|
|
In 1895, military defeat forced China to cede Taiwan to Japan. Taiwan reverted to Chinese control after World War II. Following the Communist victory on the mainland in 1949, 2 million Nationalists fled to Taiwan and established a government using the 1947 constitution drawn up for all of China. Over the next five decades, the ruling authorities gradually democratized and incorporated the local population within the governing structure. In 2000, Taiwan underwent its first peaceful transfer of power from the Nationalist to the Democratic Progressive Party. Throughout this period, the island prospered and became one of East Asia's economic "Tigers." The dominant political issues continue to be the relationship between Taiwan and China - specifically the question of Taiwan's eventual status - as well as domestic political and economic reform.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Eastern Asia, islands bordering the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, South China Sea, and Taiwan Strait, north of the Philippines, off the southeastern coast of China
|
|
|
|
|
23 30 N, 121 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 35,980 sq km
country comparison to the world: 138
land:
32,260 sq km
water:
3,720 sq km
note:
includes the Pescadores, Matsu, and Quemoy islands
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Maryland and Delaware combined
|
|
|
|
|
0 km
|
|
|
|
|
1,566.3 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
tropical; marine; rainy season during southwest monsoon (June to August); cloudiness is persistent and extensive all year
|
|
|
|
|
eastern two-thirds mostly rugged mountains; flat to gently rolling plains in west
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: South China Sea 0 m
highest point:
Yu Shan 3,952 m
|
|
|
|
|
small deposits of coal, natural gas, limestone, marble, and asbestos
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 24%
permanent crops:
1%
other:
75% (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
67 cu km (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
earthquakes; typhoons
volcanism:
Kueishantao Island (elev. 401 m), east of Taiwan, is its only historically active volcano, although it has not erupted in centuries
|
|
|
|
|
air pollution; water pollution from industrial emissions, raw sewage; contamination of drinking water supplies; trade in endangered species; low-level radioactive waste disposal
|
|
|
|
|
party to: none of the selected agreements because of Taiwan's international status
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location adjacent to both the Taiwan Strait and the Luzon Strait
|
|
|
|
|
|
23,071,779 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 15.6% (male 1,875,359/female 1,732,007)
15-64 years:
73.4% (male 8,538,881/female 8,406,716)
65 years and over:
10.9% (male 1,198,591/female 1,320,225) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 37.6 years
male:
36.9 years
female:
38.3 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.193% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
|
|
|
|
|
8.9 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 211
|
|
|
|
|
7 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
|
|
|
|
|
0.03 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.084 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.08 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.92 male(s)/female
total population:
1.02 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 5.18 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 181
male:
5.46 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
4.88 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 78.32 years
country comparison to the world: 51
male:
75.5 years
female:
81.36 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.15 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 220
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Taiwan (singular and plural)
note:
example - he or she is from Taiwan; they are from Taiwan
adjective:
Taiwan
|
|
|
|
|
Taiwanese (including Hakka) 84%, mainland Chinese 14%, indigenous 2%
|
|
|
|
|
mixture of Buddhist and Taoist 93%, Christian 4.5%, other 2.5%
|
|
|
|
|
Mandarin Chinese (official), Taiwanese (Min), Hakka dialects
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
96.1%
male:
NA
female:
NA (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form:
Taiwan
local long form:
none
local short form:
Taiwan
former:
Formosa
|
|
|
|
|
multiparty democracy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Taipei
geographic coordinates:
25 03 N, 121 30 E
time difference:
UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
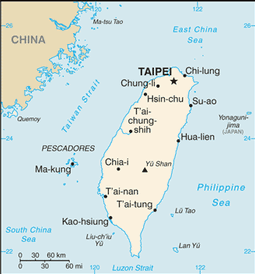
includes main island of Taiwan plus smaller islands nearby and off coast of China's Fujian Province; Taiwan is divided into 14 counties (hsien, singular and plural), 3 municipalities (shih, singular and plural), and 5 special municipalities (chih-hsia-shih, singular and plural)
note:
Taiwan uses a variety of romanization systems; while a modified Wade-Giles system still dominates, the city of Taipei has adopted a Pinyin romanization for street and place names within its boundaries; other local authorities use different romanization systems; names for administrative divisions that follow are taken from the Taiwan Yearbook 2007 published by the Government Information Office in Taipei.
