|
|
Modern Turkey was founded in 1923 from the Anatolian remnants of the defeated Ottoman Empire by national hero Mustafa KEMAL, who was later honored with the title Ataturk or "Father of the Turks." Under his authoritarian leadership, the country adopted wide-ranging social, legal, and political reforms. After a period of one-party rule, an experiment with multi-party politics led to the 1950 election victory of the opposition Democratic Party and the peaceful transfer of power. Since then, Turkish political parties have multiplied, but democracy has been fractured by periods of instability and intermittent military coups (1960, 1971, 1980), which in each case eventually resulted in a return of political power to civilians. In 1997, the military again helped engineer the ouster - popularly dubbed a "post-modern coup" - of the then Islamic-oriented government. Turkey intervened militarily on Cyprus in 1974 to prevent a Greek takeover of the island and has since acted as patron state to the "Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus," which only Turkey recognizes. A separatist insurgency begun in 1984 by the Kurdistan Workers' Party (PKK) - now known as the People's Congress of Kurdistan or Kongra-Gel (KGK) - has dominated the Turkish military's attention and claimed more than 30,000 lives. After the capture of the group's leader in 1999, the insurgents largely withdrew from Turkey mainly to northern Iraq. In 2004, KGK announced an end to its ceasefire and attacks attributed to the KGK increased. Turkey joined the UN in 1945 and in 1952 it became a member of NATO. In 1964, Turkey became an associate member of the European Community. Over the past decade, it has undertaken many reforms to strengthen its democracy and economy; it began accession membership talks with the European Union in 2005.
|
|
|
|
|
|
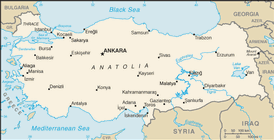
Southeastern Europe and Southwestern Asia (that portion of Turkey west of the Bosporus is geographically part of Europe), bordering the Black Sea, between Bulgaria and Georgia, and bordering the Aegean Sea and the Mediterranean Sea, between Greece and Syria
|
|
|
|
|
39 00 N, 35 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 783,562 sq km
country comparison to the world: 37
land:
769,632 sq km
water:
13,930 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly larger than Texas
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2,648 km
border countries:
Armenia 268 km, Azerbaijan 9 km, Bulgaria 240 km, Georgia 252 km, Greece 206 km, Iran 499 km, Iraq 352 km, Syria 822 km
|
|
|
|
|
7,200 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 6 nm in the Aegean Sea; 12 nm in Black Sea and in Mediterranean Sea
exclusive economic zone:
in Black Sea only: to the maritime boundary agreed upon with the former USSR
|
|
|
|
|
temperate; hot, dry summers with mild, wet winters; harsher in interior
|
|
|
|
|
high central plateau (Anatolia); narrow coastal plain; several mountain ranges
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Mediterranean Sea 0 m
highest point:
Mount Ararat 5,166 m
|
|
|
|
|
coal, iron ore, copper, chromium, antimony, mercury, gold, barite, borate, celestite (strontium), emery, feldspar, limestone, magnesite, marble, perlite, pumice, pyrites (sulfur), clay, arable land, hydropower
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 29.81%
permanent crops:
3.39%
other:
66.8% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
52,150 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
234 cu km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 39.78 cu km/yr (15%/11%/74%)
per capita:
544 cu m/yr (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
severe earthquakes, especially in northern Turkey, along an arc extending from the Sea of Marmara to Lake Van
volcanism:
Turkey experiences little volcanic activity; its three historically active volcanoes; Ararat, Nemrut Dagi, and Tendurek Dagi have not erupted since the 19th century or earlier
|
|
|
|
|
water pollution from dumping of chemicals and detergents; air pollution, particularly in urban areas; deforestation; concern for oil spills from increasing Bosporus ship traffic
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Environmental Modification
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location controlling the Turkish Straits (Bosporus, Sea of Marmara, Dardanelles) that link Black and Aegean Seas; Mount Ararat, the legendary landing place of Noah's ark, is in the far eastern portion of the country
|
|
|
|
|
|
78,785,548 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 26.6% (male 10,707,793/female 10,226,999)
15-64 years:
67.1% (male 26,741,332/female 26,162,757)
65 years and over:
6.3% (male 2,259,422/female 2,687,245) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 28.5 years
male:
28.1 years
female:
28.8 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.235% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
17.93 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
6.1 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
|
|
|
|
|
0.51 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 70% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
1.7% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Istanbul 10.378 million; ANKARA (capital) 3.846 million; Izmir 2.679 million; Bursa 1.559 million; Adana 1.339 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.84 male(s)/female
