|
|
French Togoland became Togo in 1960. Gen. Gnassingbe EYADEMA, installed as military ruler in 1967, ruled Togo with a heavy hand for almost four decades. Despite the facade of multiparty elections instituted in the early 1990s, the government was largely dominated by President EYADEMA, whose Rally of the Togolese People (RPT) party has maintained power almost continually since 1967 and maintains a majority of seats in today's legislature. Upon EYADEMA's death in February 2005, the military installed the president's son, Faure GNASSINGBE, and then engineered his formal election two months later. Democratic gains since then allowed Togo to hold its first relatively free and fair legislative elections in October 2007. After years of political unrest and condemnation from international organizations for human rights abuses, Togo is finally being re-welcomed into the international community.
|
|
|
|
|
|
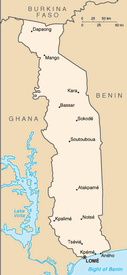
Western Africa, bordering the Bight of Benin, between Benin and Ghana
|
|
|
|
|
8 00 N, 1 10 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 56,785 sq km
country comparison to the world: 125
land:
54,385 sq km
water:
2,400 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than West Virginia
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,647 km
border countries:
Benin 644 km, Burkina Faso 126 km, Ghana 877 km
|
|
|
|
|
56 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 30 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
tropical; hot, humid in south; semiarid in north
|
|
|
|
|
gently rolling savanna in north; central hills; southern plateau; low coastal plain with extensive lagoons and marshes
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Mont Agou 986 m
|
|
|
|
|
phosphates, limestone, marble, arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 44.2%
permanent crops:
2.11%
other:
53.69% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
70 sq km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
14.7 cu km (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 0.17 cu km/yr (53%/2%/45%)
per capita:
28 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
hot, dry harmattan wind can reduce visibility in north during winter; periodic droughts
|
|
|
|
|
deforestation attributable to slash-and-burn agriculture and the use of wood for fuel; water pollution presents health hazards and hinders the fishing industry; air pollution increasing in urban areas
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
the country's length allows it to stretch through six distinct geographic regions; climate varies from tropical to savanna
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,771,993 (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
note:
estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 40.9% (male 1,387,537/female 1,381,040)
15-64 years:
56% (male 1,878,114/female 1,912,132)
65 years and over:
3.1% (male 92,689/female 120,481) (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 19.3 years
male:
19 years
female:
19.5 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.762% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
|
35.58 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
|
|
|
|
|
7.96 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 43% of total population (2010)
rate of urbanization:
3.9% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
LOME (capital) 1.593 million (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.63 male(s)/female
total population:
0.97 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 51.48 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 44
male:
58.43 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
44.32 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 62.71 years
country comparison to the world: 177
male:
60.19 years
female:
65.3 years (2011 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.69 children born/woman (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|
|
3.2% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
120,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
|
|
|
|
|
7,700 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
malaria and yellow fever
water contact disease:
schistosomiasis
respiratory disease:
meningococcal meningitis
animal contact disease:
rabies
note:
highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds
(2009)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 87% of population
rural: 41% of population
total: 60% of population
unimproved:
urban: 13% of population
rural: 59% of population
total: 40% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
improved:
urban: 24% of population
rural: 3% of population
total: 12% of population
unimproved:
urban: 76% of population
rural: 97% of population
total: 88% of population (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Togolese (singular and plural)
adjective:
Togolese
|
|
|
|
|
African (37 tribes; largest and most important are Ewe, Mina, and Kabre) 99%, European and Syrian-Lebanese less than 1%
|
|
|
|
|
Christian 29%, Muslim 20%, indigenous beliefs 51%
|
|
|
|
|
French (official, the language of commerce), Ewe and Mina (the two major African languages in the south), Kabye (sometimes spelled Kabiye) and Dagomba (the two major African languages in the north)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