counties:
Changhua, Chiayi (county), Hsinchu (county), Hualien, Kinmen, Lienchiang, Miaoli, Nantou, Penghu, Pingtung, Taitung, Taoyuan, Yilan, Yunlin
municipalities:
Chiayi (city), Hsinchu (city), Keelung
special municipalities:
Kaohsiung, New Taipei, Taichung, Tainan, Taipei
|
|
|
|
|
Republic Day (Anniversary of the Chinese Revolution), 10 October (1911)
|
|
|
|
|
adopted 25 December 1946; promulgated 1 January 1947; effective 25 December 1947; amended many times
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
20 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President MA Ying-jeou (since 20 May 2008); Vice President Vincent SIEW (since 20 May 2008)
head of government:
Premier (President of the Executive Yuan) WU Den-yih (since 10 September 2009); Vice Premier (Vice President of Executive Yuan) Sean CHEN (since 17 May 2010)
cabinet:
Executive Yuan - ministers appointed by president on recommendation of premier
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for four-year terms (eligible for a second term); election last held on 22 March 2008 (next to be held on 14 January 2012); premier appointed by the president; vice premiers appointed by the president on the recommendation of the premier
election results:
MA Ying-jeou elected president; percent of vote - MA Ying-jeou 58.45%, Frank HSIEH 41.55%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Legislative Yuan (113 seats - 73 district members elected by popular vote, 34 at-large members elected on basis of proportion of islandwide votes received by participating political parties, 6 elected by popular vote among aboriginal populations; members to serve four-year terms); parties must receive 5% of vote to qualify for at-large seats
elections:
Legislative Yuan - last held on 12 January 2008 (next to be held on 14 January 2012)
election results:
Legislative Yuan - percent of vote by party - KMT 53.5%, DPP 38.2%, NPSU 2.4%, PFP 0.3%, others 1.6%, independents 4%; seats by party - KMT 81, DPP 27, NPSU 3, PFP 1, independent 1; note - following the 2008 elections, several rounds of byelections were held to fill seats vacated as a result of corruption changes; seats by party as of January 2011 - KMT 74, DPP 31, NPSU 3, independent 2, vacant 3
|
|
|
|
|
Judicial Yuan (justices appointed by the president with consent of the Legislative Yuan)
|
|
|
|
|
Democratic Progressive Party or DPP [TSAI Ing-wen]; Kuomintang or KMT (Nationalist Party) [MA Ying-jeou]; Non-Partisan Solidarity Union or NPSU [LIN Pin-kuan]; People First Party or PFP [James SOONG]
|
|
|
|
|
environmental groups; independence movement; various business groups
note:
debate on Taiwan independence has become acceptable within the mainstream of domestic politics on Taiwan; public opinion polls consistently show a substantial majority of Taiwan people supports maintaining Taiwan's status quo for the foreseeable future; advocates of Taiwan independence oppose the stand that the island will eventually unify with mainland China; advocates of eventual unification predicate their goal on the democratic transformation of the mainland
|
|
|
|
|
ADB, APEC, BCIE, ICC, IOC, ITUC, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
none; commercial and cultural relations with the people in the United States are maintained through an unofficial instrumentality, the Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States (TECRO), a private nonprofit corporation that performs citizen and consular services similar to those at diplomatic posts
representative:
Jason C. YUAN
office:
4201 Wisconsin Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20016
telephone:
[1] 202 895-1800
Taipei Economic and Cultural Offices (branch offices):
Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Guam, Houston, Honolulu, Kansas City, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, San Francisco, Seattle
|
|
|
|
|
none; commercial and cultural relations with the people on Taiwan are maintained through an unofficial instrumentality, the American Institute in Taiwan (AIT), a private nonprofit corporation that performs citizen and consular services similar to those at diplomatic posts
director:
William A. STANTON
office:
#7 Lane 134, Hsin Yi Road, Section 3, Taipei, Taiwan
telephone:
[1] [886] (02) 2162-2000
FAX:
[1] [886] (07) 238-7744
other offices:
Kaohsiung
|
|
|
|
|
red field with a dark blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing a white sun with 12 triangular rays; the blue and white design of the canton (symbolizing the sun of progress) dates to 1895; it was later adopted as the flag of the Kuomintang Party; blue signifies liberty, justice, and democracy; red stands for fraternity, sacrifice, and nationalism, white represents equality, frankness, and the people's livelihood; the 12 rays of the sun are those of the months and the twelve traditional Chinese hours (each ray equals two hours)
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Zhonghua Minguo guoge" (National Anthem of the Republic of China)
lyrics/music:
HU Han-min, TAI Chi-t'ao, and LIAO Chung-k'ai/CHENG Mao-Yun
note:
adopted 1930; the anthem is also the song of the Kuomintang Party; it is informally known as "San Min Chu I" or "San Min Zhu Yi" (Three Principles of the People); because of political pressure from China, "Guo Qi Ge" (National Banner Song) is used at international events rather than the official anthem of Taiwan; the "National Banner Song" has gained popularity in Taiwan and is commonly used during flag raisings
|
|
|
|
|
|