total population:
1.02 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 23.94 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 84
male:
25 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
22.82 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 72.5 years
country comparison to the world: 126
male:
70.61 years
female:
74.49 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.15 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
|
|
|
|
|
less than 0.1%; less than 0.1% note - no country specific models provided (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
|
|
|
|
|
4,600 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 200 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 96% of population
total: 99% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 4% of population
total: 1% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 97% of population
rural: 75% of population
total: 90% of population
unimproved:
urban: 3% of population
rural: 25% of population
total: 10% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Turk(s)
adjective:
Turkish
|
|
|
|
|
Turkish 70-75%, Kurdish 18%, other minorities 7-12% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim 99.8% (mostly Sunni), other 0.2% (mostly Christians and Jews)
|
|
|
|
|
Turkish (official), Kurdish, other minority languages
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
87.4%
male:
95.3%
female:
79.6% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 12 years
male:
12 years
female:
11 years (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
2.9% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 137
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Turkey
conventional short form:
Turkey
local long form:
Turkiye Cumhuriyeti
local short form:
Turkiye
|
|
|
|
|
republican parliamentary democracy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Ankara
geographic coordinates:
39 56 N, 32 52 E
time difference:
UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Monday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
81 provinces (iller, singular - ili); Adana, Adiyaman, Afyonkarahisar, Agri, Aksaray, Amasya, Ankara, Antalya, Ardahan, Artvin, Aydin, Balikesir, Bartin, Batman, Bayburt, Bilecik, Bingol, Bitlis, Bolu, Burdur, Bursa, Canakkale, Cankiri, Corum, Denizli, Diyarbakir, Duzce, Edirne, Elazig, Erzincan, Erzurum, Eskisehir, Gaziantep, Giresun, Gumushane, Hakkari, Hatay, Igdir, Isparta, Istanbul, Izmir (Smyrna), Kahramanmaras, Karabuk, Karaman, Kars, Kastamonu, Kayseri, Kilis, Kirikkale, Kirklareli, Kirsehir, Kocaeli, Konya, Kutahya, Malatya, Manisa, Mardin, Mersin, Mugla, Mus, Nevsehir, Nigde, Ordu, Osmaniye, Rize, Sakarya, Samsun, Sanliurfa, Siirt, Sinop, Sirnak, Sivas, Tekirdag, Tokat, Trabzon (Trebizond), Tunceli, Usak, Van, Yalova, Yozgat, Zonguldak
|
|
|
|
|
29 October 1923 (successor state to the Ottoman Empire)
|
|
|
|
|
Republic Day, 29 October (1923)
|
|
|
|
|
7 November 1982; amended several times; note - amendment passed by referendum 21 October 2007 concerning presidential elections
|
|
|
|
|
civil law system based on various European legal systems notably the Swiss civil code; note - member of the European Court of Human Rights (ECHR), although Turkey claims limited derogations on the ratified European Convention on Human Rights
|
|
|
|
|
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Abdullah GUL (since 28 August 2007)
head of government:
Prime Minister Recep Tayyip ERDOGAN (since 14 March 2003)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the president on the nomination of the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected directly for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); prime minister appointed by the president from among members of parliament
election results:
on 28 August 2007 the National Assembly elected Abdullah GUL president on the third ballot; National Assembly vote - 339
note:
in October 2007 Turkish voters approved a referendum package of constitutional amendments including a provision for direct presidential elections
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Grand National Assembly of Turkey or Turkiye Buyuk Millet Meclisi (550 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held on 22 July 2007 (next to be held by 12 June 2011)
election results:
percent of vote by party - AKP 46.7%, CHP 20.8%, MHP 14.3%, independents 5.2%, other 13.0%; seats by party - AKP 341, CHP 112, MHP 71, independents 26; note - seats by party as of 15 November 2010 - AKP 335, CHP 101, MHP 70, BDP 20, DSP 6, DP 1, TP 1, independents 7, vacant 9 (BDP entered parliament as independents; DSP entered parliament on CHP's party list; DP and TP switched to their respective parties after having been elected to parliament as an independent or on the list of another party); only parties surpassing the 10% threshold are entitled to parliamentary seats
|
|
|
|
|
Constitutional Court; High Court of Appeals (Yargitay); Council of State (Danistay); Court of Accounts (Sayistay); Military High Court of Appeals; Military High Administrative Court
|
|
|
|
|
Democratic Left Party or DSP [Masum TURKER]; Democratic Party or DP [Namik Kemal ZEYBEK]; Equality and Democracy Party or EDP [Ziva HALIS]; Felicity Party or SP [Necmettin ERBAKAN] (sometimes translated as Contentment Party); Freedom and Solidarity Party or ODP [Alper TAS]; Grand Unity Party or BBP [Yalcin TOPCU]; Justice and Development Party or AKP [Recep Tayyip ERDOGAN]; Nationalist Movement Party or MHP [Devlet BAHCELI]; Peace and Democracy Party or BDP [Selahattin DEMIRTAS]; People's Voice Party or HSP [Numan KURTULMUS]; Republican People's Party or CHP [Kemal KILICDAROGLU]; Turkey Party or TP [Abdullatif SENER]