60.9%
male:
75.4%
female:
46.9% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 10 years
male:
11 years
female:
8 years (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
4.6% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Togolese Republic
conventional short form:
Togo
local long form:
Republique togolaise
local short form:
none
former:
French Togoland
|
|
|
|
|
republic under transition to multiparty democratic rule
|
|
|
|
|
name: Lome
geographic coordinates:
6 08 N, 1 13 E
time difference:
UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
5 regions (regions, singular - region); Centrale, Kara, Maritime, Plateaux, Savanes
|
|
|
|
|
27 April 1960 (from French-administered UN trusteeship)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 27 April (1960)
|
|
|
|
|
adopted by public referendum 27 September 1992
|
|
|
|
|
customary law system
|
|
|
|
|
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; non-party state to the ICCt
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Faure GNASSINGBE (since 4 May 2005);
head of government:
Prime Minister Gilbert HOUNGBO (since 7 September 2008)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the president and the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (no term limits); election last held on 4 March 2010 (next to be held in 2015); prime minister appointed by the president
election results:
Faure GNASSINGBE reelected president; percent of vote - Faure GNASSINGBE 60.9%, Jean-Pierre FABRE 33.9%, Yawovi AGBOYIBO 3%, other 2.2%
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Assembly (81 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
elections:
last held on 14 October 2007 (next to be held in 2012)
election results:
percent of vote by party - RPT 39.4%, UFC 37.0%, CAR 8.2%, independents 2.5%, other 12.9%; seats by party - RPT 50, UFC 27, CAR 4
|
|
|
|
|
Court of Appeal or Cour d'Appel; Supreme Court or Cour Supreme
|
|
|
|
|
Action Committee for Renewal or CAR [Yawovi AGBOYIBO]; Democratic Convention of African Peoples or CDPA; Democratic Party for Renewal or PDR; Juvento [Monsilia DJATO]; Movement of the Believers of Peace and Equality or MOCEP; National Alliance for Change or ANC [Jean-Pierre FABRE]; Pan-African Patriotic Convergence or CPP; Rally for the Support for Development and Democracy or RSDD [Harry OLYMPIO]; Rally of the Togolese People or RPT [Faure GNASSINGBE]; Socialist Pact for Renewal or PSR; Union for Democracy and Social Progress or UDPS [Gagou KOKOU]; Union of Forces for Change or UFC [Gilchrist OLYMPIO]
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, ECOWAS, Entente, FAO, FZ, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WADB (regional), WAEMU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Kadangha Limbiya BARIKI
chancery:
2208 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 234-4212
FAX:
[1] (202) 232-3190
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Patricia McMahon HAWKINS
embassy:
4332 Blvd. Gnassingbe Eyadema, Cite OUA, Lome
mailing address:
B. P. 852, Lome; 2300 Lome Place, Washington, DC 20512-2300
telephone:
[228] 261-5470
FAX:
[228] 261-5501
|
|
|
|
|
five equal horizontal bands of green (top and bottom) alternating with yellow; a white five-pointed star on a red square is in the upper hoist-side corner; the five horizontal stripes stand for the five different regions of the country; the red square is meant to express the loyalty and patriotism of the people; green symbolizes hope, fertility, and agriculture; yellow represents mineral wealth and faith that hard work and strength will bring prosperity; the star symbolizes life, purity, peace, dignity, and Togo's independence
note:
uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Salut a toi, pays de nos aieux" (Hail to Thee, Land of Our Forefathers)
lyrics/music:
Alex CASIMIR-DOSSEH
note:
adopted 1960, restored 1992; this anthem was replaced by another during one-party rule between 1979 and 1992
|
|
|
|
|
|
This small, sub-Saharan economy suffers from anemic economic growth and depends heavily on both commercial and subsistence agriculture, which provides employment for 65% of the labor force. Some basic foodstuffs must still be imported. Cocoa, coffee, and cotton generate about 40% of export earnings with cotton being the most important cash crop. Togo is the world's fourth-largest producer of phosphate. The government's decade-long effort, supported by the World Bank and the IMF, to implement economic reform measures, encourage foreign investment, and bring revenues in line with expenditures has moved slowly. Progress depends on follow through on privatization, increased openness in government financial operations, progress toward legislative elections, and continued support from foreign donors. Togo is on track with its IMF Extended Credit Facility and reached a HIPC debt relief completion point in 2010 at which 95% of the country's debt was forgiven. Economic growth prospects remain marginal due to declining cotton production and underinvestment in phosphate mining.
|
|
|
|
|
$5.974 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
$5.778 billion (2009 est.)
$5.596 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$3.194 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.4% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
3.2% (2009 est.)
