384 km 1.000-m gauge (15 km electrified); 88 km 0.760-m gauge (10 km electrified) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 124,508 km
country comparison to the world: 37
paved:
124,508 km (includes 1,719 km of expressways) (2012)
|
|
|
|
|
358 km (2011)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
registered in other countries: 3 (Cyprus 1, Kazakhstan 1, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 1) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|
|
Enns, Krems, Linz, Vienna
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Land Forces (KdoLdSK), Air Forces (KdoLuSK)
|
|
|
|
|
registration requirement at age 17; males under the age of 35 must complete basic military training (6 month duration); males 17 to 50 years old in the militia or inactive reserve are subject to compulsory military service (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,941,110
females age 16-49:
1,910,434 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,579,862
females age 16-49:
1,554,130 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 48,108
female:
45,752 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.8% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 145
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Austria |
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 18,473 (Russia); 8,636 (Afghanistan) (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
transshipment point for Southwest Asian heroin and South American cocaine destined for Western Europe; increasing consumption of European-produced synthetic drugs
|
|
|
|
|
|