Taiwan has a dynamic capitalist economy with gradually decreasing government guidance of investment and foreign trade. In keeping with this trend, some large, state-owned banks and industrial firms have been privatized. Exports, led by electronics and machinery, generate about 70% of Taiwan's GDP growth, and have provided the primary impetus for economic development. This heavy dependence on exports exposes the economy to upturns and downturns in world demand. In 2009, Taiwan's GDP contracted 1.9%, due primarily to a 20% year-on-year decline in exports. In 2010 GDP grew 10.5%, as exports returned to the level of previous years. Taiwan's diplomatic isolation, low birth rate, and rapidly aging population are major long-term challenges. Free trade agreements have proliferated in East Asia over the past several years, but so far Taiwan has been excluded from this greater economic integration, largely because of its diplomatic status. Taiwan's Total Fertility rate of just over one child per woman is among the lowest in the world, raising the prospect of future labor shortages, falling domestic demand, and declining tax revenues. Taiwan's population is aging quickly, with the number of people over 65 accounting for 10.9% of the island's total population as 2011. The island runs a large trade surplus, and its foreign reserves are the world's fourth largest, behind China, Japan, and Russia. Since President MA Ying-jeou took office in May 2008, cross-Strait economic ties have increased significantly. Since 2005 China has overtaken the US to become Taiwan's second-largest source of imports after Japan. China is also the island's number one destination for foreign direct investment. Taiwan has focused much of its efforts on improving the cross-Strait economic relationship. Three financial memorandums of understanding, covering banking, securities, and insurance, took effect in mid-January 2010, opening the island to greater investments from the mainland's financial firms and institutional investors, and providing new opportunities for Taiwan financial firms to operate in China. Taiwan and the mainland in June 2010 signed the landmark Economic Cooperation Framework Agreement (ECFA), an agreement that the Taiwan authorities hope will eventually lead to a free-trade arrangement that will increase cross-Strait economic ties by lowering tariffs on a number of goods and by reducing market access barriers for services. The Taiwan authorities have said that the ECFA will serve as a stepping stone toward trade pacts with other regional partners and they announced that formal negotiations towards an economic cooperation agreement with Singapore would begin in 2011. Closer economic links with the mainland brings greater opportunities for the Taiwan economy, but also poses new challenges. For example, FDI in China has resulted in Chinese import substitution away from Taiwan's exports and a restriction of potential job creation in Taiwan.
|
|
|
|
|
$821.8 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
$741.5 billion (2009 est.)
$756.1 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$430.6 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10.8% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
-1.9% (2009 est.)
0.7% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$35,700 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
$32,300 (2009 est.)
$33,000 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 1.4%
industry:
31.1%
services:
67.5% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
11.07 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 5.2%
industry:
35.9%
services:
58.8% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.2% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
5.9% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.16% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 6.4%
highest 10%:
40.3% (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
32.6 (2000)
country comparison to the world: 100
|
|
|
|
|
21.8% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $72.24 billion
expenditures:
$79.65 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
33.9% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
33.1% of GDP (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
-0.9% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
1.625% (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 132
1.25% (February 2009)
|
|
|
|
|
2.68% (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 152
2.56% (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$377.3 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
$328.2 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.022 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
$911.9 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$751.5 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
$671 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$784.1 billion (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 14
$657.3 billion (31 December 2009)
$354.7 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
rice, vegetables, fruit, tea, flowers; pigs, poultry; fish
|
|
|
|
|
electronics, communications and information technology products, petroleum refining, armaments, chemicals, textiles, iron and steel, machinery, cement, food processing, vehicles, consumer products, pharmaceuticals
|
|
|
|
|
26.4% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
|
|
|
|
|
229.1 billion kWh (2009)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
|
220.8 billion kWh (2009)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
276,800 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
|
|
|
|
|
834,000 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
303,000 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
|
|
|
|
|
876,300 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
2.8 million bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
350.7 million cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
11.63 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 190
|
|
|
|
|
11.59 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
6.229 billion cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
|
|
|
|
|
$39 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