2.4% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$900 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 216
$900 (2009 est.)
$900 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 47.4%
industry:
25.4%
services:
27.2% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.595 million (2007)
country comparison to the world: 110
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 65%
industry:
5%
services:
30% (1998 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
32% (1989 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3.3%
highest 10%:
27.1% (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
18.2% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $602.3 million
expenditures:
$692.1 million (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.6% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
2% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.25% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 96
4.75% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
$754.5 million (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
$789.7 million (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.238 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
$1.306 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$817.7 million (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
$862.4 million (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
coffee, cocoa, cotton, yams, cassava (tapioca), corn, beans, rice, millet, sorghum; livestock; fish
|
|
|
|
|
phosphate mining, agricultural processing, cement, handicrafts, textiles, beverages
|
|
|
|
|
2.5% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
|
|
|
|
|
230 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 175
|
|
|
|
|
640 million kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
514 million kWh; note - electricity supplied by Ghana (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
|
|
|
|
|
21,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
|
|
|
|
|
1,547 bbl/day (2005)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|
|
15,270 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 186
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 194
|
|
|
|
|
$-339 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
$-236 million (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$859 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
$818 million (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
reexports, cotton, phosphates, coffee, cocoa
|
|
|
|
|
Germany 17.57%, Ghana 12.74%, Burkina Faso 11.02%, India 10.22%, Belgium 7.1%, Benin 6.92%, Netherlands 5.94%, Mali 4.41% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.337 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
$1.261 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, foodstuffs, petroleum products
|
|
|
|
|
China 36.58%, France 8.64%, Netherlands 6.76%, India 5.06%, US 4.4% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$686 million (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
$703.2 million (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2010)
$1.573 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) per US dollar -
495.28 (2010)
472.19 (2009)
447.81 (2008)
482.71 (2007)
522.59 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
178,700 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 129
|
|
|
|
|
2.187 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 129
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: fair system based on a network of microwave radio relay routes supplemented by open-wire lines and a mobile-cellular system
domestic:
microwave radio relay and open-wire lines for conventional system; combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity roughly 40 telephones per 100 persons with mobile-cellular use predominating
international:
country code - 228; satellite earth stations - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean), 1 Symphonie
|
|
|
|
|
2 state-owned TV stations with multiple transmission sites; 5 private TV stations broadcast locally; cable TV service is available; state-owned radio network with multiple stations; several dozen private radio stations and a few community radio stations; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters are obtainable (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.tg
|
|
|
|
|
860 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 168
|
|
|
|
|
356,300 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 123
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 163
|
|
|
|
|
total: 2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 6
914 to 1,523 m:
4
under 914 m:
2 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 532 km
country comparison to the world: 110
narrow gauge:
532 km 1.000-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 7,520 km
country comparison to the world: 146
paved:
2,376 km
unpaved:
5,144 km (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
50 km (seasonally navigable by small craft on the Mono River depending on rainfall) (2009)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|
|
total: 53
country comparison to the world: 69
by type:
bulk carrier 5, cargo 40, chemical tanker 2, container 2, petroleum tanker 2, refrigerated cargo 1, roll on/roll off 1
foreign-owned:
23 (China 2, Greece 1, Lebanon 6, Romania 1, Syria 5, Turkey 4, UAE 1, UK 3) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Kpeme, Lome
|
|
|
|
|
|
Togolese Armed Forces (Forces Armees Togolaise, FAT): Ground Forces, Togolese Navy (Marine du Togo), Togolese Air Force (Force Aerienne Togolaise, TAF), National Gendarmerie (2011)
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age for selective compulsory and voluntary military service; 2-year service obligation (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,577,572
females age 16-49:
1,589,715 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,104,536
females age 16-49:
1,158,061 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 74,036
female:
73,515 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.6% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Togo |
|
|
in 2001, Benin claimed Togo moved boundary monuments - joint commission continues to resurvey the boundary; in 2006, 14,000 Togolese refugees remain in Benin and Ghana out of the 40,000 who fled there in 2005; talks continue between Benin and Togo on funding the Adjrala hydroelectric dam on the Mona River
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 5,000 (Ghana)
IDPs:
1,500 (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
transit hub for Nigerian heroin and cocaine traffickers; money laundering not a significant problem
|
|
|
|
|