note:
the parties listed above are some of the more significant of the 61 parties that Turkey had according to the Ministry of Interior statistics current as of May 2009
|
|
|
|
|
Confederation of Businessmen and Industrialists of Turkey or TUSKON [Rizanur MERAL]; Confederation of Public Sector Unions or KESK [Sami EVREN]; Confederation of Revolutionary Workers Unions or DISK [Suleyman CELEBI]; Independent Industrialists' and Businessmen's Association or MUSIAD [Omer Cihad VARDAN]; Moral Rights Workers Union or Hak-Is [Salim USLU]; Turkish Confederation of Employers' Unions or TISK [Tugrul KUDATGOBILIK]; Turkish Confederation of Labor or Turk-Is [Mustafa KUMLU]; Turkish Confederation of Tradesmen and Craftsmen or TESK [Bendevi PALANDOKEN]; Turkish Industrialists' and Businessmen's Association or TUSIAD [Umit BOYNER]; Turkish Union of Chambers of Commerce and Commodity Exchanges or TOBB [M. Rifat HISARCIKLIOGLU]
|
|
|
|
|
ADB (nonregional member), Australia Group, BIS, BSEC, CE, CERN (observer), CICA, D-8, EAPC, EBRD, ECO, EU (candidate country), FAO, FATF, G-20, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIC, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club (associate), PCA, SECI, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIS, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Namik TAN
chancery:
2525 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 612-6700
FAX:
[1] (202) 612-6744
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Douglas A. SILLIMAN
embassy:
110 Ataturk Boulevard, Kavaklidere, 06100 Ankara
mailing address:
PSC 93, Box 5000, APO AE 09823
telephone:
[90] (312) 455-5555
FAX:
[90] (312) 467-0019
consulate(s) general:
Istanbul
consulate(s):
Adana; note - there is a Consular Agent in Izmir
|
|
|
|
|
red with a vertical white crescent moon (the closed portion is toward the hoist side) and white five-pointed star centered just outside the crescent opening; the flag colors and designs closely resemble those on the banner of Ottoman Empire, which preceded modern-day Turkey; the crescent moon and star serve as insignia for the Turks, as well as being traditional symbols of Islam; according to legend, the flag represents the reflection of the moon and a star in a pool of blood of Turkish warriors
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Istiklal Marsi" (Independence March)
lyrics/music:
Mehmet Akif ERSOY/Zeki UNGOR
note:
lyrics adopted 1921, music adopted 1932; the anthem's original music was adopted in 1924; a new composition was agreed upon in 1932
|
|
|
|
|
|
Turkey's economy is increasingly driven by its industry and service sectors, although its traditional agriculture sector still accounts for about 30% of employment. An aggressive privatization program has reduced state involvement in basic industry, banking, transport, and communication, and an emerging cadre of middle-class entrepreneurs is adding dynamism to the economy. Turkey's traditional textiles and clothing sectors still account for one-third of industrial employment, despite stiff competition in international markets that resulted from the end of the global quota system. Other sectors, notably the automotive, construction, and electronics industries, are rising in importance and have surpassed textiles within Turkey's export mix. Oil began to flow through the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipeline in May 2006, marking a major milestone that will bring up to 1 million barrels per day from the Caspian to market. Several gas pipelines also are being planned to help move Central Asian gas to Europe via Turkey, which will help address Turkey's dependence on energy imports over the long term. After Turkey experienced a severe financial crisis in 2001, Ankara adopted financial and fiscal reforms as part of an IMF program. The reforms strengthened the country's economic fundamentals and ushered in an era of strong growth - averaging more than 6% annually until 2008, when global economic conditions and tighter fiscal policy caused GDP to contract in 2009, reduced inflation to 6.3% - a 34-year low - and cut the public sector debt-to-GPD ratio below 50%. Turkey's well-regulated financial markets and banking system weathered the global financial crisis and GDP rebounded strongly to 7.3% in 2010, as exports returned to normal levels following the recession. The economy, however, continues to be burdened by a high current account deficit and remains dependent on often volatile, short-term investment to finance its trade deficit. The stock value of FDI stood at $174 billion at year-end 2010, but inflows have slowed considerably in light of continuing economic turmoil in Europe, the source of much of Turkey's FDI. Further economic and judicial reforms and prospective EU membership are expected to boost Turkey's attractiveness to foreign investors. However, Turkey's relatively high current account deficit, uncertainty related to policy-making, and fiscal imbalances leave the economy vulnerable to destabilizing shifts in investor confidence.
|
|
|
|
|
$960.5 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
$887.7 billion (2009 est.)