$42.92 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$274.6 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
$203.4 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
electronics, flat panels, machinery; metals; textiles, plastics, chemicals; optical, photographic, measuring, and medical instruments
|
|
|
|
|
China 28.1%, Hong Kong 13.8%, US 11.5%, Japan 6.6%, Singapore 4.4% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$251.4 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
$174.4 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
electronics, machinery, crude petroleum, precision instruments, organic chemicals, metals
|
|
|
|
|
Japan 20.7%, China 14.2%, US 10%, South Korea 6.4%, Saudi Arabia 4.7% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$387.2 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
$353 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$91.41 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
$82.02 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$111.1 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$107.2 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$162.9 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
$145.3 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
New Taiwan dollars (TWD) per US dollar -
31.642 (2010)
33.061 (2009)
31.53 (2008)
32.84 (2007)
32.534 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.596 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
26.959 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 33
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: provides telecommunications service for every business and private need
domestic:
thoroughly modern; completely digitalized
international:
country code - 886; roughly 15 submarine fiber cables provide links throughout Asia, Australia, the Middle East, Europe, and the US; satellite earth stations - 2
|
|
|
|
|
5 free-to-air nationwide television networks operating roughly 75 TV stations; about 85% of households utilize multi-channel cable TV; national and regional radio networks with about 170 radio stations broadcasting (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.tw
|
|
|
|
|
6.336 million (2010)
country comparison to the world: 15
|
|
|
|
|
16.147 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|
|
|
41 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|
|
total: 38
over 3,047 m:
8
2,438 to 3,047 m:
8
1,524 to 2,437 m:
11
914 to 1,523 m:
7
under 914 m:
4 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3
1,524 to 2,437 m:
2
under 914 m:
1 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
4 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 412 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,482 km
country comparison to the world: 79
standard gauge:
340 km 1.435-m gauge
narrow gauge:
1,085 km 1.067-m gauge; 57 km 0.762-m gauge
note:
the 0.762 gauge track belong to three entities, Taiwan Cement, TaiPower, and the Forestry Bureau (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 41,475 km
country comparison to the world: 87
paved:
41,033 km (includes 720 km of expressways)
unpaved:
442 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 101
country comparison to the world: 50
by type:
bulk carrier 28, cargo 19, chemical tanker 2, container 27, passenger/cargo 4, petroleum tanker 12, refrigerated cargo 7, roll on/roll off 2
foreign-owned:
2 (France 1, Vietnam 1)
registered in other countries:
574 (Cambodia 1, Honduras 2, Hong Kong 26, Indonesia 1, Italy 11, Kiribati 5, Liberia 88, Marshall Islands 2, Panama 337, Philippines 1, Sierra Leone 1, Singapore 79, Thailand 1, UK 11, unknown 8) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Chilung (Keelung), Kaohsiung, Hualian, Taichung
|
|
|
|
|
|
Army, Navy (includes Marine Corps), Air Force, Coast Guard Administration, Armed Forces Reserve Command, Combined Service Forces Command, Armed Forces Police Command
|
|
|
|
|
19-35 years of age for male compulsory military service; service obligation - 2 years; women may enlist; women in Air Force service are restricted to noncombat roles; reserve obligation to age 30 (Army); the Ministry of Defense is in the process of implementing a voluntary enlistment system over the period 2010-2015, although nonvolunteers will still be required to perform alternative service or go through 4 months of military training (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 6,183,567
females age 16-49:
6,006,676 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 5,074,173
females age 16-49:
4,951,088 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 166,190
female:
155,306 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.2% of GDP; note - in 2009, the Taiwanese president pledged to maintain defense spending at 3.0% or higher; projected 2.73% for 2011 (2009)
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Taiwan |
|
|
involved in complex dispute with Brunei, China, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Vietnam over the Spratly Islands, and with China and the Philippines over Scarborough Reef; the 2002 "Declaration on the Conduct of Parties in the South China Sea" has eased tensions but falls short of a legally binding "code of conduct" desired by several of the disputants; Paracel Islands are occupied by China, but claimed by Taiwan and Vietnam; in 2003, China and Taiwan became more vocal in rejecting both Japan's claims to the uninhabited islands of the Senkaku-shoto (Diaoyu Tai) and Japan's unilaterally declared exclusive economic zone in the East China Sea where all parties engage in hydrocarbon prospecting
|
|
|
|
|
regional transit point for heroin, methamphetamine, and precursor chemicals; transshipment point for drugs to Japan; major problem with domestic consumption of methamphetamine and heroin; rising problems with use of ketamine and club drugs
|
|
|
|
|