$931.4 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$741.9 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
8.2% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
-4.7% (2009 est.)
0.7% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$12,300 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
$11,600 (2009 est.)
$12,300 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 8.8%
industry:
25.7%
services:
65.5% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
24.73 million
country comparison to the world: 24
note:
about 1.2 million Turks work abroad (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 29.5%
industry:
24.7%
services:
45.8% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
12.4% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
14.1% (2009 est.)
note:
underemployment amounted to 4% in 2008
|
|
|
|
|
17.11% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 1.9%
highest 10%:
33.2% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
41 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 55
43.6 (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
18% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $159.4 billion
expenditures:
$189.6 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
48.1% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
46.3% of GDP (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
8.7% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191
6.3% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
15% (22 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 6
25% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
$57.02 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
$44.94 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$255.5 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
$202.2 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$401.8 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
$373.1 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$225.7 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 35
$117.9 billion (31 December 2008)
$286.6 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
tobacco, cotton, grain, olives, sugar beets, hazelnuts, pulse, citrus; livestock
|
|
|
|
|
textiles, food processing, autos, electronics, mining (coal, chromate, copper, boron), steel, petroleum, construction, lumber, paper
|
|
|
|
|
6% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|
|
198.4 billion kWh (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|
|
198.1 billion kWh (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
1.12 billion kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
790 million kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
52,980 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
|
|
|
|
|
579,500 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|
|
133,100 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
|
|
|
|
|
734,600 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
|
262.2 million bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
|
|
|
|
|
1.014 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
|
|
|
|
|
35.07 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
|
|
|
|
|
708 million cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|
|
35.77 billion cu m (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
|
|
|
|
|
6.088 billion cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|
|
$-38.82 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
$-13.94 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$117.4 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
$109.6 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
apparel, foodstuffs, textiles, metal manufactures, transport equipment
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 9.6%, France 6.1%, UK 5.8%, Italy 5.8%, Iraq 5% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$166.3 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
$134.5 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery, chemicals, semi-finished goods, fuels, transport equipment
|
|
|
|
|
Russia 14%, Germany 10%, China 9%, US 6.1%, Italy 5.4%, France 5% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$78 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
$75 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$270.7 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
$268.3 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$84.45 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
$174 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$16.42 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
$15.42 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Turkish liras (TRY) per US dollar -
1.5181 (2010)
1.55 (2009)
1.3179 (2008)
1.319 (2007)
1.4286 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.534 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
|
62.78 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 17
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: comprehensive telecommunications network undergoing rapid modernization and expansion especially in mobile-cellular services
domestic:
additional digital exchanges are permitting a rapid increase in subscribers; the construction of a network of technologically advanced intercity trunk lines, using both fiber-optic cable and digital microwave radio relay, is facilitating communication between urban centers; remote areas are reached by a domestic satellite system; the number of subscribers to mobile-cellular telephone service is growing rapidly
international:
country code - 90; international service is provided by the SEA-ME-WE-3 submarine cable and by submarine fiber-optic cables in the Mediterranean and Black Seas that link Turkey with Italy, Greece, Israel, Bulgaria, Romania, and Russia; satellite earth stations - 12 Intelsat; mobile satellite terminals - 328 in the Inmarsat and Eutelsat systems (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
national public broadcaster Turkish Radio and Television Corporation (TRT) operates multiple TV and radio networks and stations; multiple privately-owned national television stations and up to 300 private regional and local television stations; multi-channel cable TV subscriptions are obtainable; more than 1,000 private radio broadcast stations (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
.tr
|
|
|
|
|
3.433 million (2010)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
27.233 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 15
|
|
|
|
|
|
99 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|
|
total: 88
over 3,047 m:
16
2,438 to 3,047 m:
33
1,524 to 2,437 m:
19
914 to 1,523 m:
16
under 914 m:
4 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 11
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
6
under 914 m:
4 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
20 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 10,706 km; oil 3,636 km (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 8,697 km
country comparison to the world: 24
standard gauge:
8,697 km 1.435-m gauge (1,920 km electrified) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 352,046 km
country comparison to the world: 19
paved:
313,151 km (includes 2,010 km of expressways)
unpaved:
38,895 km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
1,200 km (2008)
country comparison to the world: 59
|
|
|
|
|
total: 645
country comparison to the world: 18
by type:
bulk carrier 95, cargo 290, chemical tanker 85, combination ore/oil 1, container 40, liquefied gas 6, passenger 1, passenger/cargo 59, petroleum tanker 31, refrigerated cargo 1, roll on/roll off 34, specialized tanker 2
foreign-owned:
3 (Germany 1, Italy 2)
registered in other countries:
686 (Albania 1, Antigua and Barbuda 7, Azerbaijan 1, Bahamas 3, Barbados 1, Belize 18, Cambodia 26, Comoros 16, Cook Islands 4, Dominica 1, Georgia 22, Italy 3, Kiribati 3, Liberia 15, Malta 211, Marshall Islands 72, Moldova 18, Mongolia 1, former Netherlands Antilles 8, Panama 79, Russia 104, Saint Kitts and Nevis 22, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 18, Sierra Leone 14, Slovakia 2, Tanzania 7, Togo 4, Turkmenistan 1, Tuvalu 1, UK 1, unknown 2) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Aliaga, Diliskelesi, Eregli, Izmir, Izmit (Kocaeli), Mercin (Icel), Limani, Yarimca
|
|
|
|
|
|
Turkish Armed Forces (TSK): Turkish Land Forces (Turk Kara Kuvvetleri), Turkish Naval Forces (Turk Deniz Kuvvetleri; includes naval air and naval infantry), Turkish Air Force (Turk Hava Kuvvetleri) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
19-41 years of age for male compulsory military service; 18 years of age for voluntary service; 15 months conscript obligation for non-university graduates, 6-12 months for university graduates; women serve in the Turkish Armed Forces only as officers; reserve obligation to age 41 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 21,079,077
females age 16-49:
20,558,696 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 17,664,510
females age 16-49:
17,340,816 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 700,079
female:
670,328 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.3% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
|
|
|
|
|
a "National Security Policy Document" adopted in October 2005 increases the Turkish Armed Forces (TSK) role in internal security, augmenting the General Directorate of Security and Gendarmerie General Command (Jandarma); the TSK leadership continues to play a key role in politics and considers itself guardian of Turkey's secular state; in April 2007, it warned the ruling party about any pro-Islamic appointments; despite on-going negotiations on EU accession since October 2005, progress has been limited in establishing required civilian supremacy over the military; primary domestic threats are listed as fundamentalism (with the definition in some dispute with the civilian government), separatism (the Kurdish problem), and the extreme left wing; Ankara strongly opposed establishment of an autonomous Kurdish region; an overhaul of the Turkish Land Forces Command (TLFC) taking place under the "Force 2014" program is to produce 20-30% smaller, more highly trained forces characterized by greater mobility and firepower and capable of joint and combined operations; the TLFC has taken on increasing international peacekeeping responsibilities, and took charge of a NATO International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) command in Afghanistan in April 2007; the Turkish Navy is a regional naval power that wants to develop the capability to project power beyond Turkey's coastal waters; the Navy is heavily involved in NATO, multinational, and UN operations; its roles include control of territorial waters and security for sea lines of communications; the Turkish Air Force adopted an "Aerospace and Missile Defense Concept" in 2002 and has initiated project work on an integrated missile defense system; Air Force priorities include attaining a modern deployable, survivable, and sustainable force structure, and establishing a sustainable command and control system (2008)
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Turkey |
|
|
complex maritime, air, and territorial disputes with Greece in the Aegean Sea; status of north Cyprus question remains; Syria and Iraq protest Turkish hydrological projects to control upper Euphrates waters; Turkey has expressed concern over the status of Kurds in Iraq; in 2009, Swiss mediators facilitated an accord reestablishing diplomatic ties between Armenia and Turkey, but neither side has ratified the agreement and the rapprochement effort has faltered; Turkish authorities have complained that blasting from quarries in Armenia might be damaging the medieval ruins of Ani, on the other side of the Arpacay valley;
|
|
|
|
|
IDPs: 1-1.2 million (fighting 1984-99 between Kurdish PKK and Turkish military; most IDPs in southeastern provinces) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
key transit route for Southwest Asian heroin to Western Europe and, to a lesser extent, the US - via air, land, and sea routes; major Turkish and other international trafficking organizations operate out of Istanbul; laboratories to convert imported morphine base into heroin exist in remote regions of Turkey and near Istanbul; government maintains strict controls over areas of legal opium poppy cultivation and over output of poppy straw concentrate; lax enforcement of money-laundering controls
|
|
|
|
|